Method and device for mobile load balancing and air interface resource utilization statistics
A mobile load balancing and air interface resource technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of download rate reduction, video service interruption (data buffering, user experience will not cause a major impact, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing impact and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
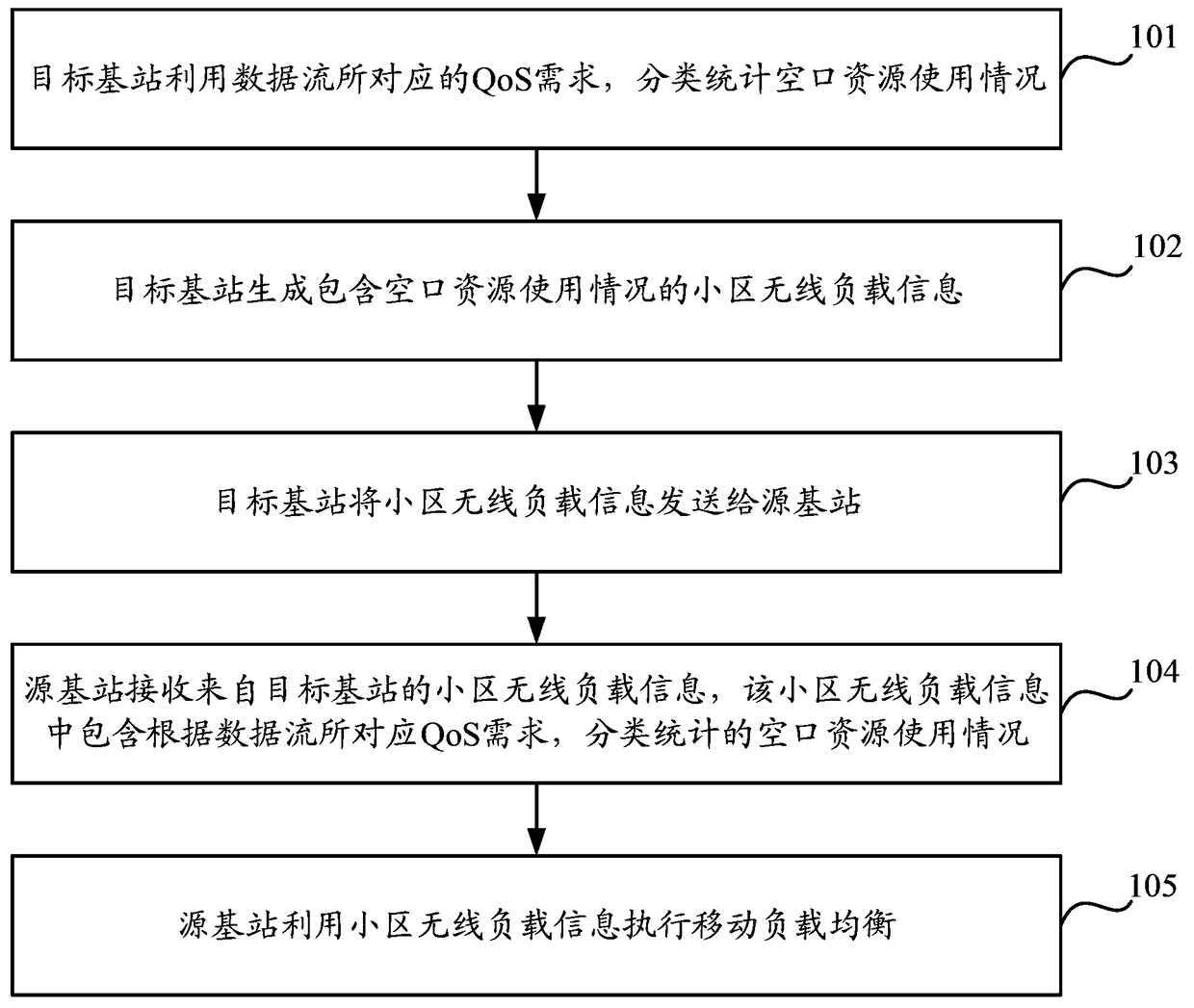
[0041] Mobile load balancing means that the source base station automatically adjusts the mobility parameters to transfer part of the services of the heavy-loaded cell under its jurisdiction to other light-loaded adjacent or same-covered cells, so as to realize the reasonable distribution of service load among the cells. In the LTE system, the mobile load balancing mechanism is applicable to the network deployment scenarios of Intra-LTE (that is, between LTE base station equipment) and Inter-RAT (that is, between LTE base station equipment and other system access network nodes); In the implementation process of , the source base station monitors the load status of the cell under its jurisdiction, and exchanges load information with the adjacent target base station through the X2 or S1 interface. According to the obtained load information, the source base station adjusts the mobility parameters of the overloaded cell so that its The served UE (UserEquipment: user equipment) can ...
