Determining a risk of aquaplaning
A slippery, risky technology, applied in the directions of brakes, transportation and packaging, input parameters of external conditions, etc., can solve problems such as motor vehicle slippage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
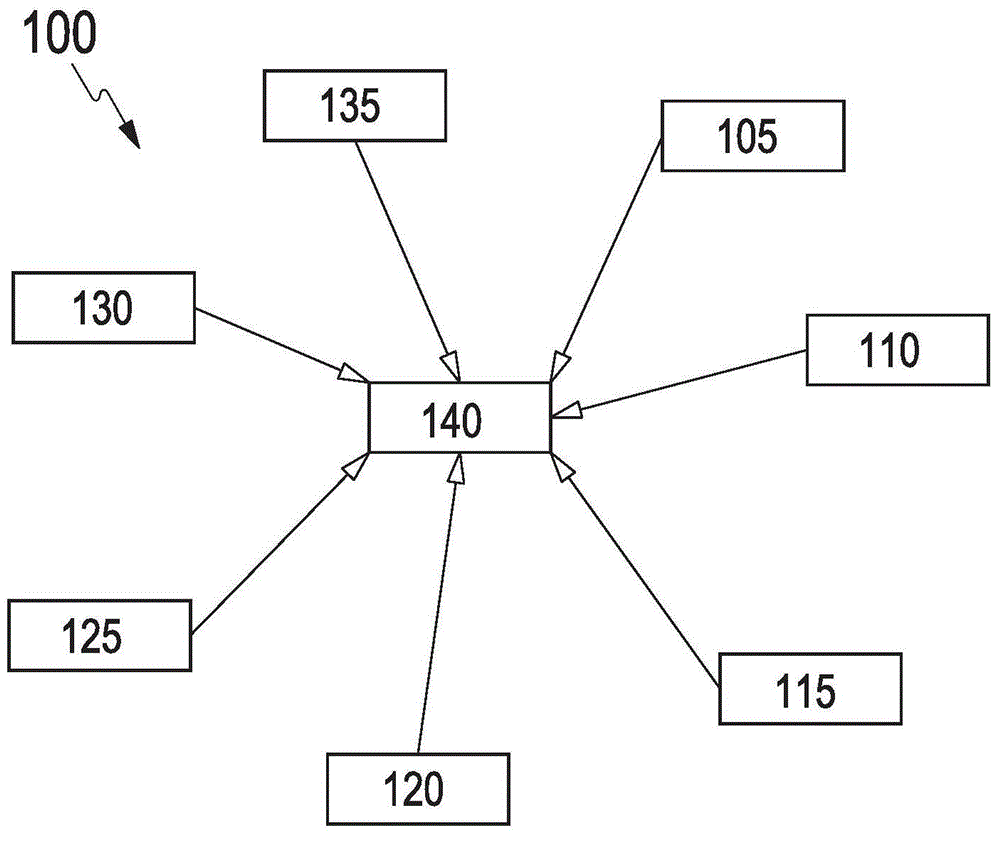
[0047] figure 1 A flow chart of a method 100 for determining the risk of skidding is shown. The method 100 is based on the interconnection of a plurality of information items, which may be determined independently of each other from different sources. In this context, it is assumed that a motor vehicle comprises at least one wheel with tires in contact with the road. The motor vehicle moves at a natural speed on the road, wherein the tires are preferably rolled.
[0048] In a first step 105 it is determined that there is water on the road. In particular, it is possible to determine whether the road is wet, or how high the water is on the road if water has accumulated on the road. This determination in step 105 is preferably independent of the source of the water on the road. It is thus possible, for example, to take into account that water will fall in the area of the motor vehicle even without precipitation.
[0049] In a step 110, precipitation in the area of the mo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com