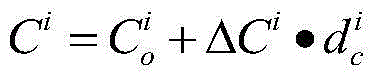Generalized displacement hybrid monitoring damaged cable load progressive identification method
A progressive identification and mixed monitoring technology, applied in the direction of measuring force, measuring device, measuring heat, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0055] The method employs an algorithm that is used to identify damaged cables and load changes. During specific implementation, the following steps are one of various steps that may be taken.
[0056] Step 1: First identify the amount of possible varying loads that the cable structure will be subjected to. According to the characteristics of the loads borne by the cable structure, confirm "all possible changing loads", or regard all the loads as "all possible changing loads", and assume a total of JZW possible changing loads, this method passes Identify the change degree of these JZW "all possible changeable loads" to express the change amount of "all possible changeable loads".
[0057] Let the sum of the number of supporting cables of the cable structure and the number of JZW "all possible changing loads" be N. For the convenience of description, this method collectively refers to the evaluated support cables and "all possible changing loads" as "evaluated objects", and t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com