Adjustment method of real-time data time label, upper computer and distributed control system
A technology of time stamping and real-time data, applied in the direction of comprehensive factory control, comprehensive factory control, electrical program control, etc., can solve the problems of inaccuracy, trend curve deviation, disconnection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
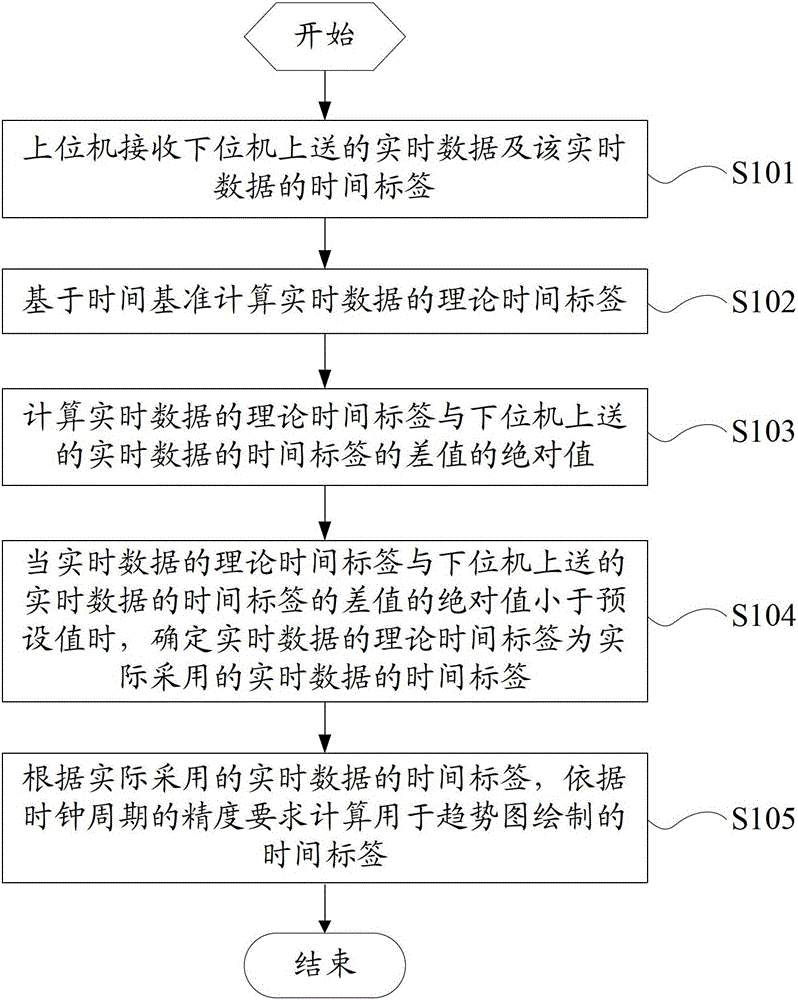
[0039] see figure 1 , which is a schematic flowchart of a method for adjusting a real-time data time tag provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, the method may include:
[0040] Step S101: The upper computer receives the real-time data and the time stamp of the real-time data sent by the lower computer.
[0041] Step S102: Calculate the theoretical time stamp of the real-time data.
[0042] Step S103: Calculate the absolute value of the difference between the theoretical time stamp of the real-time data and the time stamp of the real-time data sent from the lower computer.
[0043] Step S104: When the absolute value of the difference between the theoretical time stamp of the real-time data and the time stamp of the real-time data sent from the lower computer is less than the preset value, determine that the theoretical time stamp of the real-time data is the time stamp of the real-time data actually used.
[0044] Step S105: According to the time label of the real...
Embodiment 2
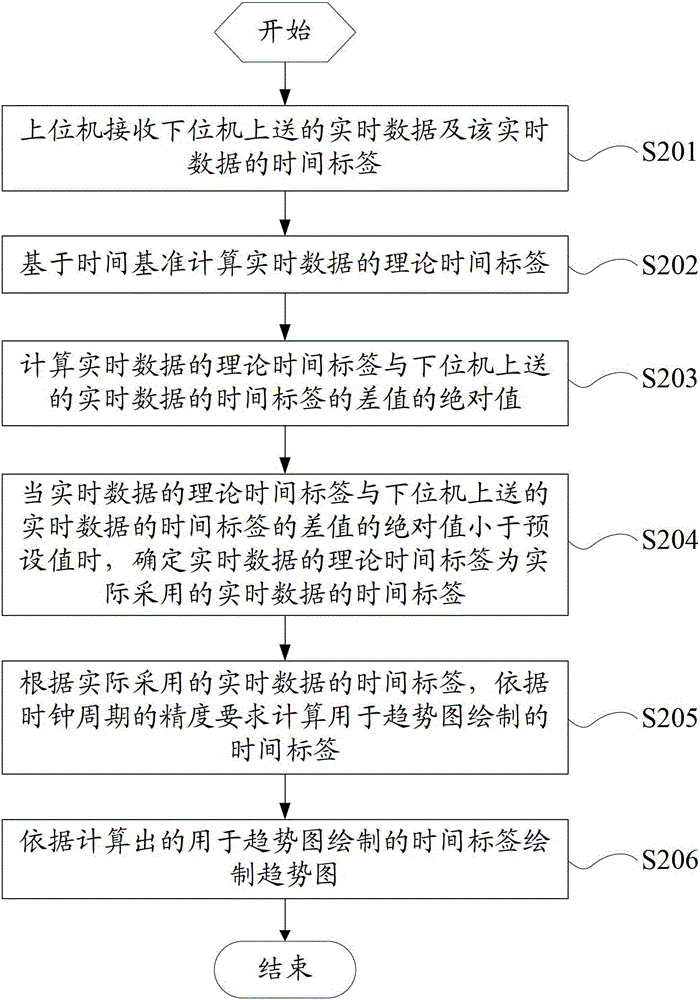
[0047] see figure 2 , which is a schematic flowchart of a method for adjusting a real-time data time tag provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, the method may include:
[0048] Step S201: The upper computer receives the real-time data and the time stamp of the real-time data sent by the lower computer.
[0049] Step S202: Calculate the theoretical time stamp of the real-time data.
[0050] In this embodiment, the calculation of the theoretical time stamp of the real-time data specifically includes: adding the time stamp used for drawing the trend graph in the previous period, the time reference and the clock cycle to obtain the theoretical time stamp of the real-time data.
[0051] Set the theoretical time stamp of real-time data to T t , the clock period is T, and the time label used for trend graph drawing is T p , the time base is b, then, T t = T of the previous cycle p +b+T.
[0052] It should be noted that if the host computer receives data for the fir...
Embodiment 3
[0077] see Figure 4 , is a schematic structural diagram of a host computer provided in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, the host computer may include: a data receiving unit 101, a first computing unit 102, a second computing unit 103, a judging unit 104, a determining unit 105 and a third computing unit 106 . in:
[0078] The data receiving unit 101 is used for receiving the real-time data and the time stamp of the real-time data sent from the lower computer.
[0079] The first computing unit 102 is configured to calculate a theoretical time tag of real-time data.
[0080] The second calculation unit 103 is used to calculate the absolute value of the difference between the theoretical time stamp of the real-time data and the time stamp of the real-time data sent from the lower computer.
[0081] The judging unit 104 is configured to judge whether the absolute value of the difference between the theoretical time stamp of the real-time data and the time stamp of the re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com