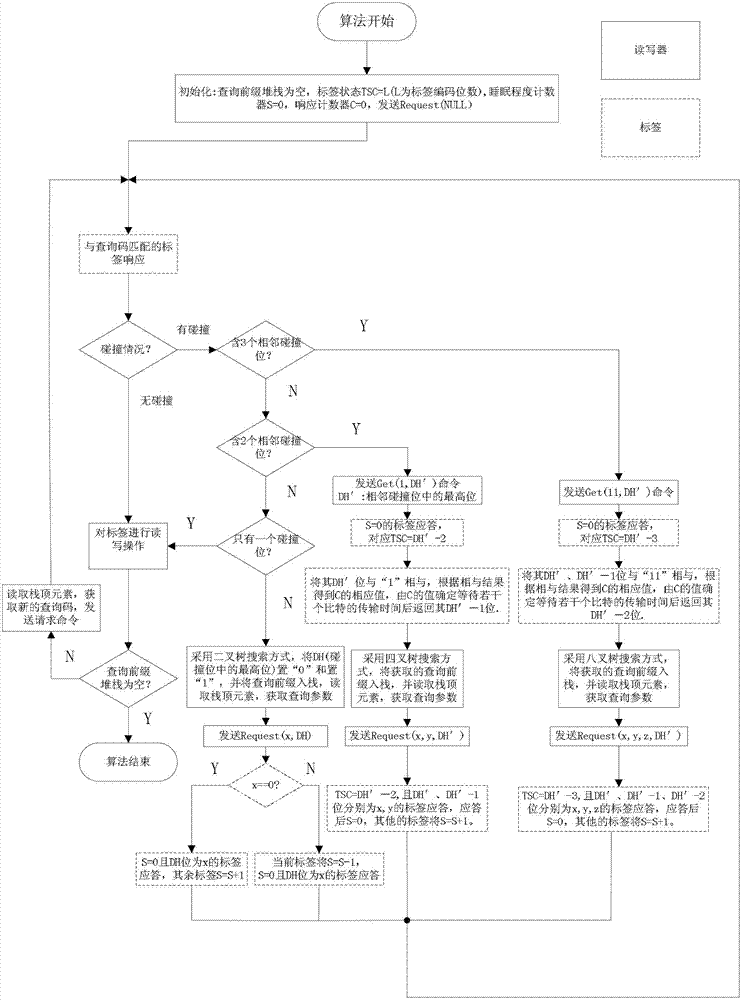
Multi-way tree anti-collision algorithm applicable to radio frequency identification (RFID) system
An anti-collision algorithm and multi-tree technology, applied in the field of tag anti-collision, can solve the problems of large data transmission, long recognition time of collision tags, slow search speed, etc., to improve recognition efficiency, overcome slow splitting speed, and reduce overhead. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
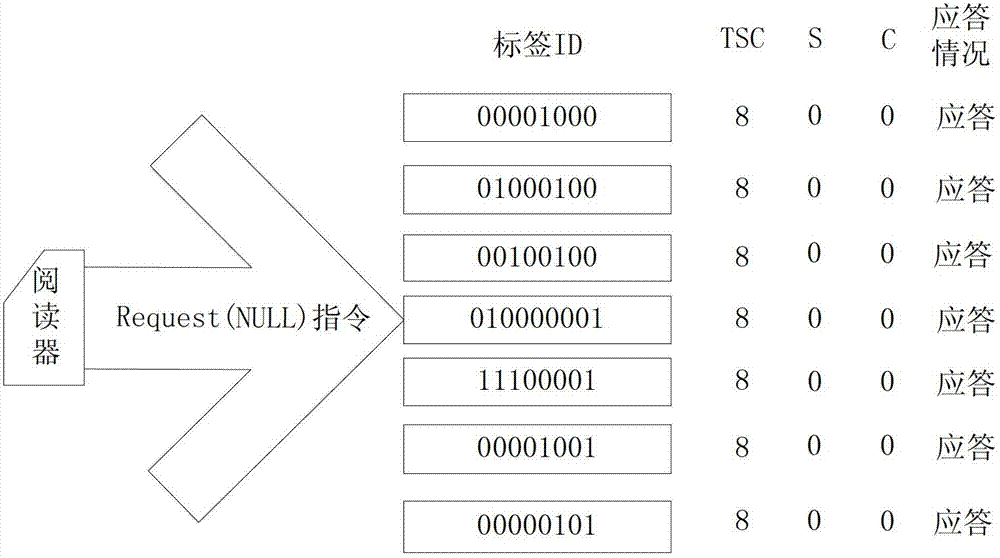
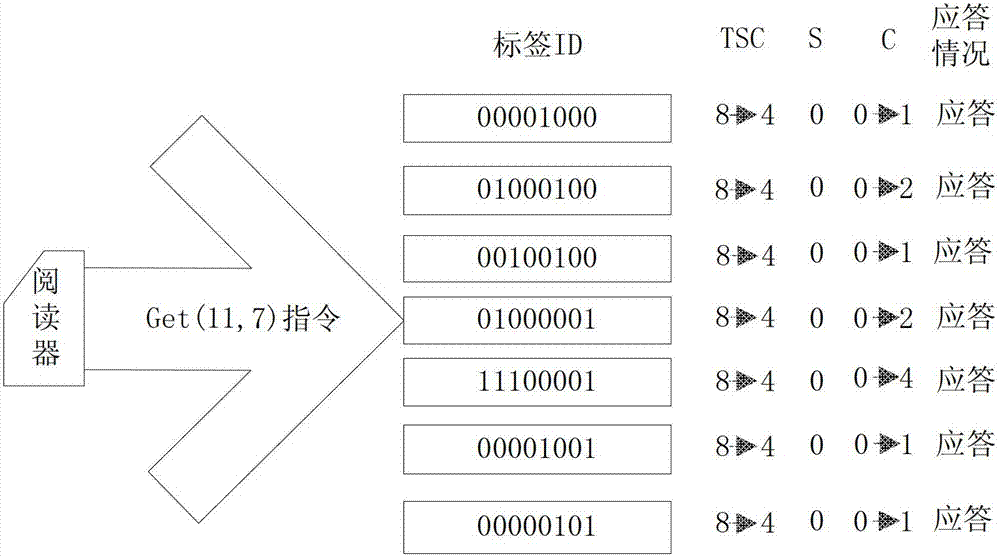
[0057] The following example illustrates a specific implementation process of the algorithm. The process is as follows: figure 1 As shown, assuming that there are 7 tags within the scope of the reader, the tag length is 8, tag1 is 0000 1000, tag2 is 0100 0100, tag3 is 0010 0100, tag4 is 0100 0001, tag5 is 1110 0001, and tag6 is 0000 1001 , tag7 is 0000 0101. In this group of tag ID numbers, the left is the high bit, the highest bit is the seventh bit, and the lowest bit is the 0th bit. Use Di to represent the data of the i-th bit, such as D7 to represent the data of the 7th bit, and use "?" to represent the collision bit.
[0058] Step 1) Initialize the prefix stack: The reader initializes the prefix stack to make it empty. Initially, the sleep level counter S=0, the response counter C=0, the response flag bit TSC=8, the sleep level counter S=0, and 8 means the tag The length of the ID, and then send the request command Request(NULL) to request all tags to respond, the proce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com