Main and auxiliary database synchronization method and device
A primary database and database technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve the problems of low synchronization efficiency of the primary and standby databases, and achieve the effects of improving synchronization efficiency, reducing delay, and increasing availability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
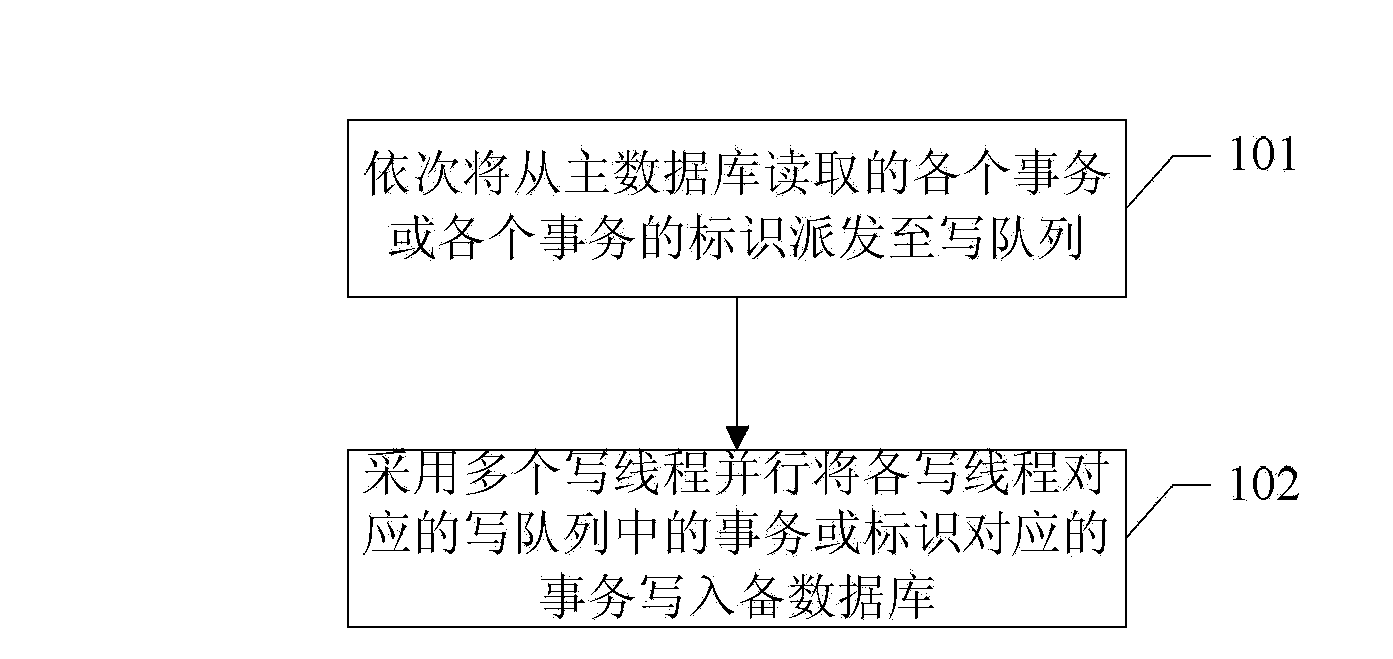
[0033] The method for synchronizing the active and standby databases in the embodiment of the present application, such as figure 1 As shown, it is used for data synchronization between the primary database and the standby database, and the method includes:
[0034] Step 101: a transaction dispatching step, sequentially dispatching each transaction or the identifier of each transaction read from the main database to the write queue;
[0035] The order in which the transactions read from the master database in this embodiment of the present application are read out is the order in which they are committed in the master database and written into a log.
[0036] The transaction dispatch step is implemented by a dispatch thread.
[0037] In the transaction dispatch step, the write queue is selected for the current transaction according to the shortest write queue principle or the transaction hash value.
[0038] Preferably, the shortest write queue principle is adopted, that is,...
