Robot joint driver with variable rigidity
A technology of robot joints and drives, applied in the directions of manipulators, manufacturing tools, joints, etc., can solve the problems of independent elastic links and adjustment mechanisms.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0014] Embodiments of the present invention are described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
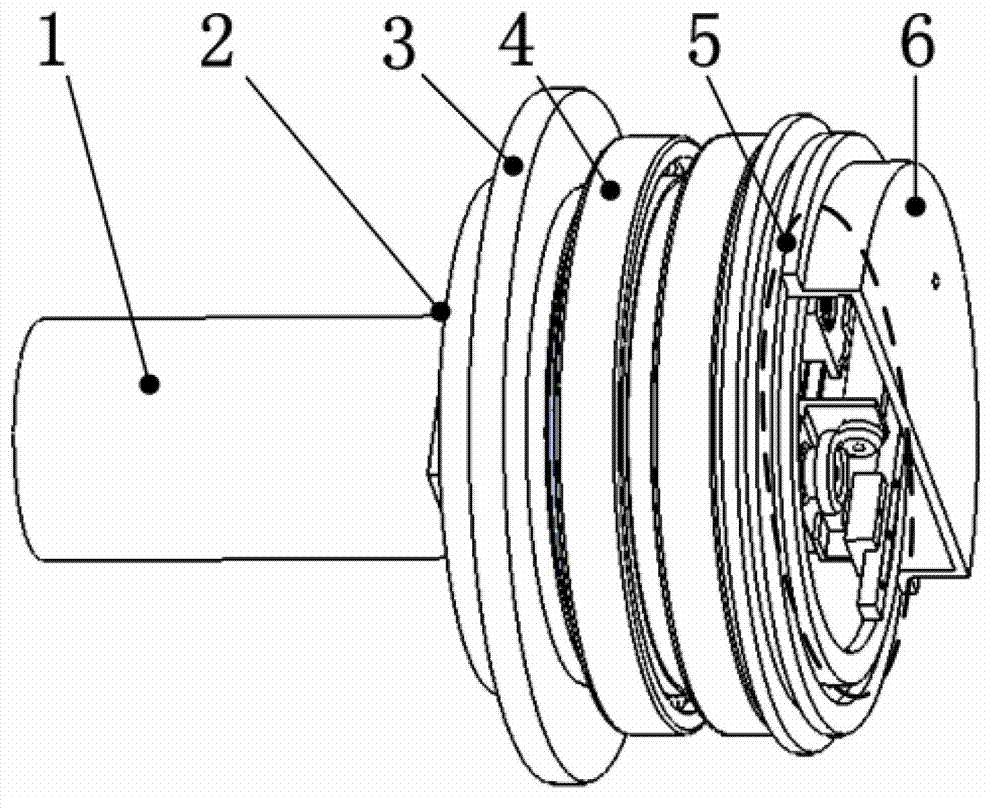
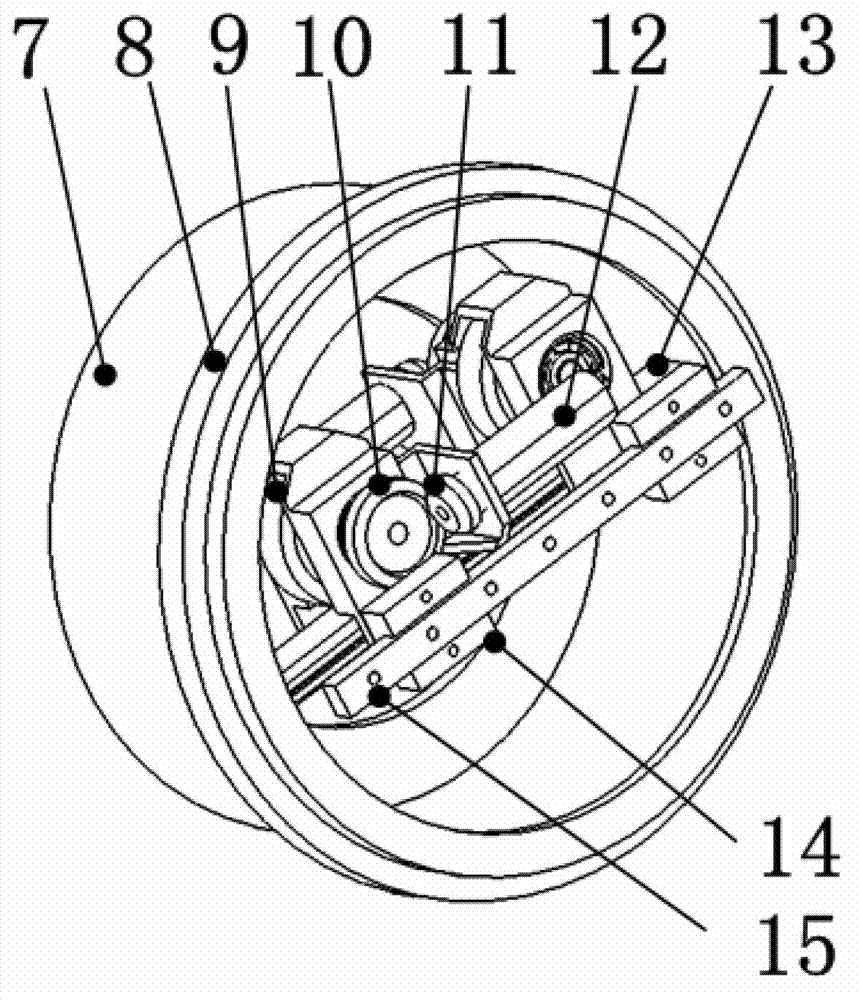
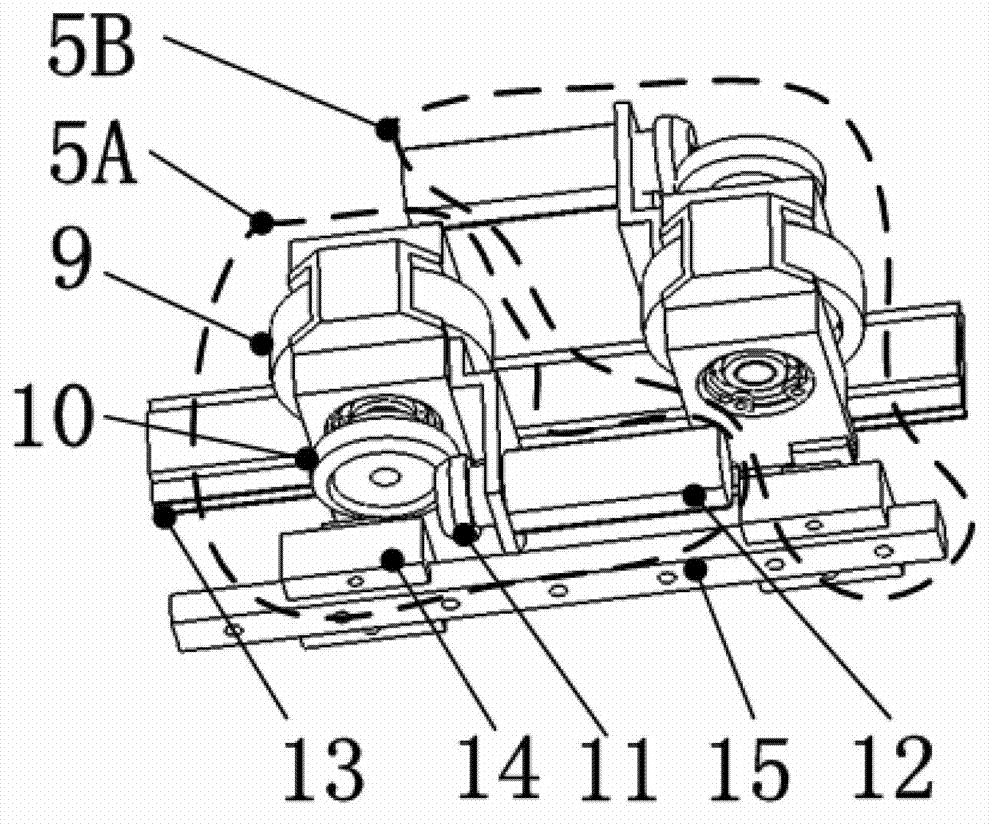
[0015] A typical feature of the variable stiffness robot joint driver is that the elastic link and the adjustment mechanism are combined into one by using a metal flexible rack mechanism. A metal flexible rack is connected in series between the output end of the rigid reducer of the joint driver and the shutdown link. The flexible rack itself has a certain degree of elasticity, which can effectively store and release energy, so as to avoid the rigid collision between the joint connecting rod and the environment; the flexible rack has its own gear pair, which is convenient for the adjustment of joint stiffness. Need to quickly increase or decrease joint stiffness.
[0016] In the process of man-machine collaborative operation, contact or even collision between humans and robots is inevitable. Therefore, how to ensure that the impact force does not harm the human bod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com