Embodiment 2
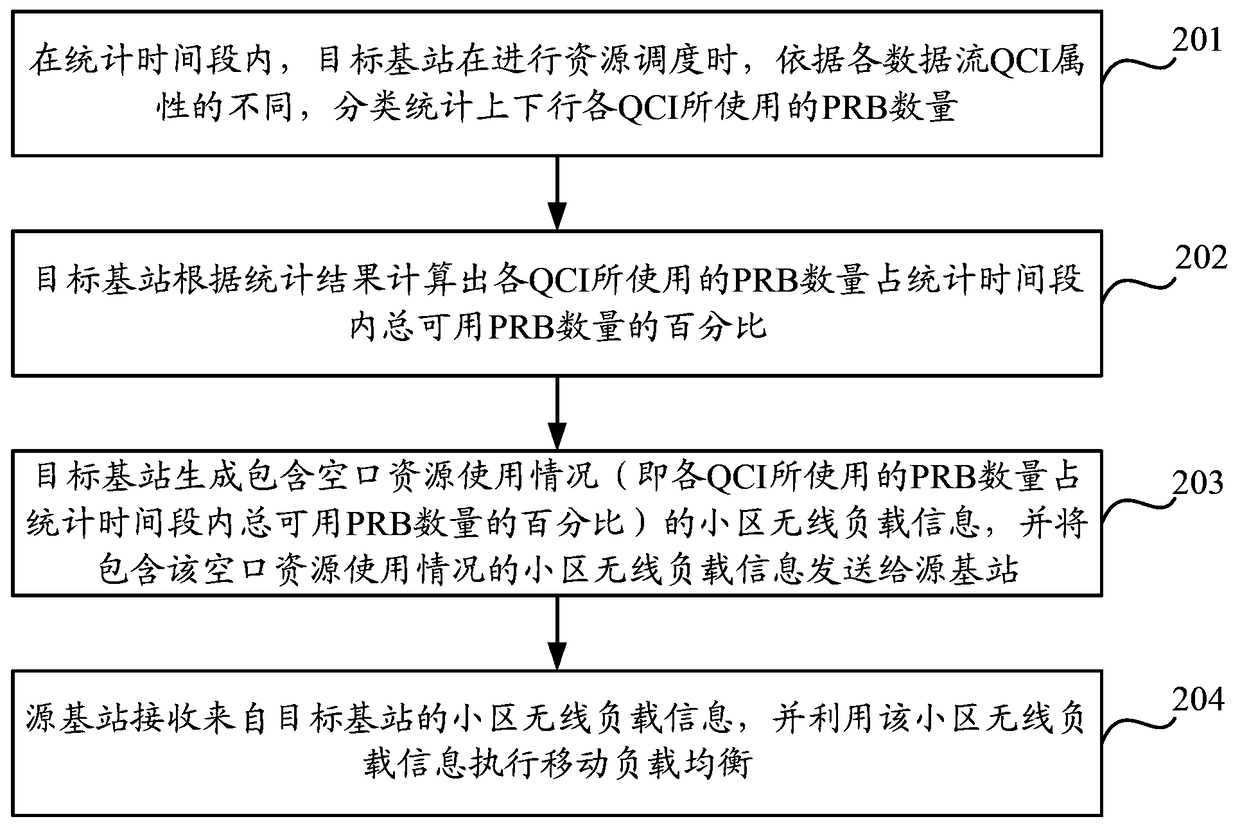
[0071] Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a mobile load balancing method. In the embodiment of the present invention, the QoS requirement is QCI as an example for illustration, that is, the target base station needs to classify and count the data occupied by various QCIs according to the different QCIs of the data streams. The number of PRBs; where, the QCI is a number used to indicate the scheduling priority of the data flow, the comprehensive attributes of the delay indicator and the packet loss / error rate indicator; for example, a data flow with a QCI of 1 can be defined, and the corresponding scheduling priority It is 2, the maximum delay that can be tolerated is 100ms, and the maximum packet loss / error rate is 0.01.