Embodiment 2
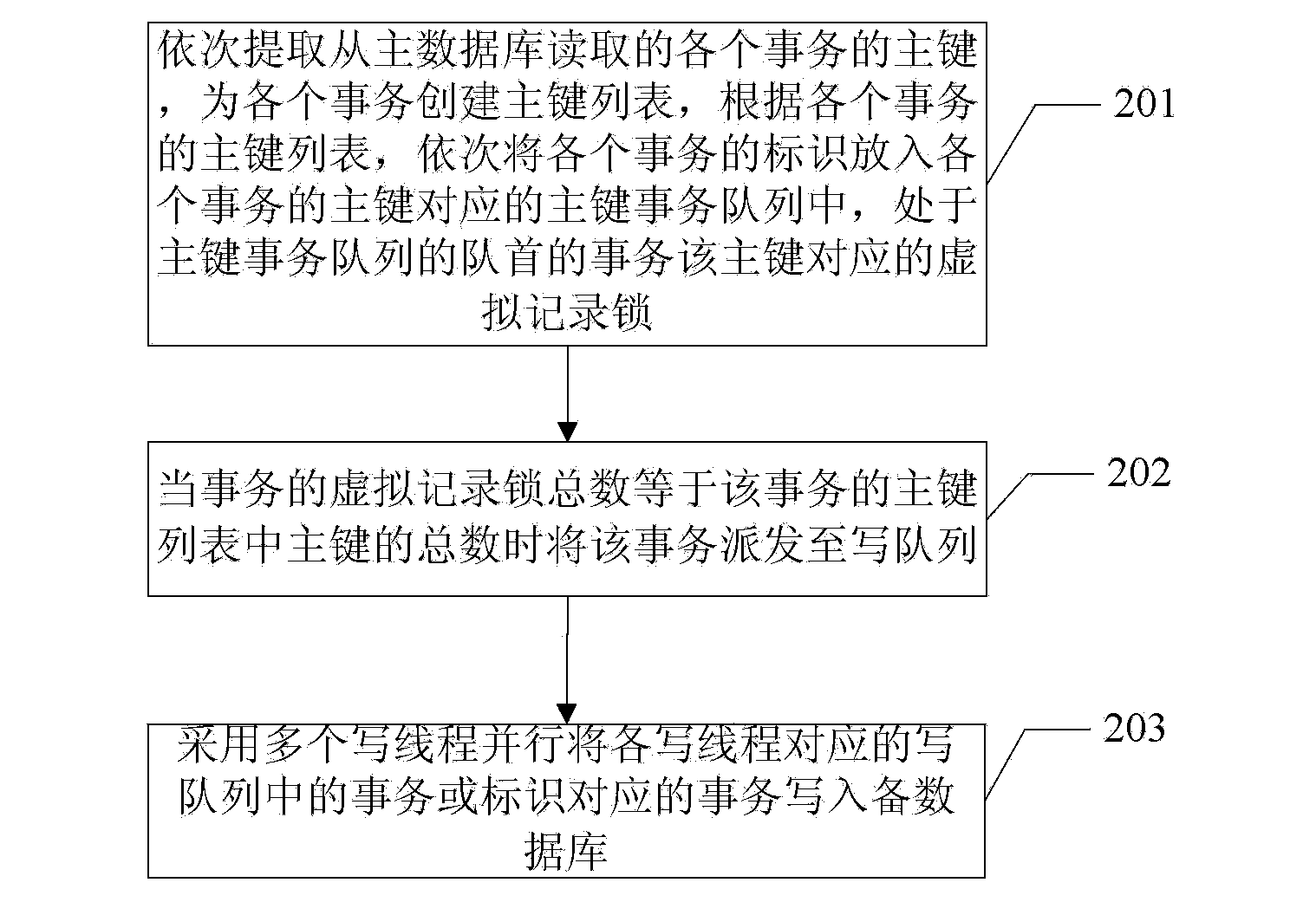
[0044] The method for synchronizing the master and standby databases in this application, such as figure 2 As shown, it is used for data synchronization between the primary database and the standby database, and the method includes:
[0045] Step 201: a preprocessing step, sequentially extracting the primary key of each transaction read from the master database, creating a primary key list for each transaction, and sequentially putting the identification of each transaction into the primary key transaction corresponding to the primary key of each transaction according to the primary key list of each transaction In the queue, the virtual record lock corresponding to the primary key of the transaction at the head of the primary key transaction queue;
[0046] In this paper, a primary key corresponds to a primary key transaction queue, and different primary keys correspond to different primary key transaction queues. Before a transaction is written to the standby database, it n...
