Magnetic liquid magnetization viscosity testing method and device
A magnetic liquid and testing device technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, flow characteristics, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as unusable, gap surface displacement, magnetic liquid support, etc., to achieve convenient adjustment, large radius of gyration, and small inertia Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
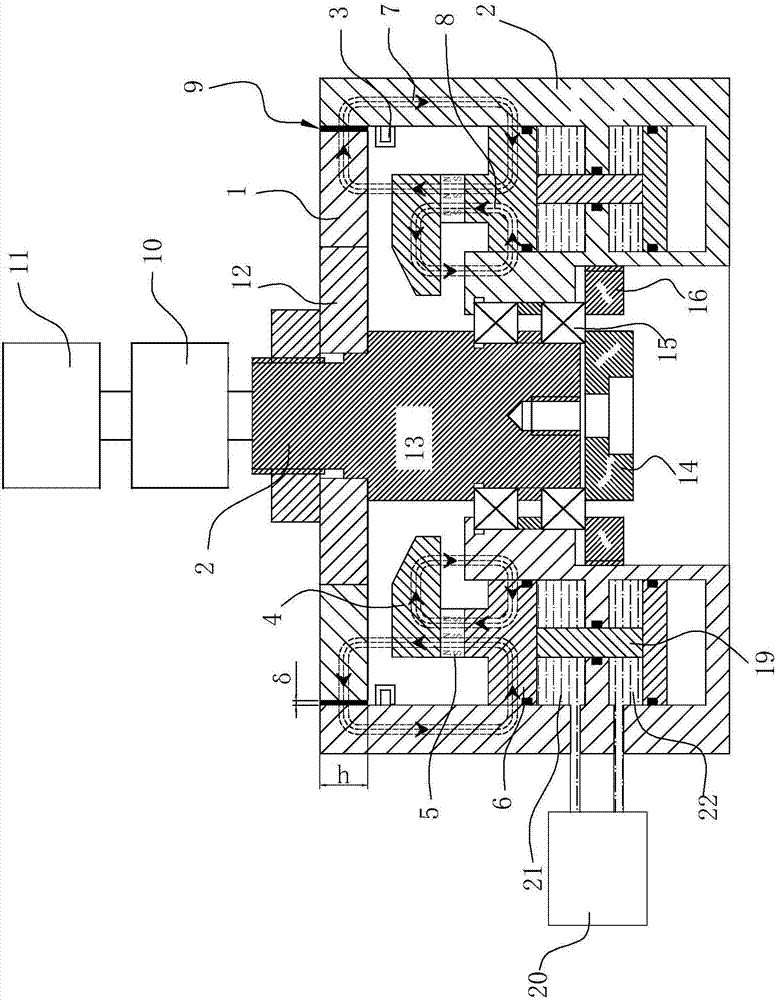
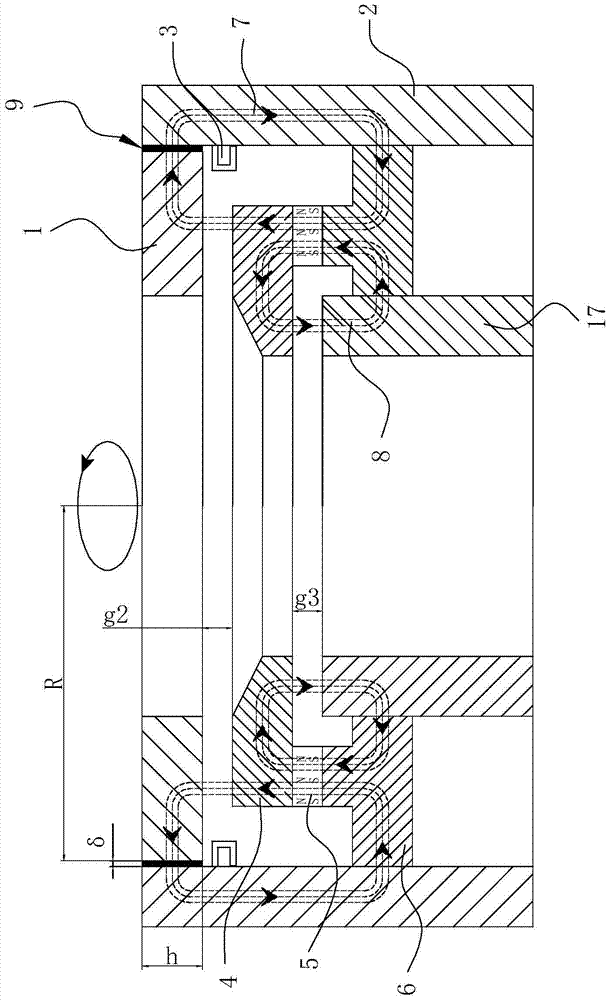
[0046] The magnetic liquid magnetization viscosity testing device of the present embodiment comprises a magnetically permeable rotor 1, an external magnetically permeable stator 2, an electromagnetic induction coil 3, an upper pole shoe ring 4, a permanent magnet ring 5, a lower pole shoe ring 6, a magnetic liquid 9, and a torque It is composed of a rotating speed testing device 10, a speed regulating motor 11, a non-magnetic centering rotor 12, a rotating shaft 13, a bearing 15 and its solid parts, wherein the torque and rotating speed testing device 10 is connected to the upper end of the rotating shaft 13, and the torque at the upper end of the rotating shaft 13 is There is a step below the rotational speed testing device 10, and the non-magnetic centering rotor 12 is sleeved on the step surface and is connected and fixed with the rotating shaft 13 by fasteners, and the magnetically conductive rotor 1 is fixed on the outside of the nonmagnetic centering rotor 12; the inner gu...
