Method for regulating and controlling diapause of agryponflexorius
A technology for the diapause and grassland, which is applied in the field of regulating the diapause of the meadow moth, can solve the problems of restricting the large-scale application of natural enemy insects, the lack of diapause control technology, and the extension of the storage period, so as to promote large-scale Multiply, improve the efficiency of pest control, prolong the shelf life of products and the effect of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1, the induction of diapause of the meadow borer Agia japonica
[0039] 1. Determination of the diapause temperature and photoperiod of the meadow moth Agia
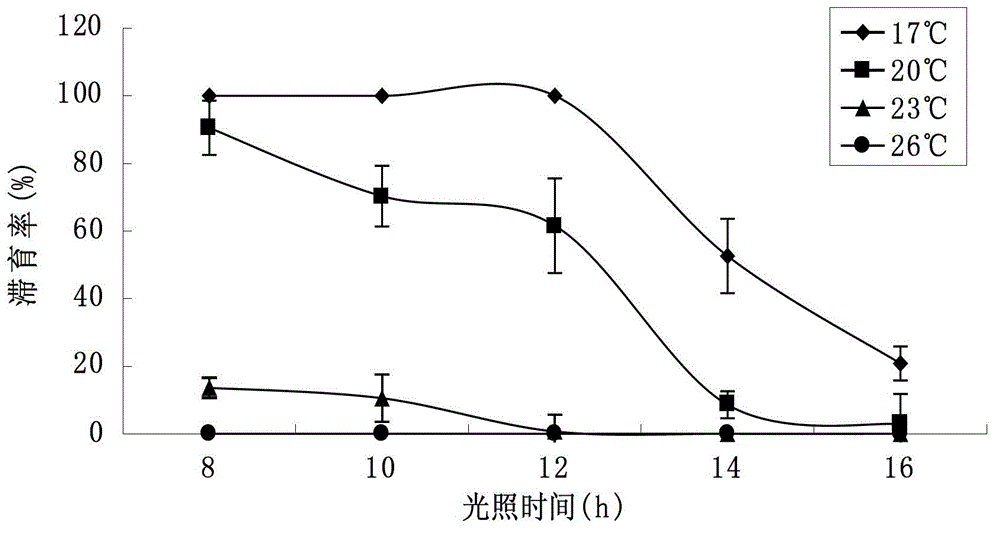
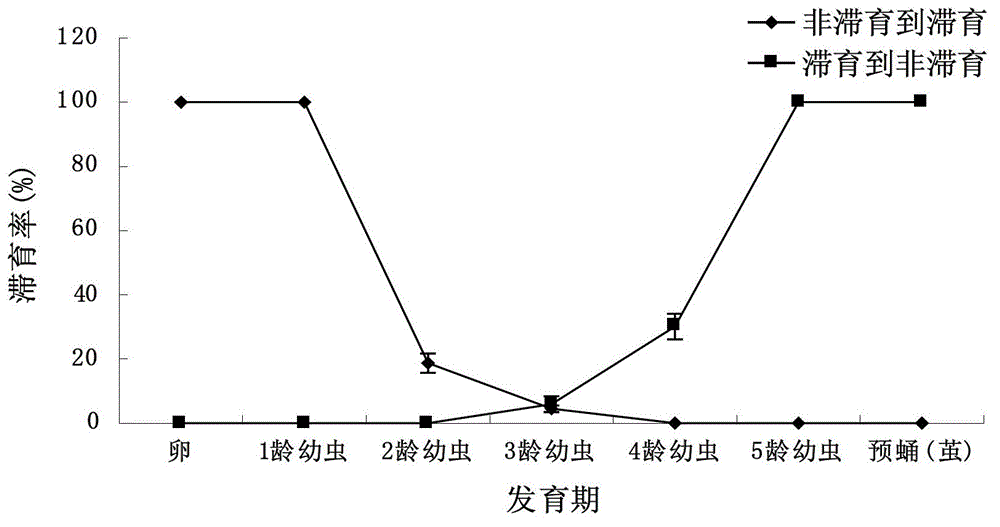
[0040]Using the two-factor orthogonal test method, set 5 different photoperiods (L8:D16, L10:D14, L12:D12, L14:D10, L16:D8) and 4 different temperatures (17°C, 20°C, 23°C, 26°C), a total of 20 treatments, 30 meadow borer larvae (hosts) for each treatment, repeated 3 times, and the meadow moth larvae were parasitized by the meadow borer larvae after mating for 1 day, and then transferred to sandy soil Put them into the artificial climate box with different photoperiod and temperature treatment (among them, the light intensity during the light is 4000-5000LX, and the relative air humidity is 70%-80%). Carry out diapause induction (diapause induction is regarded as starting from the stage of "egg"), and the induction time is 2 days. After induction, it is transferred to the normal feeding conditions of th...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Embodiment 2, the maintenance of diapause of the meadow borer Agia
[0055] In this example, the time for low-temperature storage of the diapause cocoons of the meadowborer Agna was determined by measuring the eclosion rate of the diapause cocoon of the meadowborer, and the lifespan, oviposition period, and parasitism rate of the adult bees after emergence. details as follows:
[0056] 1. The eclosion rate of the diapause cocoons of the meadow moth A.
