GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) resolving method based on block particle filter
A particle filtering and particle technology, applied in the field of GNSS solution, which can solve the problems of high dimension of iterative vector, easy divergence, and restricting the accuracy of positioning solution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
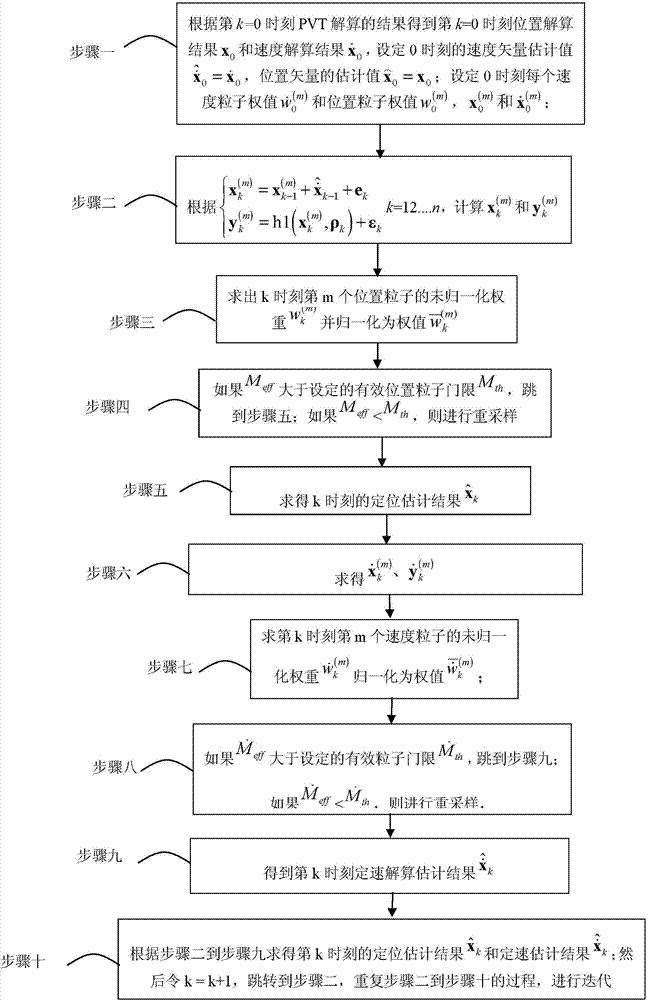
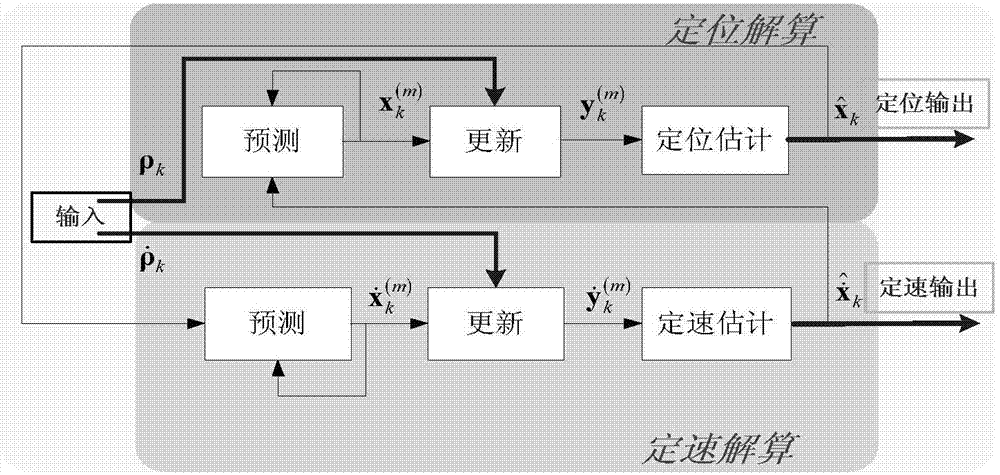
[0026] Specific embodiment one: a kind of GNSS solution method based on block particle filter of this embodiment is specifically carried out according to the following steps:
[0027] Step 1, according to the result of PVT (Position, Velocity, Time) solution at the k=0th moment, the position solution x at the k=0th moment is obtained 0 and velocity solution results Set the velocity vector estimate at time 0 Estimated value of the position vector Set the weight of each speed particle at time 0 and position particle weights make And determine the M four-dimensional position particles at time 0 and M four-dimensional velocity particles in Evenly distributed in around, Evenly distributed in around; define the mth position particle as in respectively represent the three-dimensional coordinates of the mth position particle at time 0, Represents the clock deviation between the state of the mth position particle and the satellite at time 0; define the posit...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0041] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: in step two is the kth moment, the N-dimensional observation vector of the particle at the mth position is defined as:
[0042] y k ( m ) = ρ 1 , k - ( x 1 , k - x U ,...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0044] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: ρ k is an N-dimensional pseudorange vector, defined as:
[0045] ρ k =[ρ 1,k ,ρ 2,k ,...,ρ N,k ] T (5)
[0046] The state vector particle passing through the user at the kth moment Calculate the observed pseudorange:
[0047] ρ n , k = ( x n , k - x U , k ) 2 + ( y n , k ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com