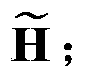Incremental learning and face recognition method based on locality preserving nonnegative matrix factorization ( LPNMF)
A non-negative matrix decomposition, face recognition technology, applied in the field of incremental learning face recognition, can solve the problems of low recognition rate of eigenface method, inability to extract local features, slow decomposition speed, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] The present invention will be further described below. Referring to the attached picture:
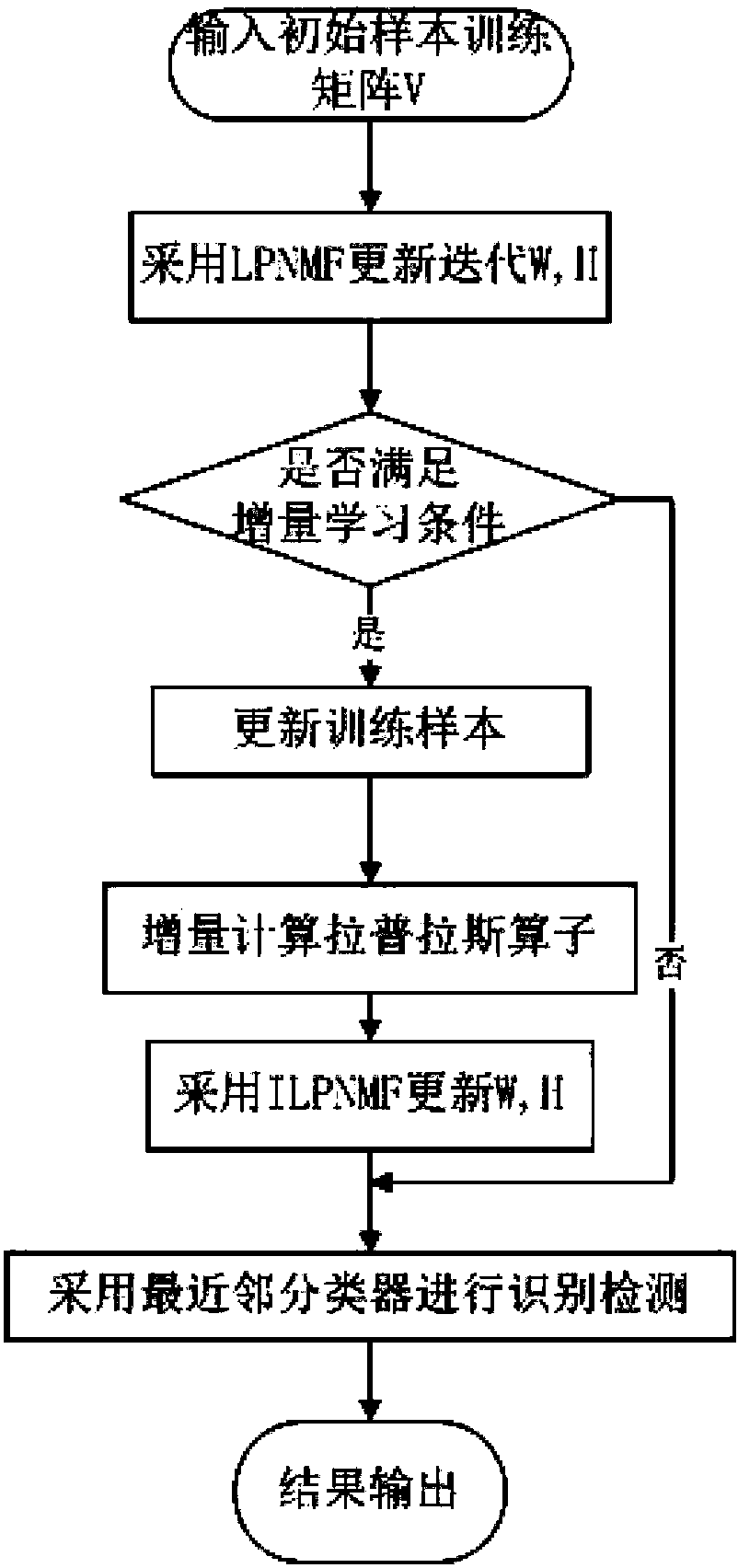
[0040] A method of incremental learning face recognition based on locally preserving non-negative matrix factorization, comprising the following steps:
[0041] a) Preprocessing of face images: normalize each face image into a sample of the same specification;
[0042] b) Initial sample training: Use the LPNMF algorithm to calculate the base matrix W and coefficient matrix H of the initial sample:
[0043] 1) Put each sample v i Constructed into an initial sample training matrix V=[v 1 ,v 2 ,...,v n ];
[0044] 2) Set the maximum number of iterations t, iteratively update W and H mutually, so that WH≈V;
[0045] 3) In step 2, W and H are updated according to the following rules:
[0046] W ia ← W ia ( V H ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com