Double pipe for heat exchanger
A heat exchanger, double-layer tube technology, applied in heat exchange equipment, heat exchanger types, indirect heat exchangers, etc., can solve the problem of blockage of the outer flow path, flow path area, flow path fluidity deterioration, and flow path thermal efficiency. Reduce and other problems to achieve the effect of excellent heat exchange performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1)
[0069] Regarding the double-layer pipe for heat exchanger of the present invention, use Figure 1 to Figure 4 Be explained.
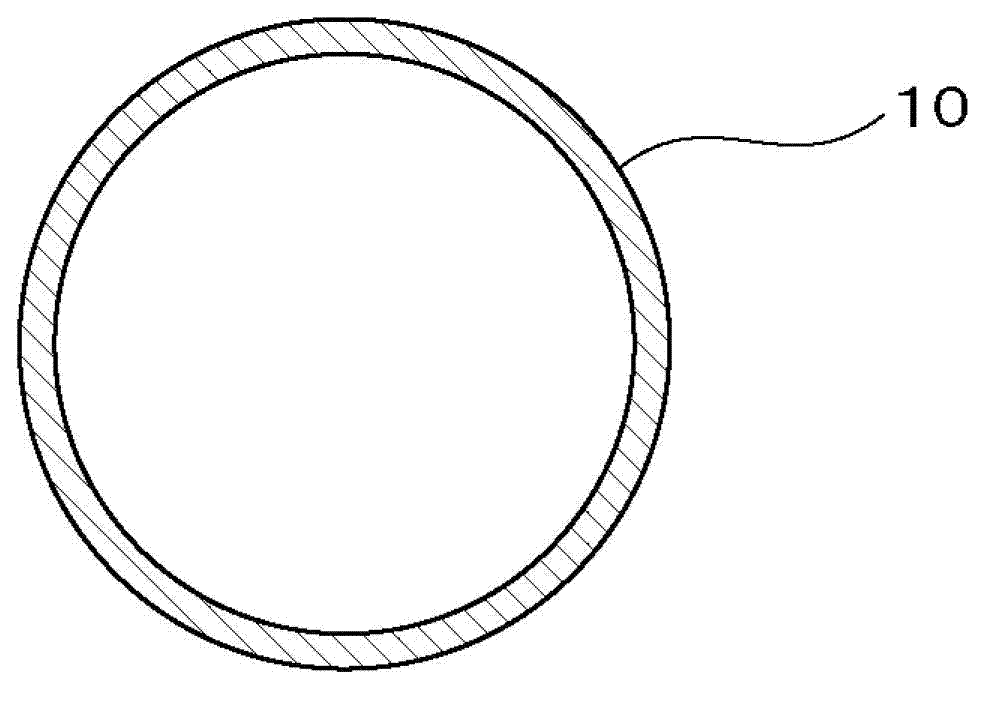
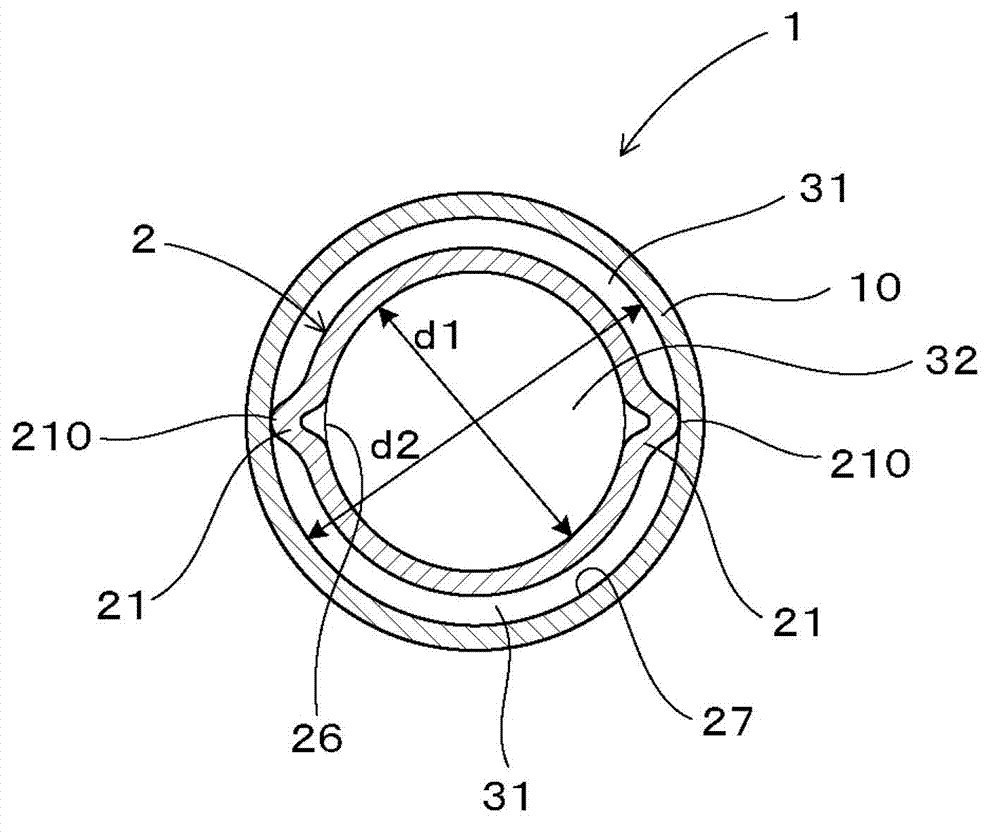
[0070] Such as image 3 As shown, the double-layer tube 1 of the present embodiment is a double-layer tube for a heat exchanger, and has a double-layer tube structure in which an inner tube 2 is arranged inside an outer tube 10, and is used to communicate with the fluid flowing inside the inner tube 2. Heat exchange between the fluid flowing between the inner tube 2 and the outer tube 10 .
