Numerically simulating structural behaviors of a product by using explicit finite element analysis with a mass scaling enhanced subcycling technique
A structural performance, finite element technique used in the field of numerical simulation of product structural performance using explicit finite element analysis and mass scaling enhanced sub-cycle technology, which can solve problems such as changing structural dynamic performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
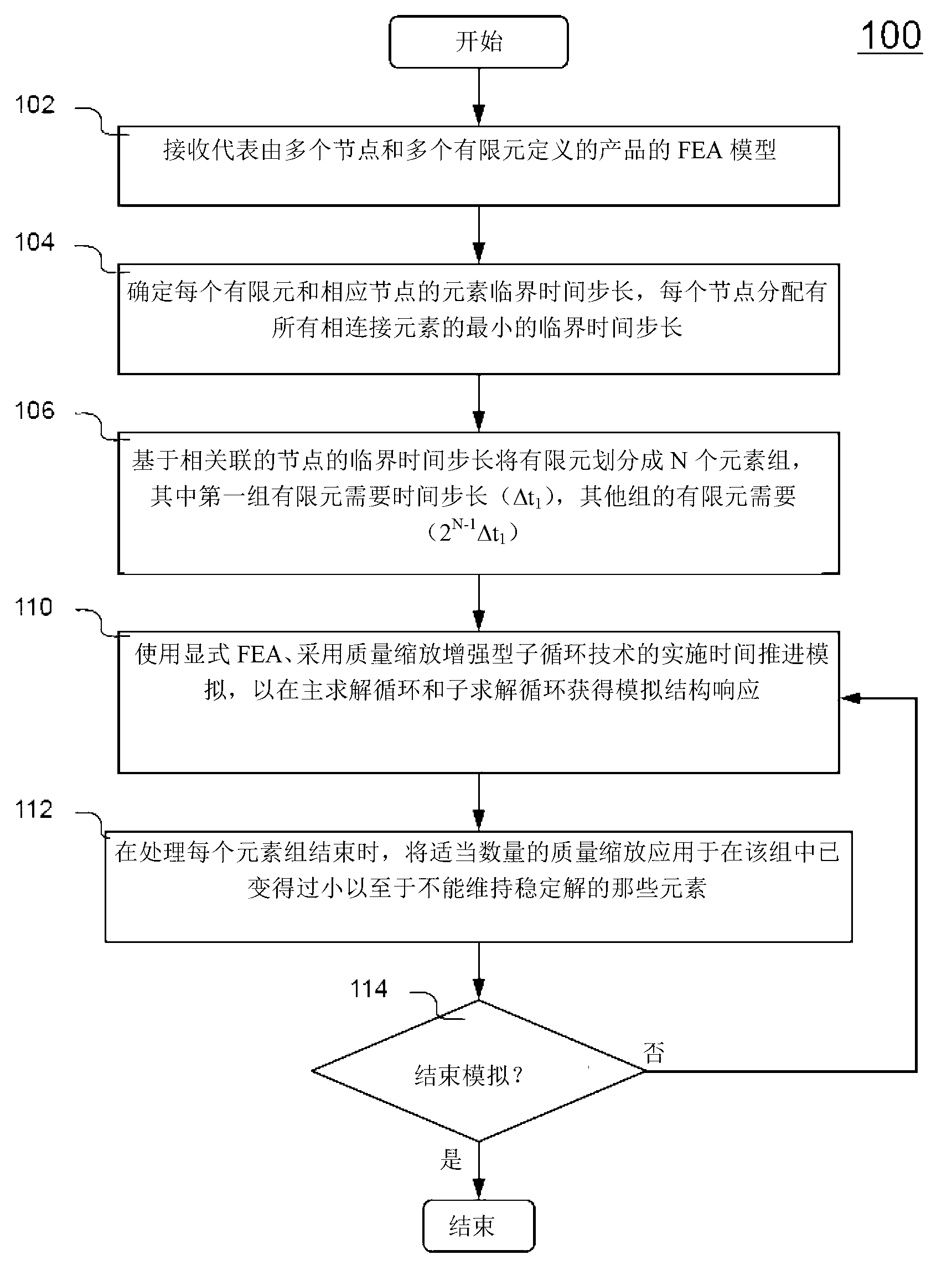
[0021] figure 1 is a flowchart illustrating an exemplary process 100 for numerically simulating structural performance of a product using explicit finite element analysis (FEA) with mass scaling enhanced sub-cycle techniques, according to an embodiment of the present invention. Preferably, process 100 is understood in conjunction with the preceding figures and is implemented in software.