[0072] Such as figure 2 As shown, the mobile load balancing method may include the following steps:
[0073] Step 201: During the statistical time period, when performing resource scheduling, the target base station classifies and counts the nu...
Embodiment 3
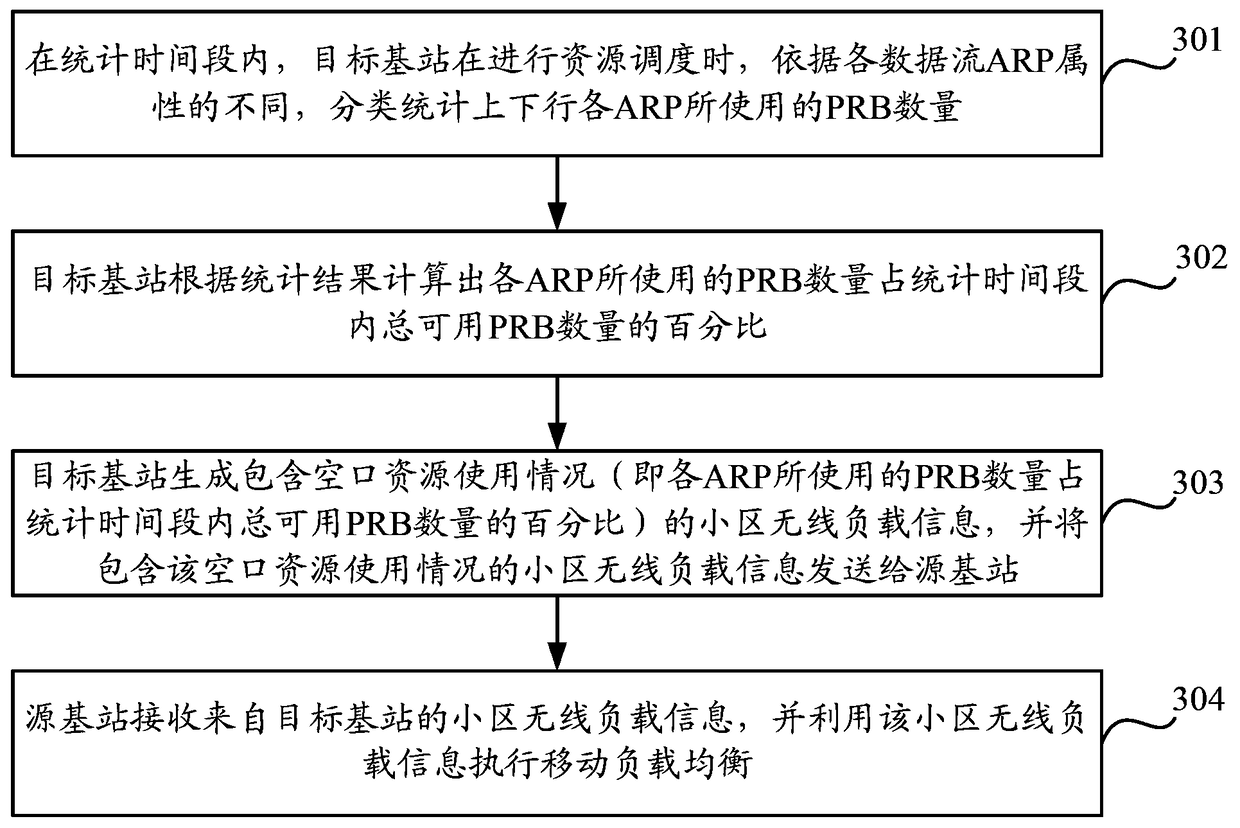
[0087] Embodiment 3 of the present invention provides a mobile load balancing method. In the embodiment of the present invention, the QoS requirement is ARP as an example for illustration, that is, the target base station needs to classify and count the resources occupied by various ARP data according to the different ARPs of the data streams. The number of PRBs; among them, ARP is used to indicate the priority of the data flow, the ability to preempt other services, and the attribute whether it can be preempted by other services. For example, considering the factors of user experience and network efficiency, operators usually set high priority for real-time service-related data transmission, and have the ability to preempt low-priority service resources, and the occupied resources cannot be preempted by other services; And non-real-time business, such as periodic email sending and receiving related data transmission is set to low priority, it does not have the ability to preem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com