Embodiment 2
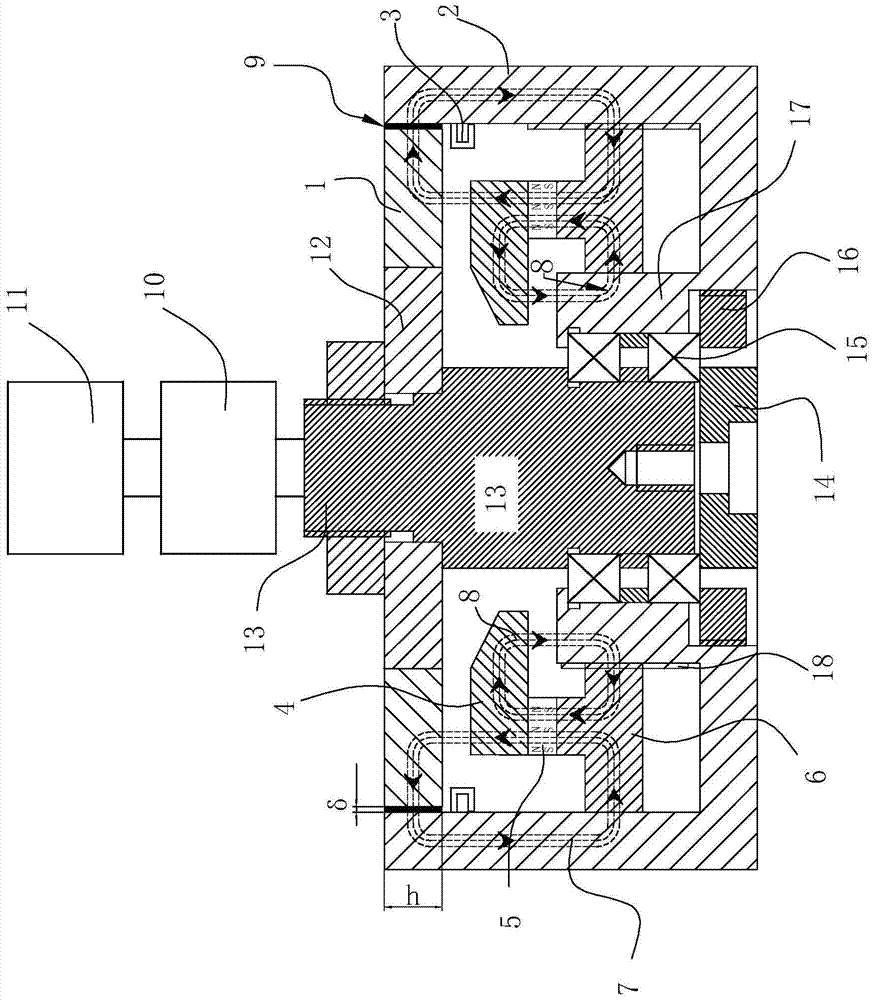
[0050] Such as image 3 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that an external driving thread 180 is set between the outer magnetically conductive stator 2 and the lower pole shoe ring 6, and the outer driving thread 180 is realized by rotating the outer magnetically conductive fixed ring and the lower pole shoe ring. The upper pole shoe ring 4, the permanent magnet ring 5 and the lower pole shoe ring 6 move up and down, so as to realize the continuous change of the magnetic field intensity in the axial constant gap δ.
Embodiment 3
[0052] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 is that the lower pole shoe ring 6 is connected to the hydraulic drive connecting rod 19, and the hydraulic drive connecting rod 19 passes through the hydraulic unit 20, the upper hydraulic chamber 21, and the lower hydraulic chamber 22. The hydraulic pressure formed inside forms the upper and lower driving forces. When the hydraulic oil is pumped from the upper hydraulic chamber 21 into the lower hydraulic chamber 22, the driving connecting rod 19 moves upward. When the hydraulic oil is pumped from the lower hydraulic chamber 22 into the upper hydraulic chamber 21 , the driving connecting rod 19 moves downward, and the driving connecting rod 19 drives the upper pole shoe ring 4, the permanent magnet ring 5, and the lower pole shoe ring 6 to move up and down, thereby realizing the continuous change of the magnetic field intensity in the axial constant gap δ.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com