Beacon missed reading detection method for trains
A detection method and beacon technology, which is applied in the field of missing-reading detection of beacons on trains, and can solve the problems that beacons can no longer be read and beacons are missed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
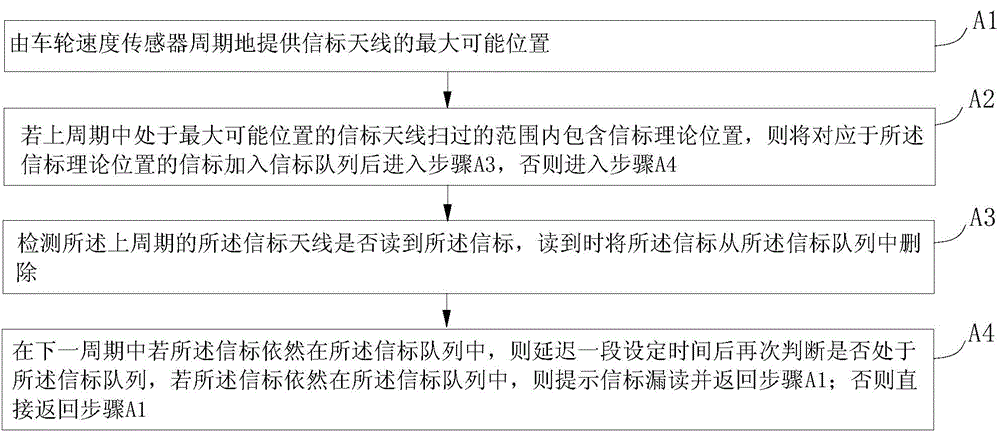
[0025] figure 1 The method for detecting missed reading of a train's beacon in the first embodiment of the present invention is shown, and the method specifically includes the following steps:
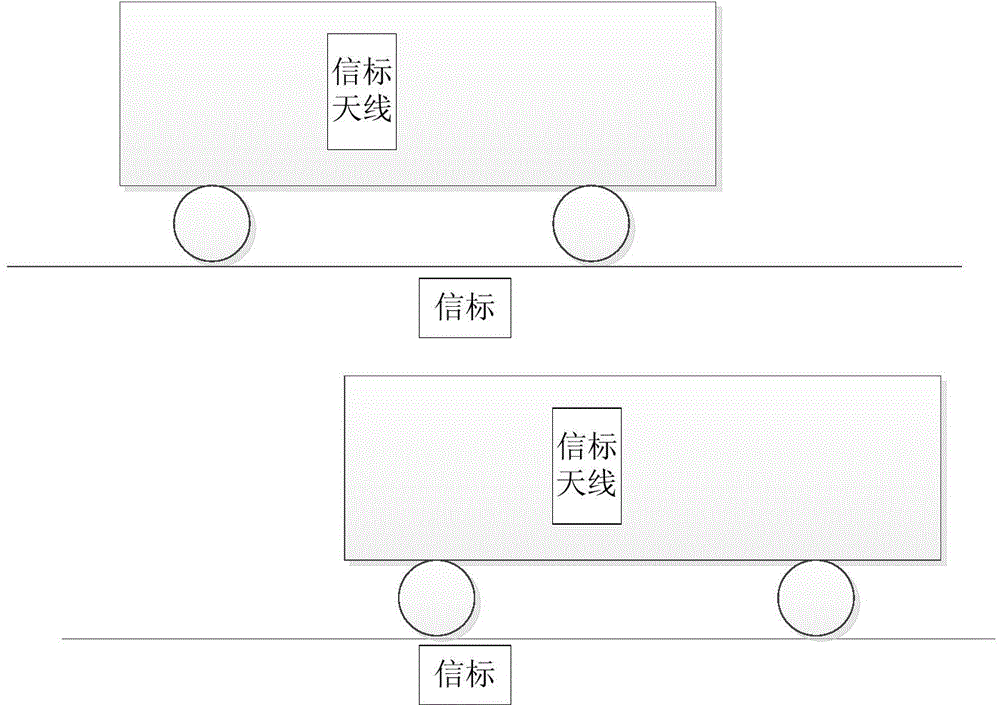
[0026] Step A1: The wheel speed sensor periodically provides the maximum possible position of the beacon antenna;
[0027] Step A2: If the theoretical position of the beacon is included in the range swept by the beacon antenna at the largest possible position in the previous cycle, the beacon corresponding to the theoretical position of the beacon is added to the beacon queue and then enter step A3, otherwise, enter Step A4;
[0028] Step A3: Detect whether the beacon is read by the beacon antenna of the previous cycle, and delete the beacon from the beacon queue when it is read;
[0029] Step A4: In the next cycle, if the beacon is still in the beacon queue, after a delay of a set time, judge whether it is in the beacon queue again, and if the beacon is still in the beacon queue If it is, it...
Embodiment 2
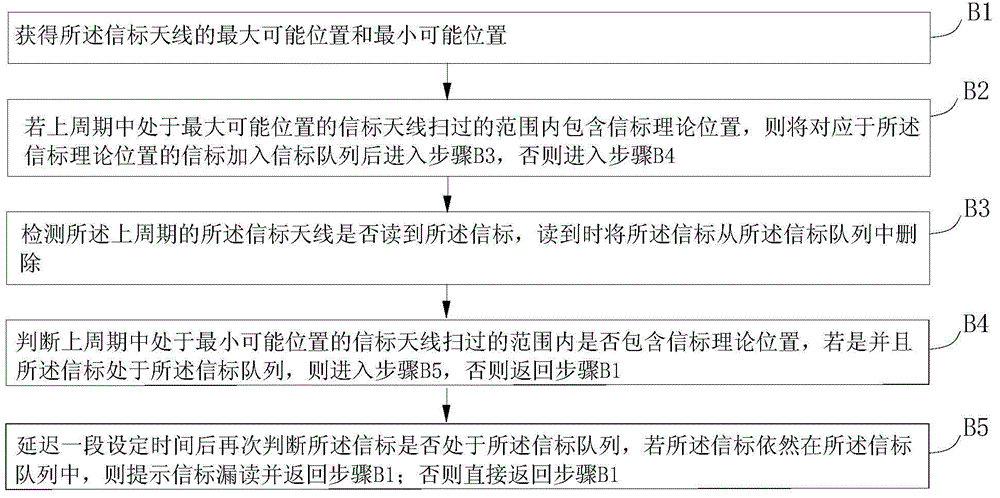
[0037] image 3 The method for detecting missed reading of train beacons according to the second embodiment of the present invention is shown. The method specifically includes the following steps:
[0038] Step B1: Obtain the maximum possible position and the minimum possible position of the beacon antenna;
[0039] Step B2: If the theoretical position of the beacon is included in the range swept by the beacon antenna at the largest possible position in the last cycle, the beacon corresponding to the theoretical position of the beacon is added to the beacon queue and then enter step B3, otherwise, enter Step B4;
[0040] Step B3: Detect whether the beacon is read by the beacon antenna of the previous cycle, and delete the beacon from the beacon queue when it is read;
[0041] Step B4: Determine whether the beacon's theoretical position is included in the range swept by the beacon antenna at the smallest possible position in the previous cycle, if so and the beacon is in the beacon qu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com