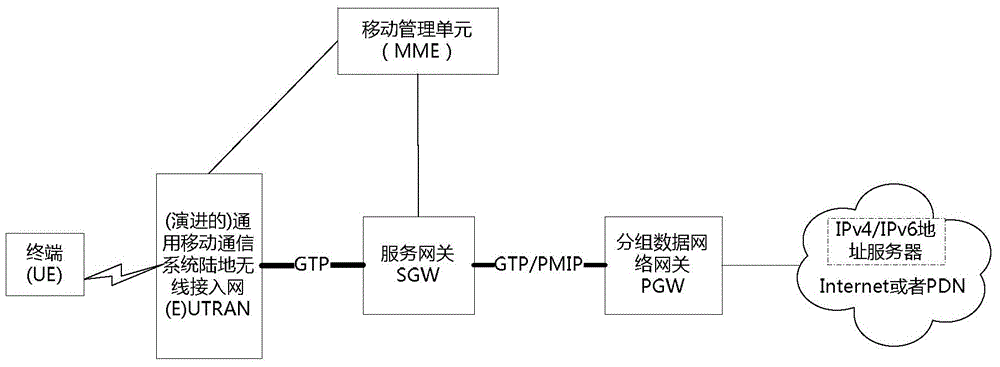
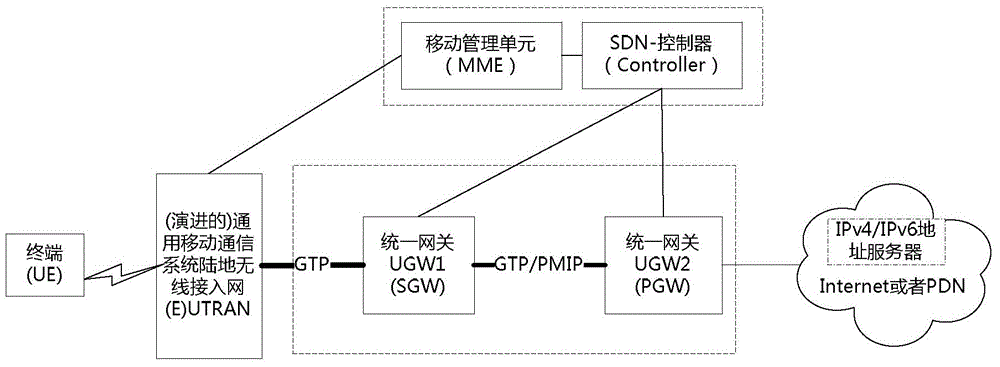
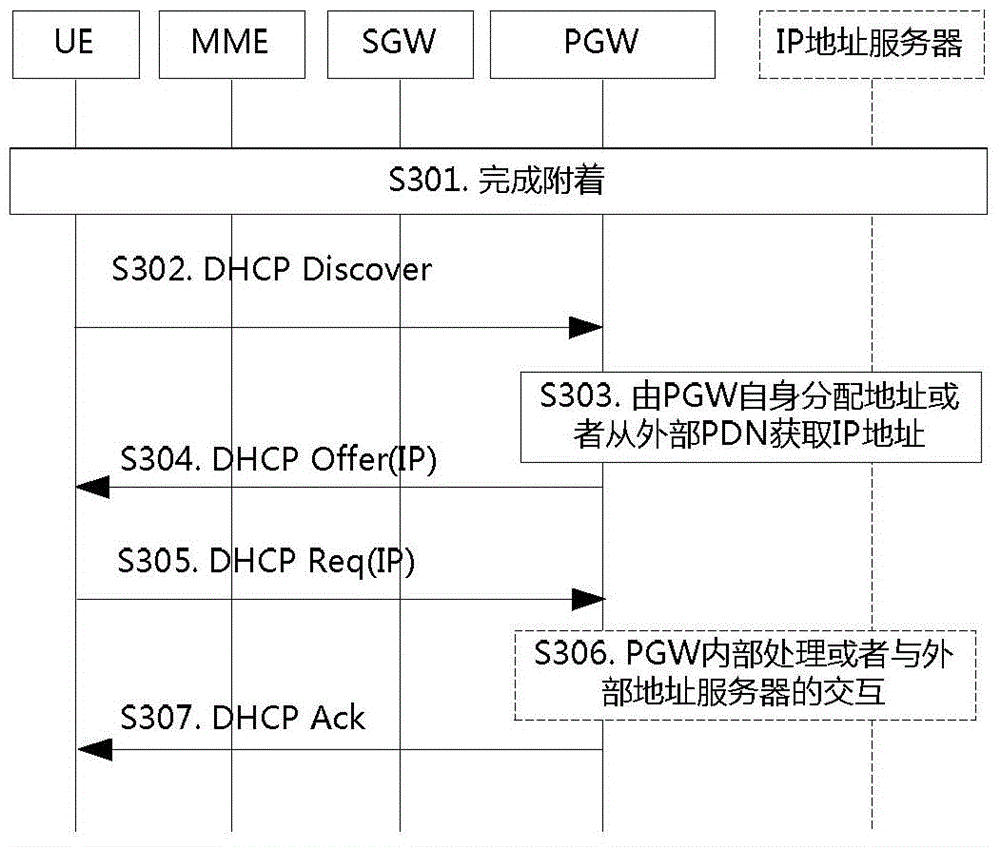
IP address distribution method, controller and gateway device in SDN-EPS
A gateway device, IP address technology, applied in the field of mobile communication, can solve the problem of IP address management not being able to be carried out
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0138] Such as Figure 5 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for allocating IP addresses in an SDN-EPS network, which is applied to a software-defined network SDN controller, and includes the following steps:
[0139] S101: The SDN controller issues flow table information for capturing address allocation signaling to the gateway device;
[0140] Wherein, the gateway device includes: a unified gateway UGW that performs a function of a serving gateway SGW, and / or a UGW that performs a function of a packet data network gateway PGW.
[0141] Wherein, the SDN controller sends the flow table information one or more times when the user equipment UE initiates the attachment process or completes the attachment, so as to ensure that the gateway device can capture the address allocation signaling; the The flow table information includes one or more pieces of flow table information used to capture different address allocation signaling.
[0142] The flow table information includ...
application example 1
[0221]This application example is aimed at the delayed allocation of IPv4 addresses and the S5 / 8 interface between the SGW and the PGW is based on the GTP protocol. Wherein, the IP address type of the terminal UE may be IPv4 or IPv4v6. A scene can be a roaming scene or a non-roaming scene. SGW / UGW and PGW / UGW can belong to the same network operator, and the controller controls the two network elements at the same time; or the controller only controls PGW / UGW, and SGW is a traditional network element. This is software-defined network and traditional network interoperability. scene. Interworking scenarios are further divided into interworking scenarios within a network and interworking scenarios involving roaming between multiple networks. In the above multiple situations, the implementation mechanism of the present invention is the same, and here it is only introduced that the invention can be used in these scenarios.
[0222] The delayed allocation of the IPv4 address means...
application example 2
[0242] This application example is aimed at the allocation of IPv6 address prefixes, and the S5 / 8 interface between the SGW and the PGW can be the GTP protocol or the PMIP protocol. Wherein, the IP address type of the terminal UE may be IPv6 or IPv4v6. A scene can be a roaming scene or a non-roaming scene. SGW / UGW and PGW / UGW can belong to the same network operator, and the controller controls these two network elements at the same time; or the controller only controls PGW / UGW, and SGW is a traditional network element. This is the interworking between software-defined networks and traditional networks. scene. Interworking scenarios are divided into interworking scenarios within a network and interworking scenarios involving roaming between multiple networks. In the above multiple situations, the implementation mechanism of the present invention is the same, and here it is only introduced that the invention can be used in these scenarios.
[0243] The above IPv6 address pref...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com