Frequency domain optimization mixture staggered grid finite difference forward modeling method
A staggered grid and finite difference technology, applied in the field of frequency-domain optimized hybrid staggered grid finite-difference forward modeling, can solve the problem of lower accuracy than time-domain finite-difference forward modeling, and reduce grid anisotropy , high precision, optimize the effect of anisotropy and dispersion error
Inactive Publication Date: 2014-05-28
中国石油集团西北地质研究所有限公司
View PDF2 Cites 20 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
[0005] The purpose of the present invention is to overcome the defect that the grid difference system of the prior art is lower than the time-domain finite difference forward modeling accuracy, and to provide an optimized hybrid of conventional s
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
 Login to View More
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
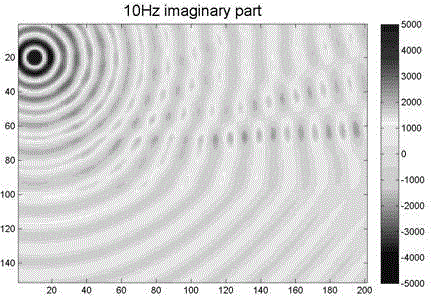
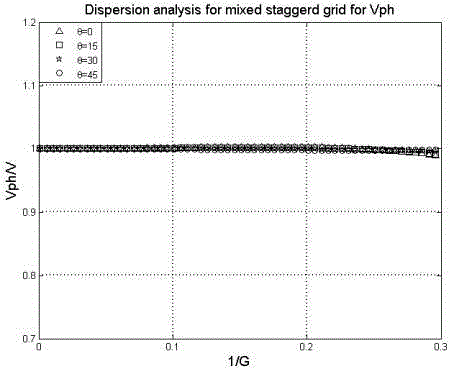
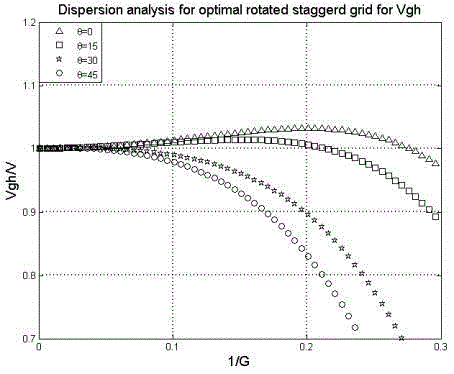
A frequency domain optimization mixture staggered grid finite difference forward modeling method comprises the following steps: 1) providing a time-domain two-dimension sound wave equation; 2) eliminating artificial boundary reflection and obtaining a time-domain two-dimension sound wave equation with a perfectly-matched layer boundary condition; 3) performing Fourier transform on time variables at the two sides of the equation and obtaining a frequency-domain sound wave equation; 4) carrying out finite difference discretization on the frequency-domain sound wave equation with the perfectly-matched layer boundary condition based on a conventional staggered grid and obtaining a finite difference discretization format; 5) carrying out finite difference discretization on the frequency-domain sound wave equation with the perfectly-matched layer boundary condition based on a rotation staggered grid and obtaining a finite difference discretization format; 6) performing optimization mixing on the conventional staggered grid and the rotation staggered grid, grid difference item being weighted average of the grid difference item in the two grid systems, and quality acceleration item being weighted average of a center point and eight points around the center point; and 7) under the criterion of the minimum phase velocity error, calculating an optimized coefficient. The weighting coefficient enables frequency dispersion error due to the finite difference discretization to be the smallest, and the precision of the frequency-domain forward modeling is greatly improved.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention belongs to the technical field of seismic wave forward modeling, in particular to a frequency-domain optimized hybrid staggered-grid finite-difference forward modeling method for optimal combination of two sets of grid difference systems, a frequency-domain conventional staggered grid and a frequency-domain rotated staggered grid , aiming to improve the accuracy and computational efficiency of forward modeling in the frequency domain. Background technique [0002] In the existing technical field of seismic wave forward modeling, compared with time-domain finite-difference forward modeling, frequency-domain finite-difference forward modeling has the advantages of high computational efficiency of multi-shot simulation and easy simulation of formation absorption effects. Wave equation migration and full waveform inversion usually only require a limited number of frequencies. At this time, forward modeling in the frequency domain shows its un...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): G01V1/28
Inventor 王小卫韩令贺胡自多刘威雍运动邵喜春
Owner 中国石油集团西北地质研究所有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com