Image brightness correction method
A technology of image brightness and correction coefficient, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as poor correction effect and slow running speed, achieve better and more detailed effects, improve running speed, and ensure the effect of image quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
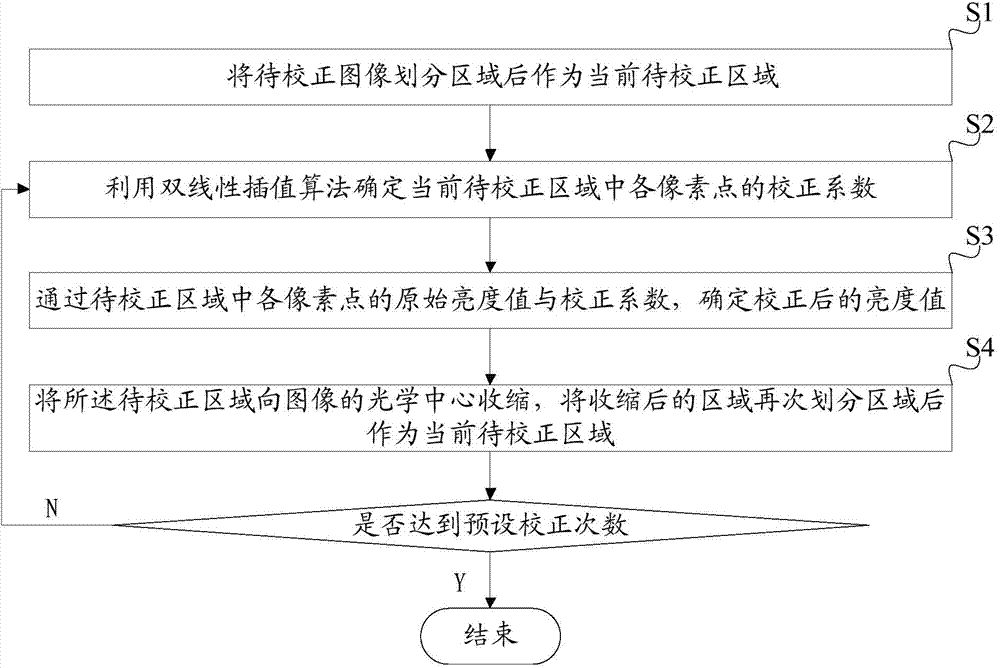
[0040] The flow chart of a specific embodiment of the image brightness correction method provided by the present invention is as follows figure 2 shown. In the above step S1, dividing the image to be corrected into regions as the current region to be corrected can be specifically as follows:
[0041] Step S11: Divide the image to be corrected into M×N sub-areas of the same size as the current area to be corrected, where M and N are both odd numbers, and the proportional relationship between M and N is proportional to the size of the image .
[0042] The above step S2 uses the bilinear interpolation algorithm to determine the correction coefficient of each pixel in the current area to be corrected. Specifically, the following steps can be taken:
[0043] Step S12: Determine the area correction coefficients of each sub-area in the current area to be corrected as the correction coefficient of the center point of each sub-area;
[0044] Specifically, the average brightness of ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] The flow chart of another specific embodiment of the image brightness correction method provided by the present invention is as follows image 3 As shown, compared with the previous embodiment, the preset number of corrections in this embodiment is set to 2, that is, two-level bilinear interpolation correction is performed. This example includes:
[0060] Step S21: Divide the area to be corrected into M×N sub-areas of the same size, where M and N are both odd numbers, and the proportional relationship between M and N is proportional to the size of the image;
[0061] Wherein, as a preferred implementation manner, the divided sub-areas may specifically be several small square areas of the same size as the first-level divided areas.
[0062] Step S22: Calculate the average brightness of the pixels in each sub-region, determine the maximum value of the average brightness, and use the ratio of the average brightness of each sub-region to the maximum value as the regional c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com