Synchronization self-adaptation short-wave communication frequency-selecting method based on ionized layer data
A short-wave communication and ionospheric technology, which is applied in the communication between multiple stations, electrical components, transmission monitoring and other directions, and can solve the problems of long time, reduced number of available channels, and low efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
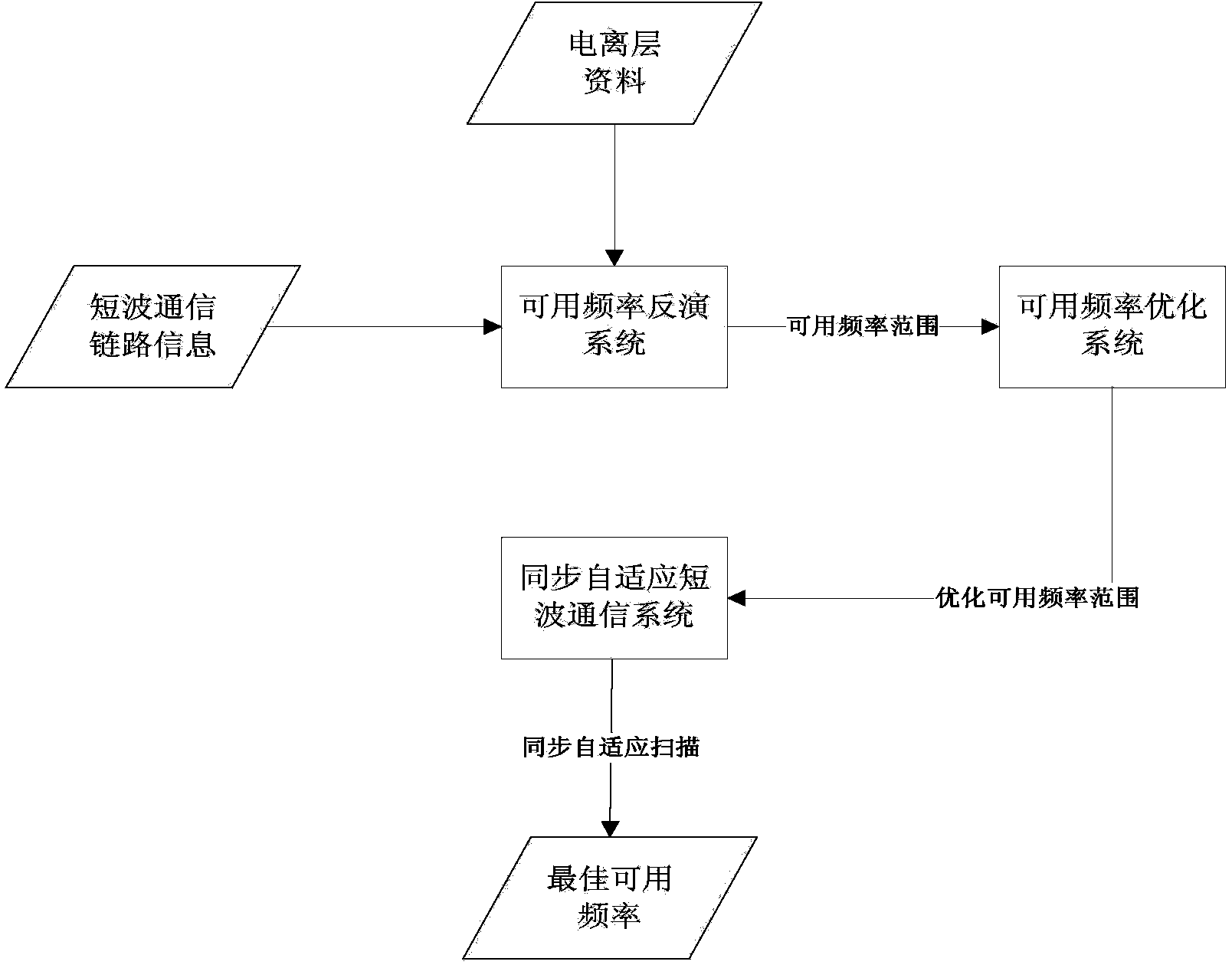
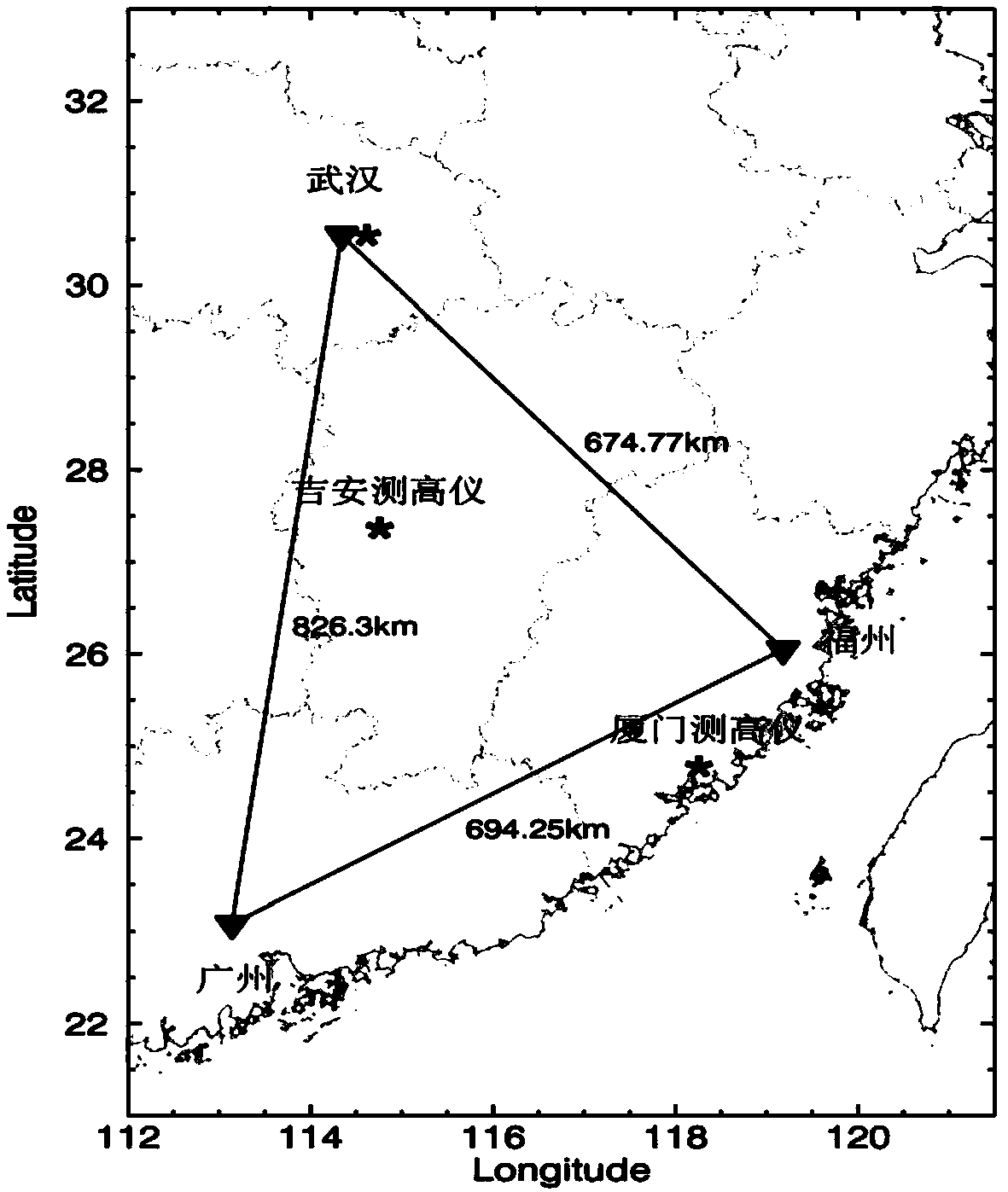
