LED radiator
A technology of LED radiators and heat sinks, which is applied in lighting and heating equipment, cooling/heating devices of lighting devices, lighting devices, etc., and can solve problems such as difficulty in dissipating heat from radiators, poor cooling effect, and reduced service life of LED light sources. , to achieve good heat dissipation effect, avoid accumulation, uniform and good heat dissipation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
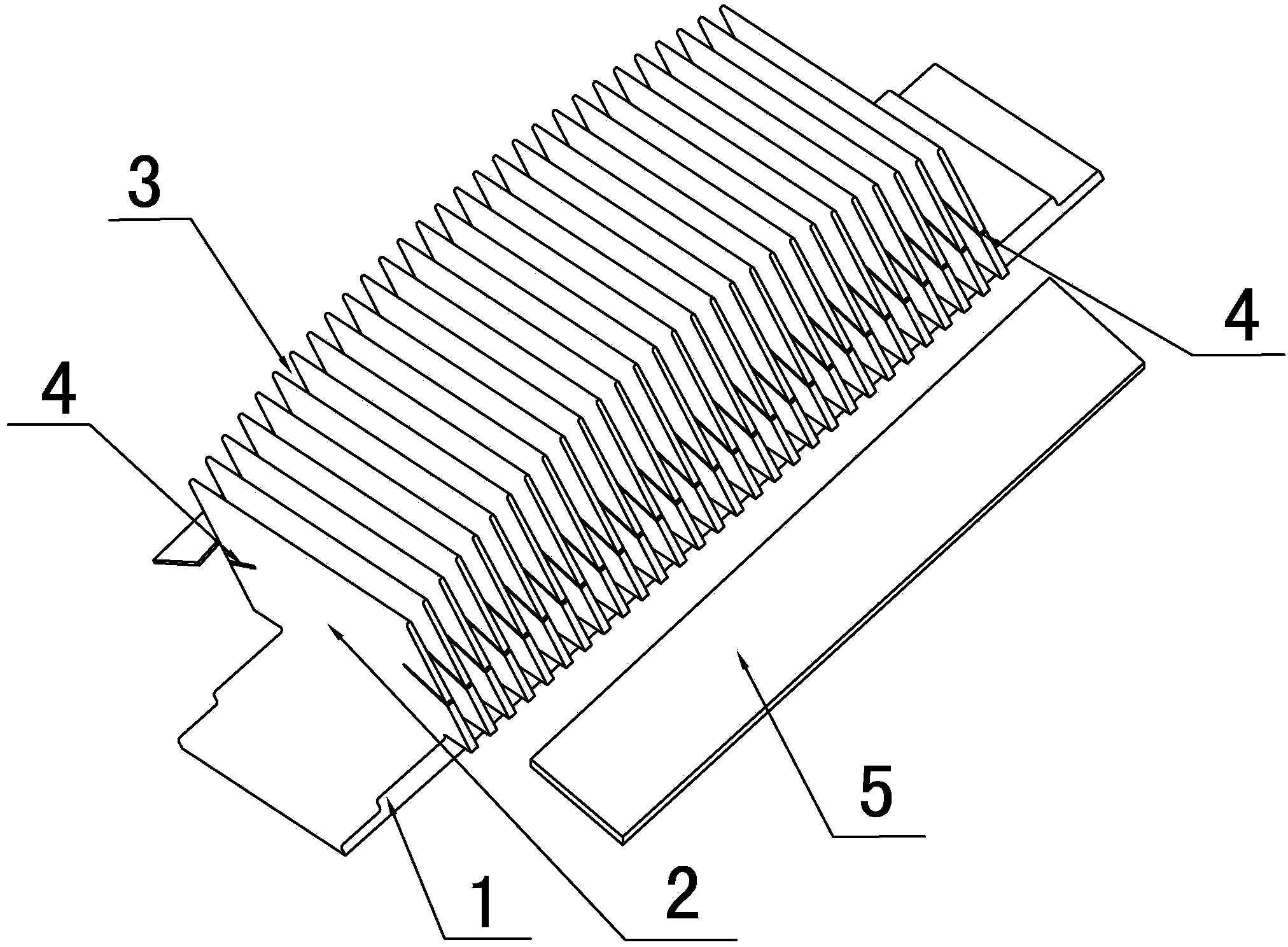
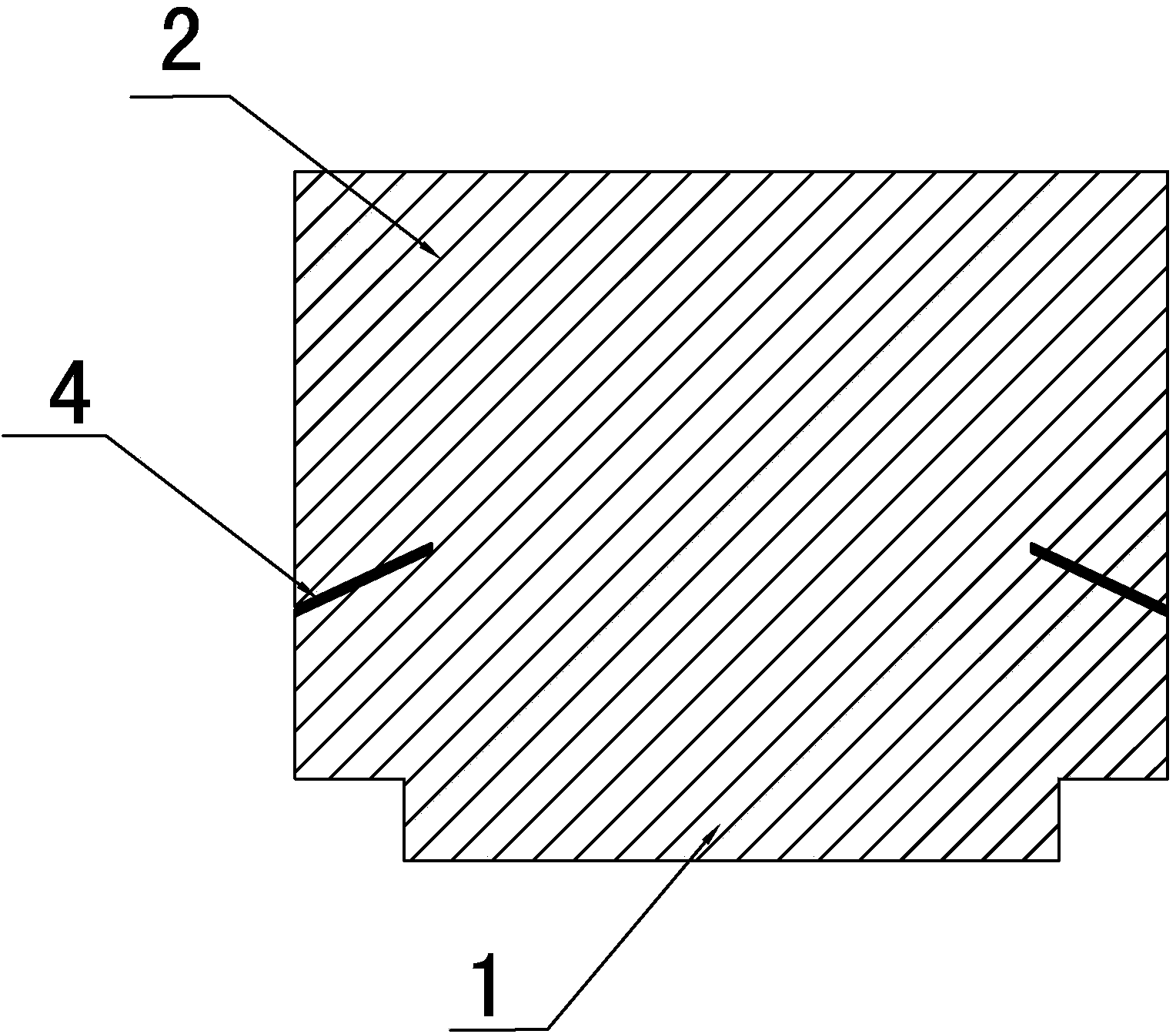
[0018] Embodiment: As shown in the figure, an LED heat sink includes a heat dissipation substrate 1 and a heat dissipation fin group 2. The heat dissipation fin group 2 includes a plurality of heat dissipation fins arranged at intervals on the top surface of the heat dissipation substrate 1, and two adjacent heat dissipation fins A heat dissipation channel 3 is formed between the fins, and the heat dissipation fins are parallel to the closed end of the heat dissipation substrate 1. One end of the plurality of heat dissipation fins on the same side extends out of the edge of the heat dissipation substrate 1. When the heat is transferred to the heat dissipation channel 3, the heat dissipation After the air in the channel 3 absorbs heat, its density decreases and rises to leave the heat dissipation channel 3, and the air with a lower temperature below the heat dissipation channel 3 outside the heat dissipation base 1 enters the heat dissipation channel 3, and it goes round and roun...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com