Embodiment 3
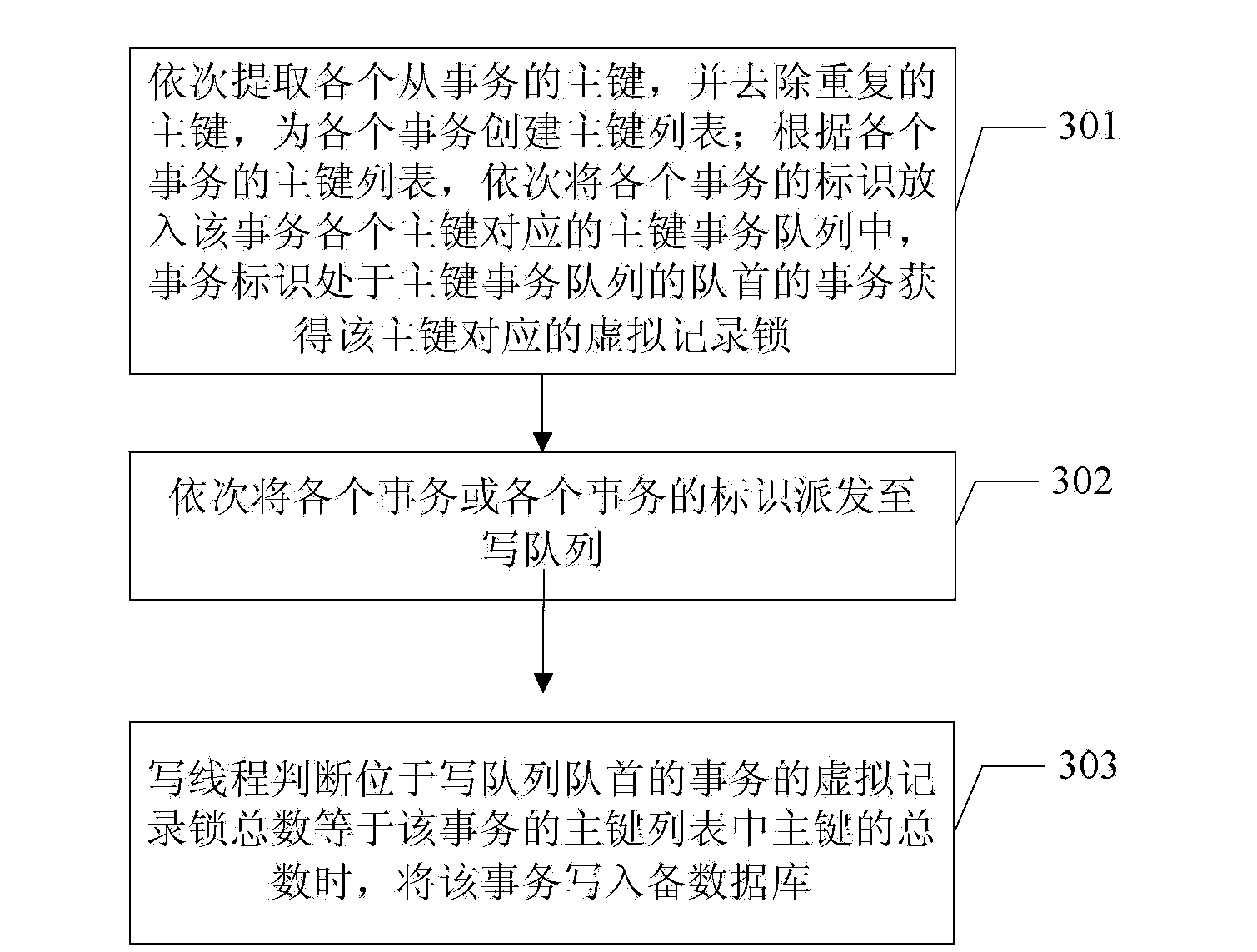
[0059] The method for synchronizing the master and standby databases in this application, such as image 3 As shown, it is used for data synchronization between the primary database and the standby database, and the method includes:
[0060] Step 301: a preprocessing step, sequentially extracting the primary keys of each transaction read from the main database, and removing duplicate primary keys, creating a list of primary keys for each transaction; Put it into the primary key transaction queue corresponding to each primary key of the transaction, and the transaction whose transaction ID is at the head of the primary key transaction queue obtains the virtual record lock corresponding to the primary key;
[0061] In step 301, the primary key is sequentially extracted from each row record of the transaction, and after duplicate primary keys are removed, one primary key corresponds to one or several row records.
[0062] The virtual record locks of each primary key are maintain...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com