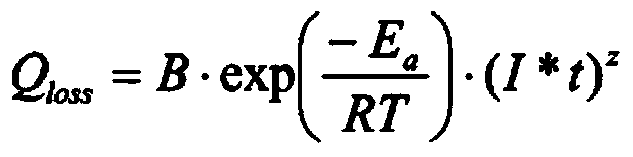Method for determining an overall loss of capacitance of a secondary cell
A capacity loss, secondary battery technology, applied in the direction of measuring electrical variables, measuring electricity, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
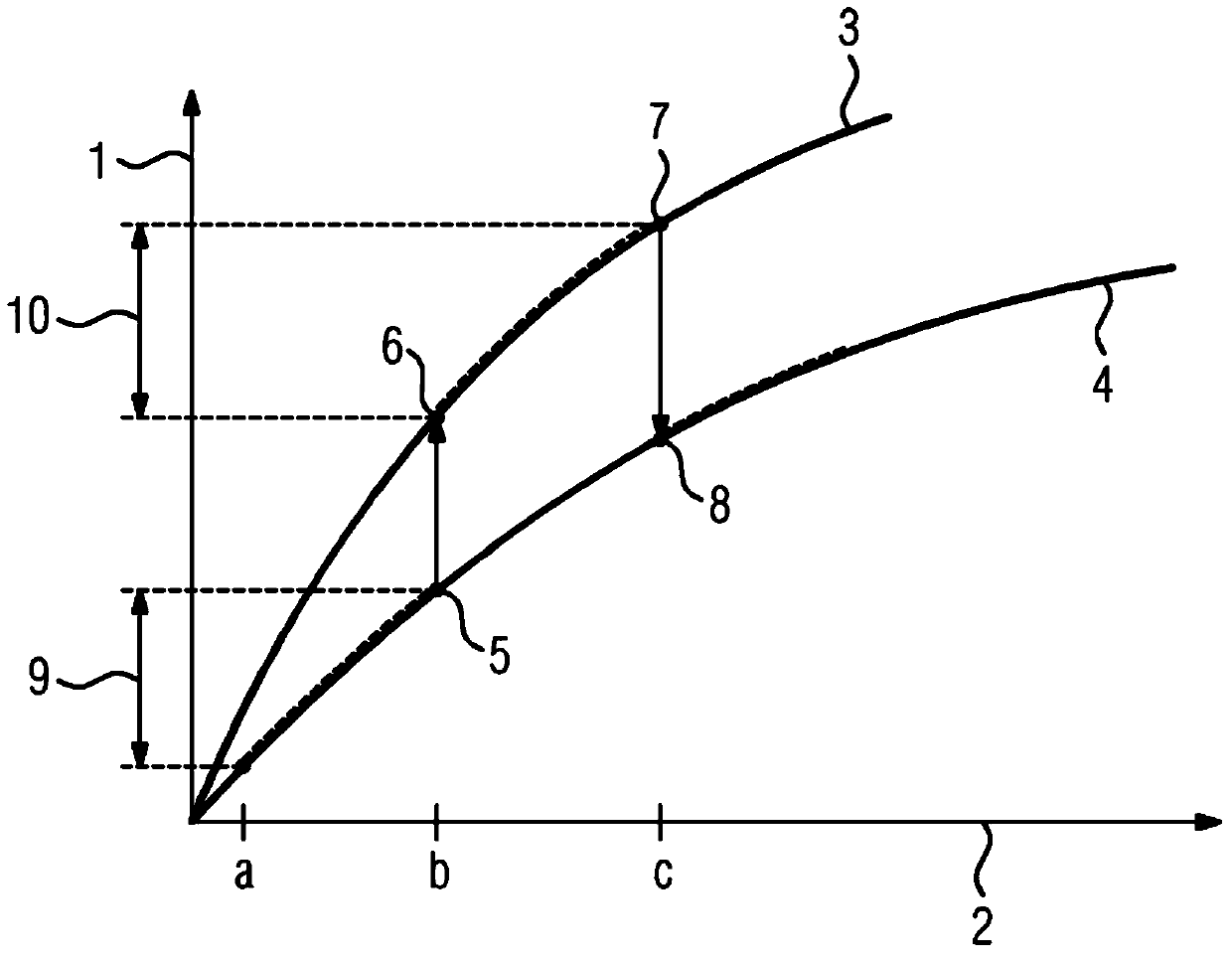
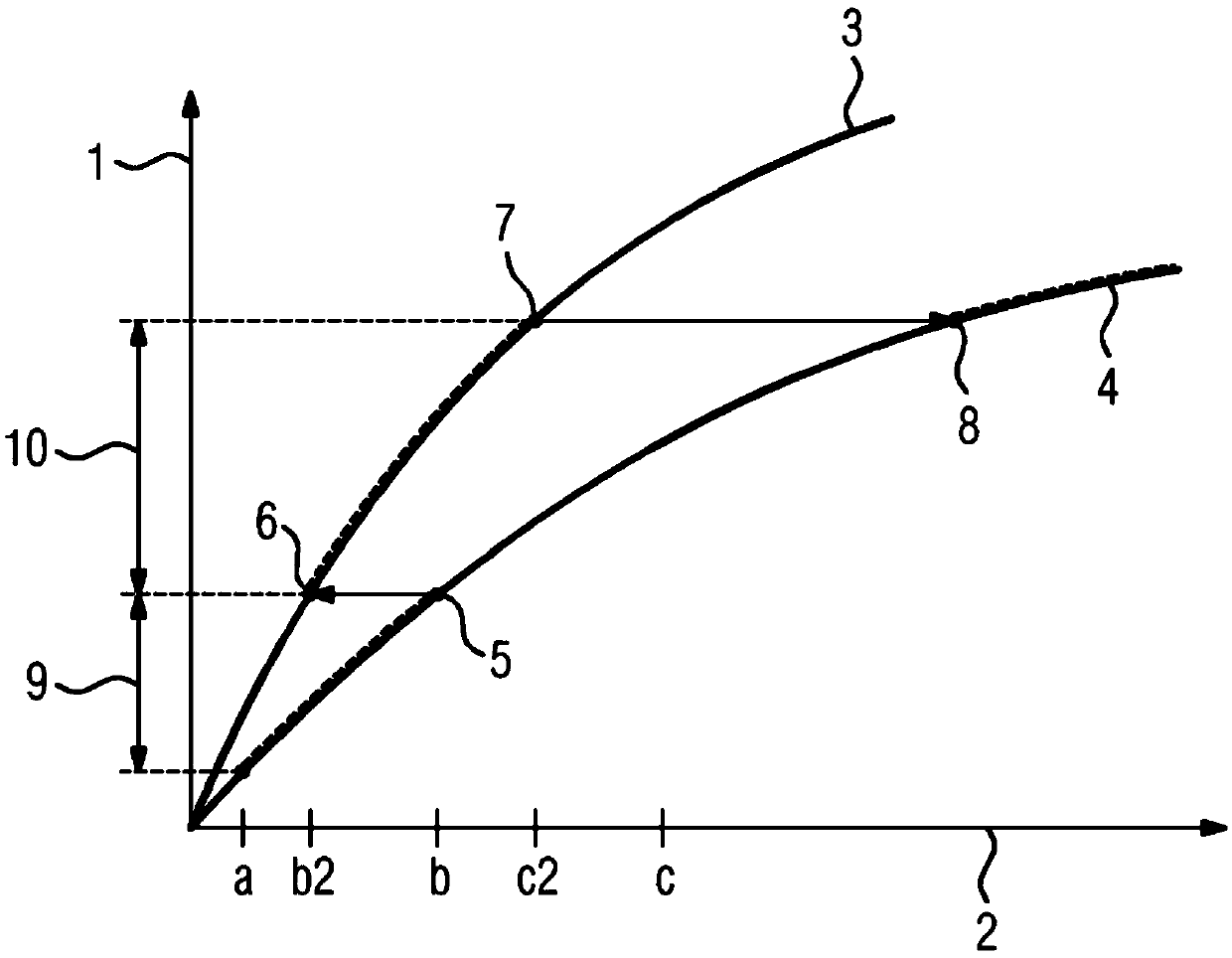
[0028]The two functions 3, 4 reflect two different boundary conditions A and B. In a first step, the secondary battery is operated under boundary conditions A from a first charge throughput a to a second charge throughput b. The boundary condition changes from A to B at the first endpoint value 5. The change from boundary condition A to B describes in this example a temperature change of 5° C. from the original operating temperature.
[0029] For the continuation under boundary condition B for the same capacity loss as the first end point value 5 of boundary condition A, an intersection point with the function for boundary condition B is determined. This point of intersection is now used as the second starting value 6 for the secondary battery operation under boundary condition B. The secondary battery is now operated under boundary condition B from the second charge throughput b to the third charge throughput c. The second charge flux b moves to the fourth charge flux b2 w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More