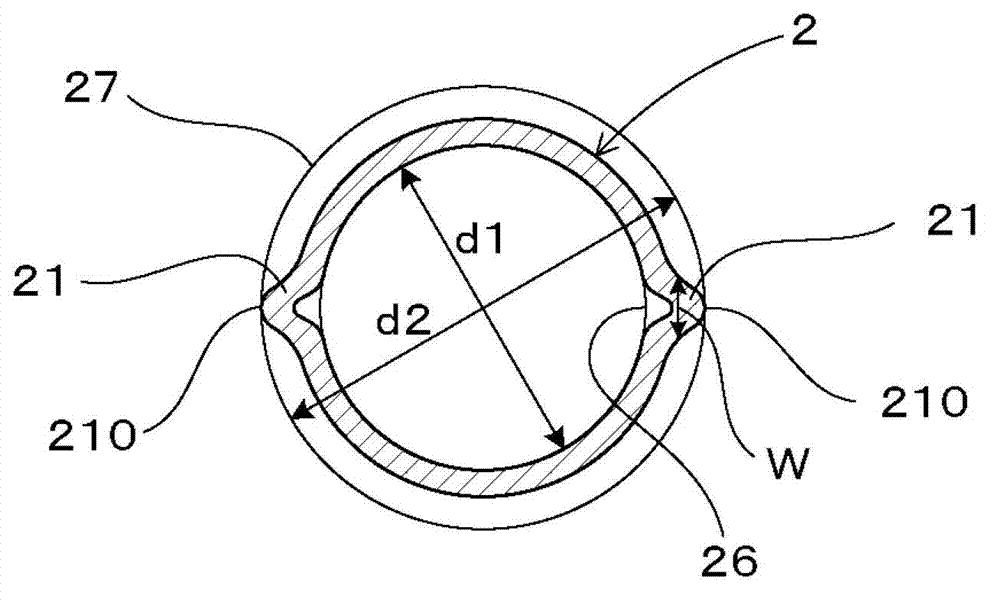
[0071] Such as figure 2 , Figure 4 As shown, the cross-sectional shape of the inner tube 2 has a shape having two protrusions 21 formed by deforming a part of the circumference of a circle so as to protrude outward of the circle. Furthermore, it has a shape in which the position of the convex part 21 is displaced helically in the longitudinal direction. The outer tube 10 has a smooth tube shape with a circular cross-sectional shape. And, if image 3 As show...
Embodiment 2)
[0086] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the cross-sectional shape of the inner tube 2 of the double-layered tube 102 of this embodiment has four protrusions 21 formed by deforming a part of the circumference of a circle so as to protrude outward of the circle at equal intervals. Therefore, if Figure 5 As shown, between the outer tube 10 and the inner tube 2, outer flow paths 31 divided into four positions in the circumferential direction at equal intervals are formed. In addition, in this embodiment, the width dimension W perpendicular to the radial direction of all the protrusions 21 becomes smaller toward the outer peripheral side. In addition, the double-layered pipe 1 of the present embodiment uses the raw material for the outer pipe with an outer diameter of φ21 mm and a wall thickness of 1.2 mm made of the material A3003, and an inner pipe material with an outer diameter of φ19 mm and a wall thickness of 1.2 mm made of the material A3003. Other than that, it produced subst...
Embodiment 3)
[0091] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the cross-sectional shape of the inner tube 2 of the double-layered tube 103 of this embodiment has eight protrusions 21 formed by deforming a part of the circumference of a circle so as to protrude to the outside of the circle at equal intervals. Therefore, if Figure 6 As shown, between the outer tube 10 and the inner tube 2, outer flow paths 31 divided into eight positions in the circumferential direction at equal intervals are formed. In addition, in this embodiment, the width dimension W perpendicular to the radial direction of all the protrusions 21 becomes smaller toward the outer peripheral side. In addition, the double-layered pipe 103 of this embodiment uses the material A3003 with an outer diameter of 23 mm and a wall thickness of 1.3 mm for the outer pipe, and the material A3003 with an outer diameter of 21 mm and a wall thickness of 1.2 mm for the inner pipe. Other than that, it produced substantially in the same manner as in E...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com