Engine blade in-situ ultrasonic detection method
A technology for engine blades and ultrasonic testing, which is applied to the analysis of solids using sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves, material analysis using sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves, and measuring devices, which can solve problems such as long cycle times and high costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
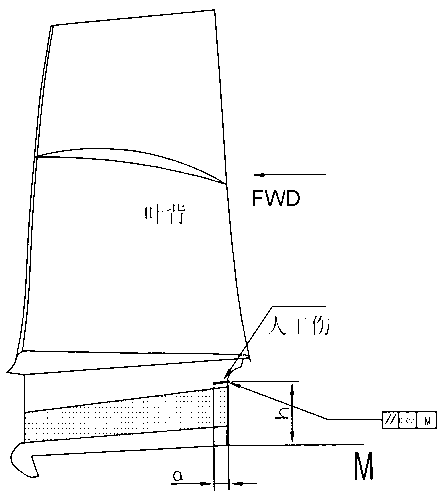
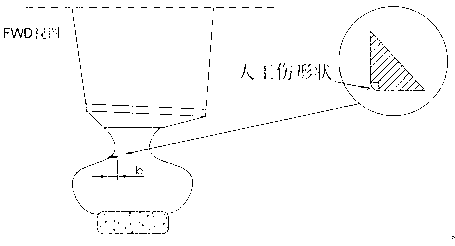
[0047]An in-situ ultrasonic detection method for engine blades. First, a special ultrasonic detection probe is made, and then the probe is used to verify the sensitivity and effectiveness of the detection device on a reference standard with artificial damage, and then the ultrasonic detection probe is put into the engine. Check the position for in-situ testing.
[0048] The in-situ ultrasonic detection method of the engine blade requires: use a special probe to perform in-situ detection in the outer field of the engine blade, obtain an A-scan waveform diagram on the ultrasonic flaw detector, and then determine the detected defects in the probe scanning area according to the A-scan waveform diagram. Whether the leaves are damaged;
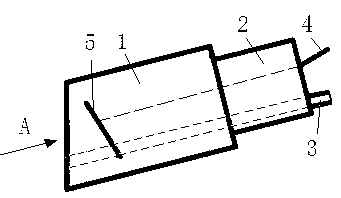
[0049] The special-purpose probe is specifically composed of the following structures: probe body 1, socket 2, water pipe 3, cable 4, piezoelectric chip 5; wherein: probe body 1 and socket 2 are fixedly connected as one; water pipe 3 and The cables...
Embodiment 2
[0093] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and its main differences are:
[0094] 1) The special probe meets the following requirements: it is a shaft-shaped or rod-shaped component as a whole, and the maximum diameter of the outer contour of the cross-section or the diameter of the circumscribed circle of the cross-section is required to be ≤ 8mm. The diameter of the round hole at the casing where the probe may protrude into the engine corresponds to this requirement. ,
[0095] 2) In the in-situ ultrasonic testing method for engine blades, the cross-sectional outer contour of the probe body 1 of the special probe is circular, and at the same time, the distance between the outer end surface of the probe body 1 facing the side of the detected object and the axis of the probe body 1 is There is an included angle of 12°.
[0096]
Embodiment 3
[0098] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and its main differences are:
[0099] 1) The special probe meets the following requirements: it is a shaft-shaped or rod-shaped component as a whole, and the maximum diameter of the outer contour of the cross-section or the diameter of the circumscribed circle of the cross-section is required to be ≤10mm. The diameter of the round hole at the casing where the probe may protrude into the engine corresponds to this requirement. ,
[0100] 2) In the in-situ ultrasonic testing method for engine blades, the cross-sectional outer contour of the probe body 1 of the special probe is circular, and at the same time, the distance between the outer end surface of the probe body 1 facing the side of the detected object and the axis of the probe body 1 is There is an included angle of 16°.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com