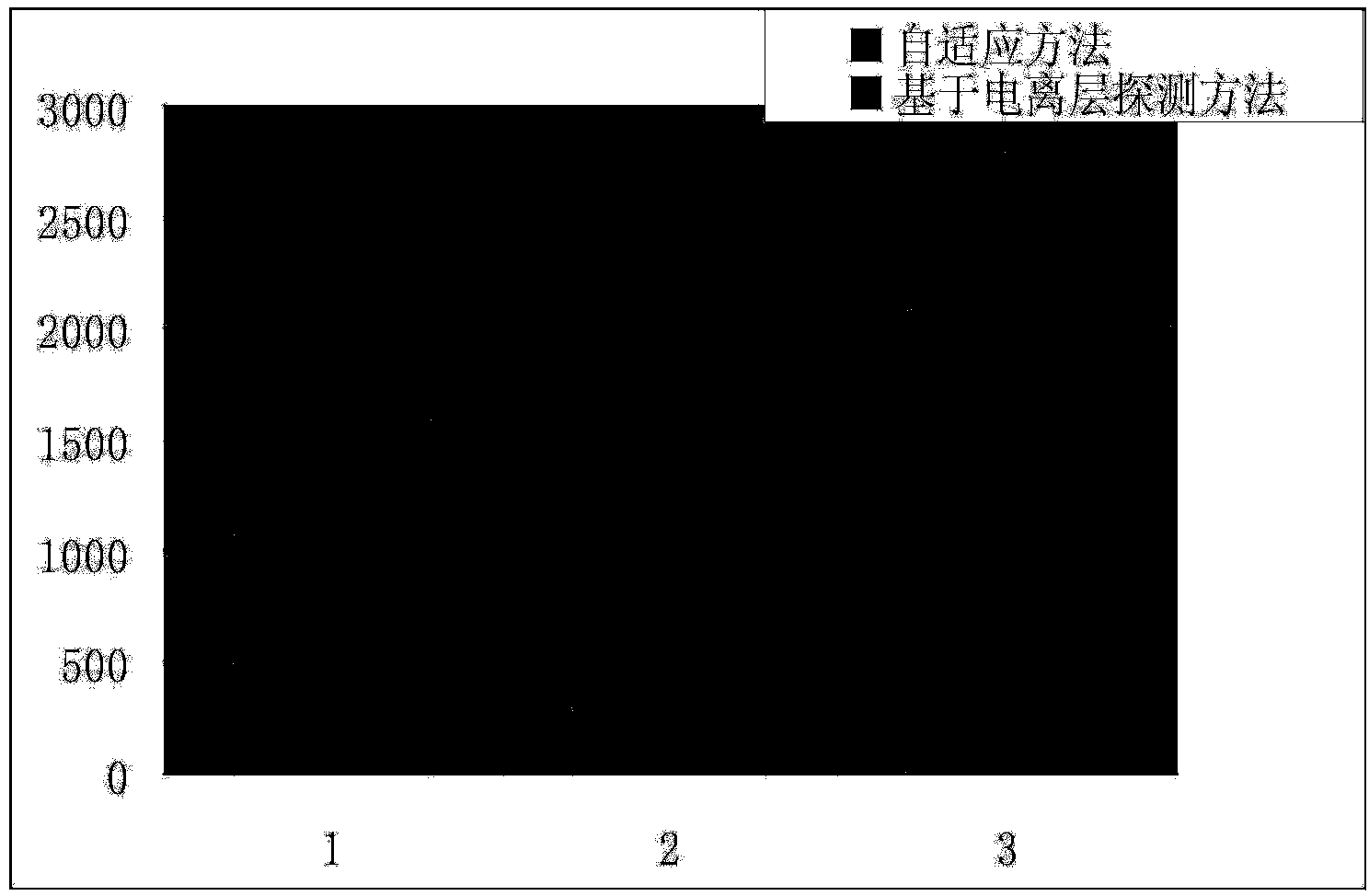
[0049] In order to make those skilled in the art more clearly understand the ionospheric data-based synchronous adaptive shortwave communication frequency selection method of the present invention, its specific implementation will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0050] When the synchronous adaptive short-wave communication system is working, the scanning frequency table and frequency scanning method set in the system are very important. Generally, channels are scanned sequentially in the order of scanning the frequency table. If there are enough frequency points in the scanning frequency table, the channel frequency range can be wide enough, and the channel frequency density can be high enough to ensure that the best available frequency for communication can be obtained during channel detection. However, if scanning is performed in such a manner, there are too many scanning frequency points, the channel detection process takes too long, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com