Artificial limb ankle joint with four passive degrees of freedom
A technology for ankle joints and prostheses, which is applied in the field of rehabilitation engineering, can solve the problems of excessive size, lack of cushioning, shock absorption and energy storage of ankle joints, and unattractive appearance, and achieve full flexibility and excellent sports performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
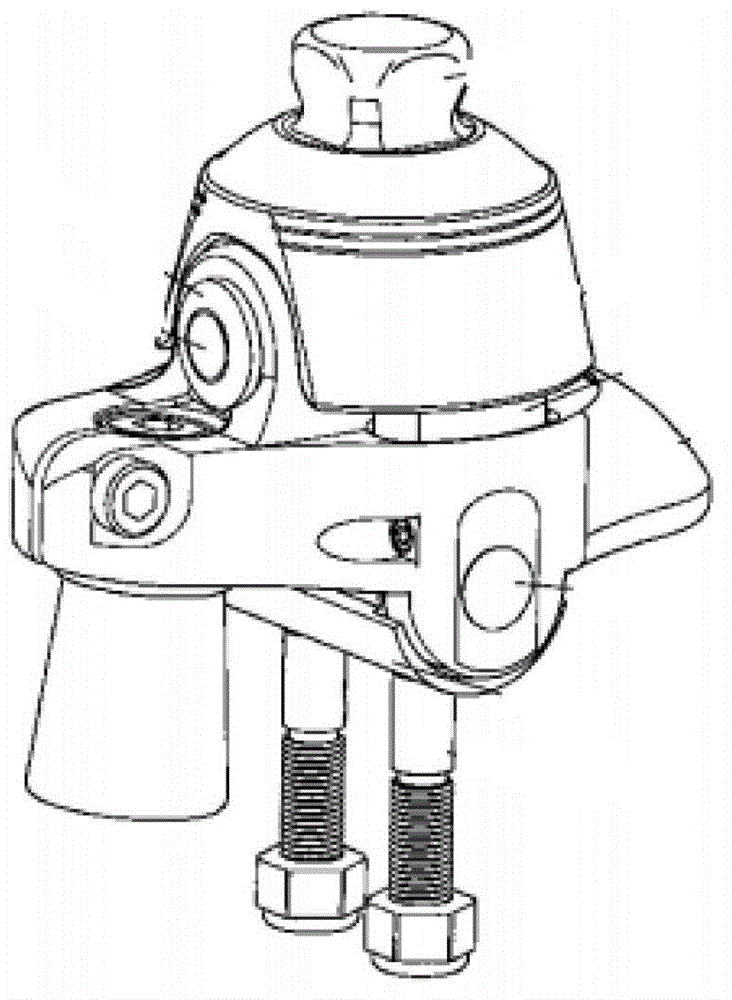
[0040] image 3It is a prosthetic ankle joint with four passive degrees of freedom in this embodiment, which includes a tibial part 1, a spherical hinge structure 3, 10, a tibial shock-absorbing torsion spring 2, a sole plate 5 and a return spring device.
[0041] The spherical joint structure is composed of two parts, including the spherical joint body 10 and the spherical joint bowl 3, which form a revolving pair, so the spherical joint body 10 can realize three degrees of freedom of rotation. The adjustment rod 9 is fixedly connected with the above-mentioned spherical joint sphere 10 by welding, the spherical joint sphere 10 is located in the middle of the adjustment rod 9, and the adjustment rod 9 is divided into an upper adjustment rod 902 and a lower adjustment rod 901, and an upper adjustment rod 902 and a lower adjustment rod 902. One end of the rod 901 is respectively welded and fixed to the ball joint 10 . The upper adjustment rod 902 passes through the tibia 1 , an...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Figure 4 , 5 . 6 is another prosthetic ankle joint with four passive degrees of freedom. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the ball bowl of the ball joint structure in Embodiment 1 is divided into two parts. In addition, the ball joint bracket 4 The connection and the structure thereof are all different with the sole plate 5.
[0050] Such as Figure 5 , as shown in 6, the tibia 1 is divided into two parts, the tibial connecting rod 101 and the spring connecting shaft 102 . The tibial connecting rod 101 is connected with the knee joint of the whole prosthesis, and the spring connecting shaft 102 is connected with the tibial shock-absorbing torsion spring 2 . The tibial shock-absorbing torsion spring is sleeved on the spring connecting shaft 102, and the spring connecting shaft 102 has a hole in the radial direction, and the end of the tibial shock-absorbing torsion spring is inserted into the above-mentioned hole. The spring connecting...
Embodiment 3
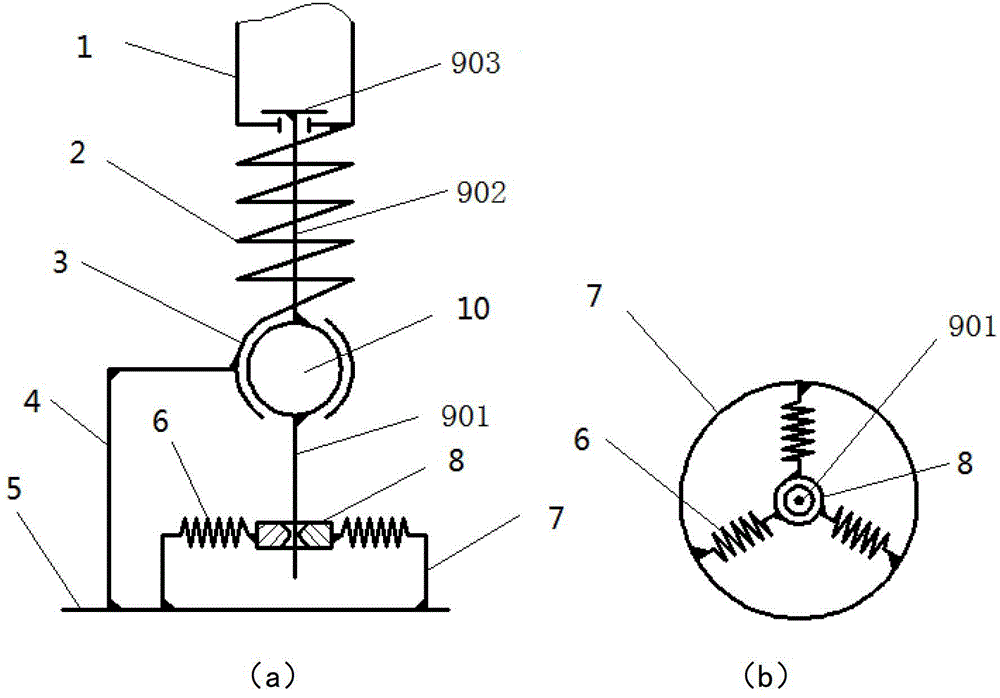
[0056] Such as Figure 9 and 10 Shown is an elastic rubber end cap, which is used to replace the return spring set in the above implementation example. The elastic rubber end cap is directly sleeved on the adjusting rod 9, and the movement of the adjusting rod 9 is directly restrained without using the adjusting sleeve 8 to restrict the movement of the adjusting rod 9. When the adjustment rod 9 is deflected due to the rotation of the spherical hinge sphere 10, it must overcome the elastic force of the elastic rubber end cap.
[0057] Such as Figure 9 and 10 As shown, a through hole is drilled in the center of the elastic rubber end cap, and the diameter is consistent with the adjustment rod 9, and the adjustment rod 9 coaxially passes through the center through hole. The elastic rubber end cap is installed on the circular support 7, and the two are connected by screws, and the circular support 7 is fixedly connected with the rear sole 501 and the rear sole pad 503 by scre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com