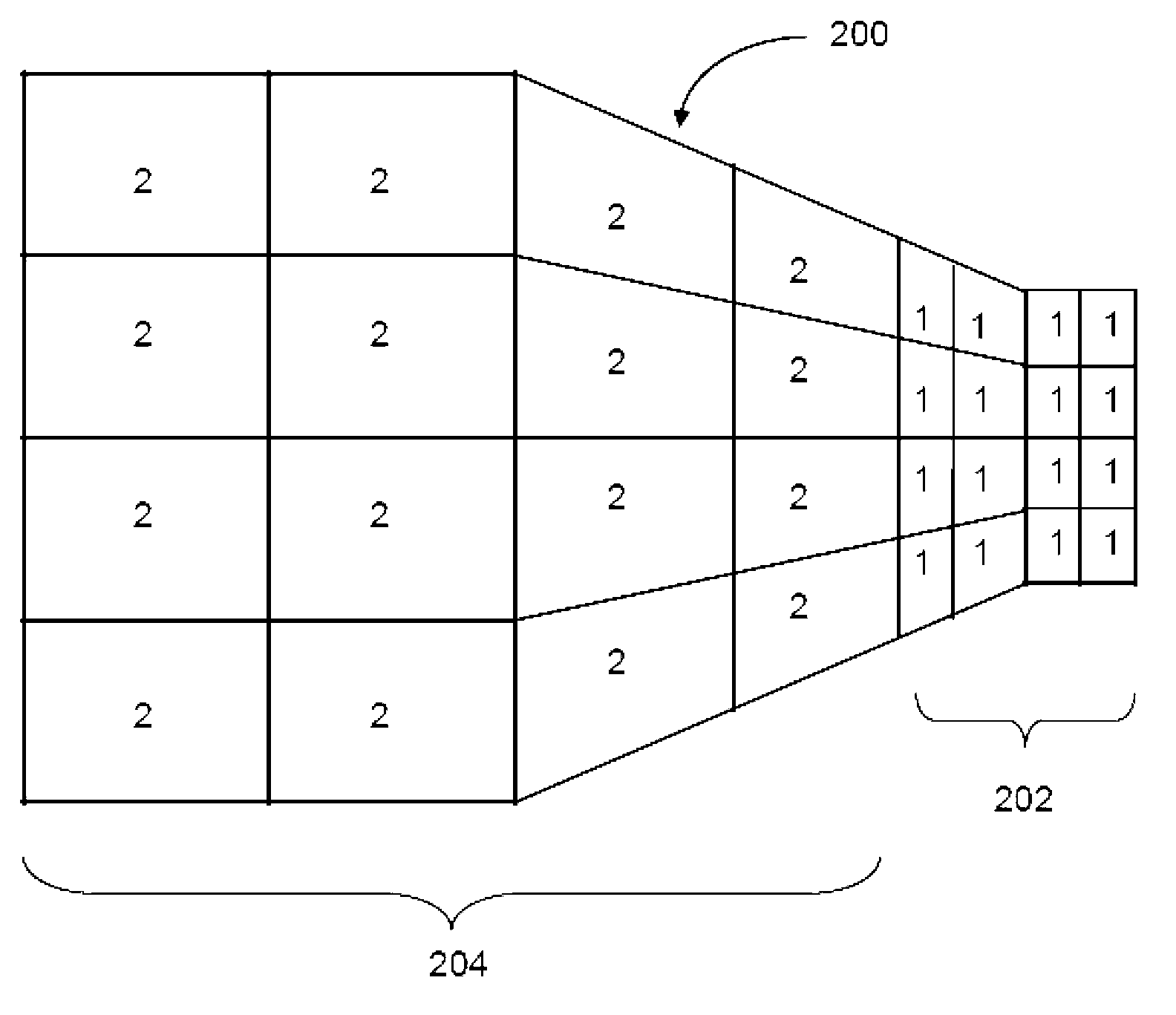
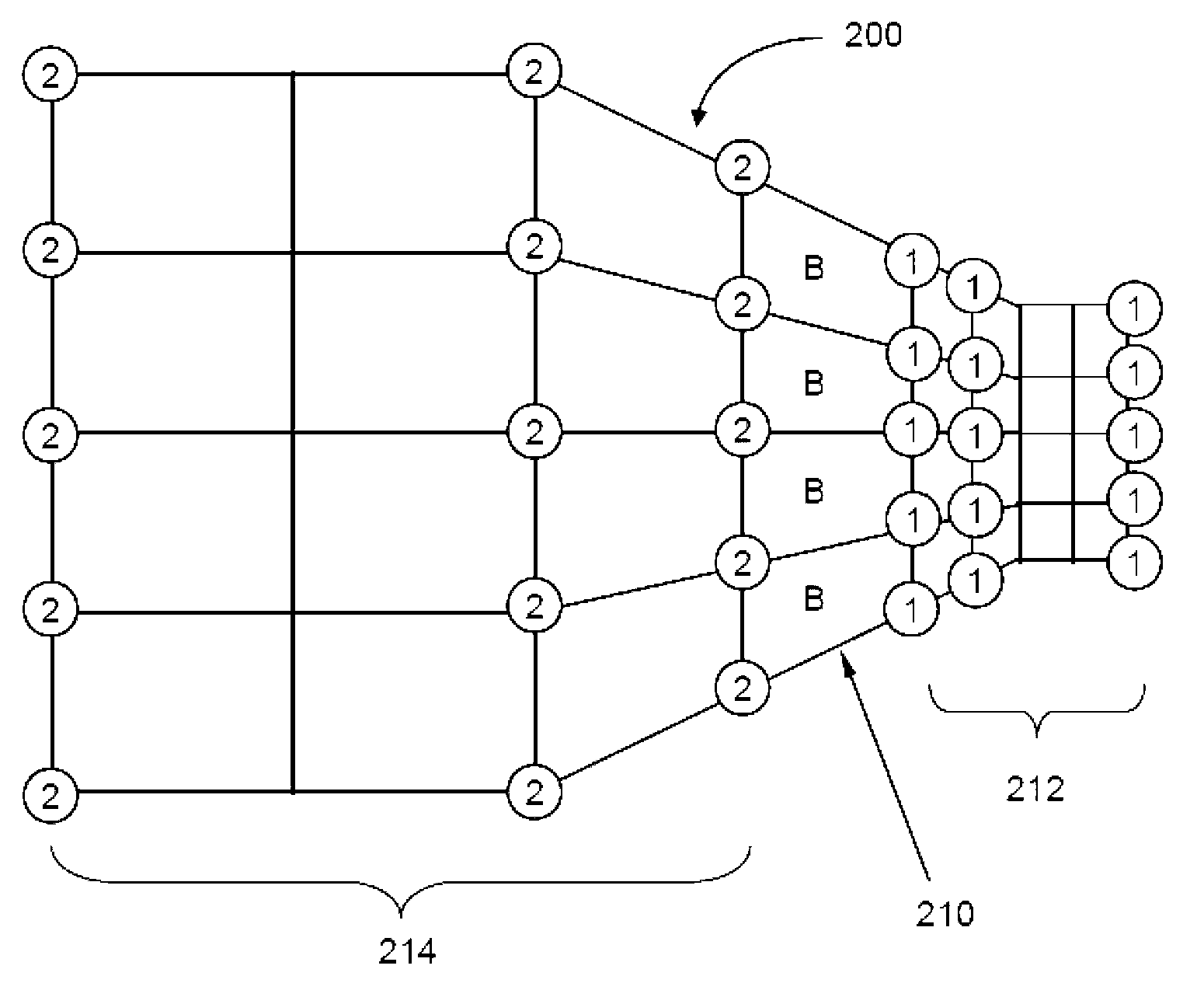
[0022] Process 100 begins by receiving a finite element analysis (FEA) model representing a product or structure (eg, automobile, aircraft, etc.) at step 102 . The FEA model includes multiple nodes and multiple finite elements associated with material properties. Next at step 104, an element critical time step is determined for each finite element (e.g. Figure 2A ). Accordingly, each node is assigned an individual node critical time step (e.g., Figure 2B ). Selects the smallest element critical time step at a particular node for all finite elements it is connected to.
[0023] In ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com