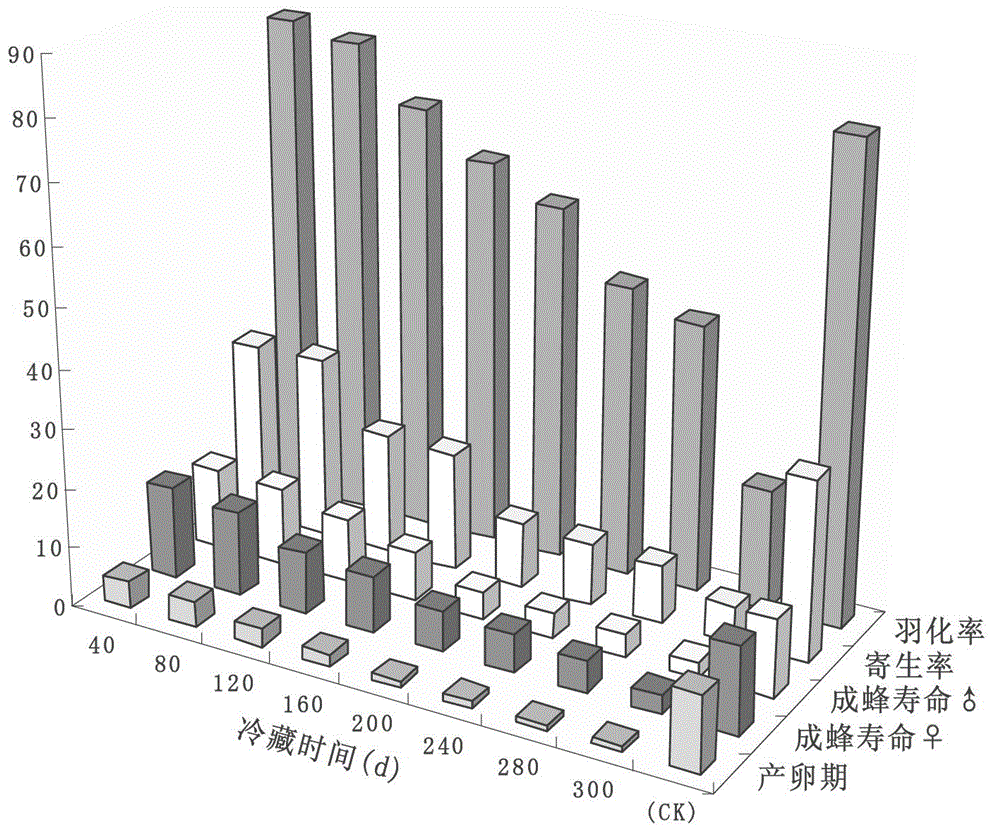
[0057] The diapause state of the diapause state of the meadow moth Agna (the appearance is a cocoon at this time) obtained by the method of Example 1 is collected in moist and soft soil, and packed into plastic bowls (diameter 10cm, height 8cm), plastic The bowl is covered with breathable gauze, stored in a refrigerator at 4°C in total darkness, sprayed with water every 3 days, and maintained at a relative humidity of 60%-70%. The diapause cocoons were regularly taken out from the refrigerator and placed in an incubato...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment 3, the diapause of the meadow moth Aguisia japonica is removed
[0067] For adopting the method of embodiment 1 to obtain the diapause state meadow moth Agna (diapause cocoon), the diapause state can be released through temperature stimulation, and enter the normal development process, the specific measures are as follows:
[0068] Place the diapause cocoons of the meadow moth A. japonica in an environment with a temperature of 23°C, a photoperiod of L14:D10 to L16:D8, and a light intensity of 4000-5000Lx. Water is sprayed every 3 days to maintain a certain humidity (RH is 70% -80%), the diapause state can be released after 20 days, and the diapause cocoons will all emerge into adult bees soon.
[0069] Among them, the induction time of 20 days is determined according to the following method:
[0070] The diapause cocoons of the meadowlark moth A. japonica were transferred to the incubator with a temperature of 23°C and a photoperiod of L14:D10 (RH is 70%-80...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com