Sensor probe for measuring electrical parameters of underground rock
A technology of sensor probes and electrical parameters, applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring devices, measuring electrical variables, etc., can solve the problem that the resistivity and dielectric constant of rock core samples cannot be obtained in real time, the electrical parameters of rocks cannot be measured, and the electrical parameters are not sensitive to changes And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
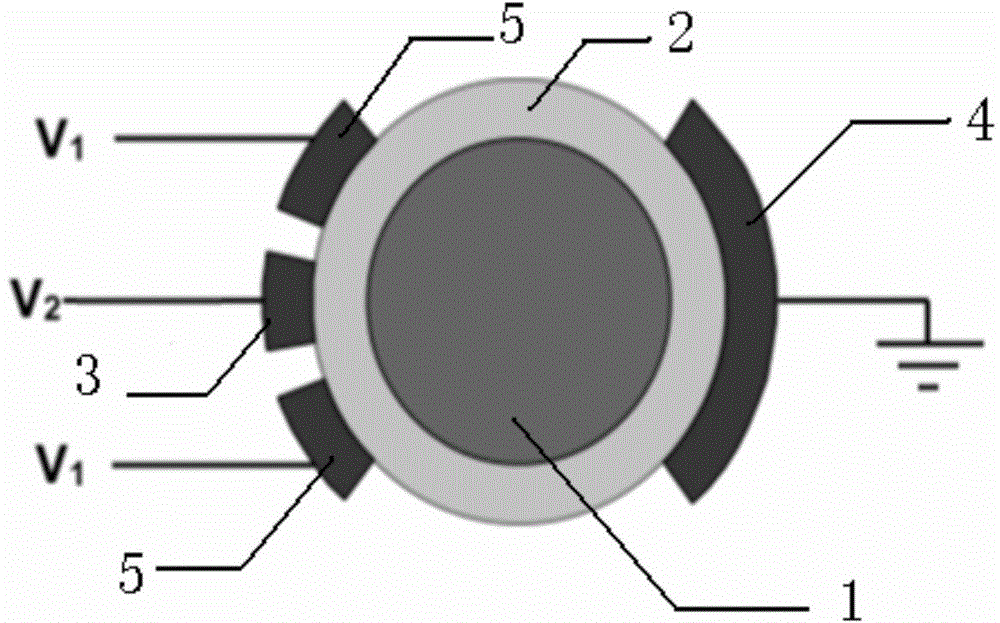
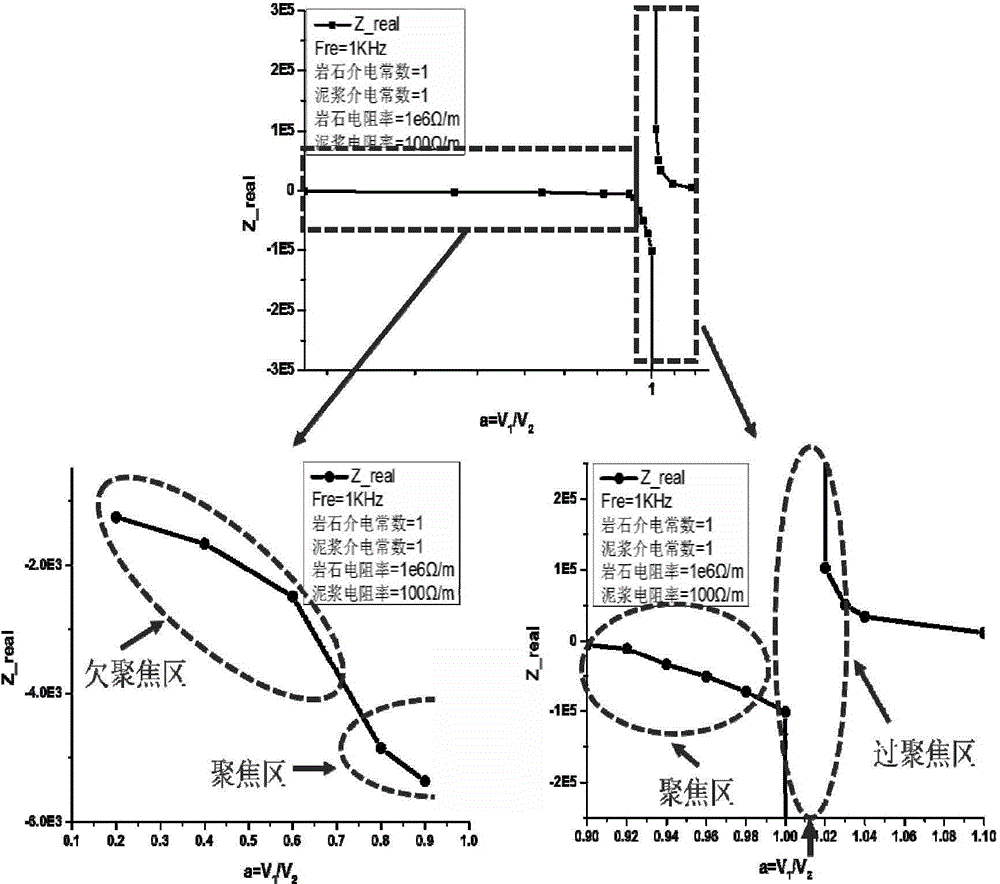
[0012] The present invention adopts specific measures to guide the current to penetrate the conductive mud and enter the inside of the rock, so as to collect and bring out the electrical parameters inside the rock.
[0013] While supplying power to the emitter electrode, by applying an appropriate voltage to the shield electrode, the surrounding of the internal electrode is relatively high potential, so that the current flowing from the emitter electrode cannot be conducted along the conductive mud. Selecting the appropriate voltage and electrode form can make The current penetrates the conductive mud, into the interior of the rock, and through the rock to the grounded plate.
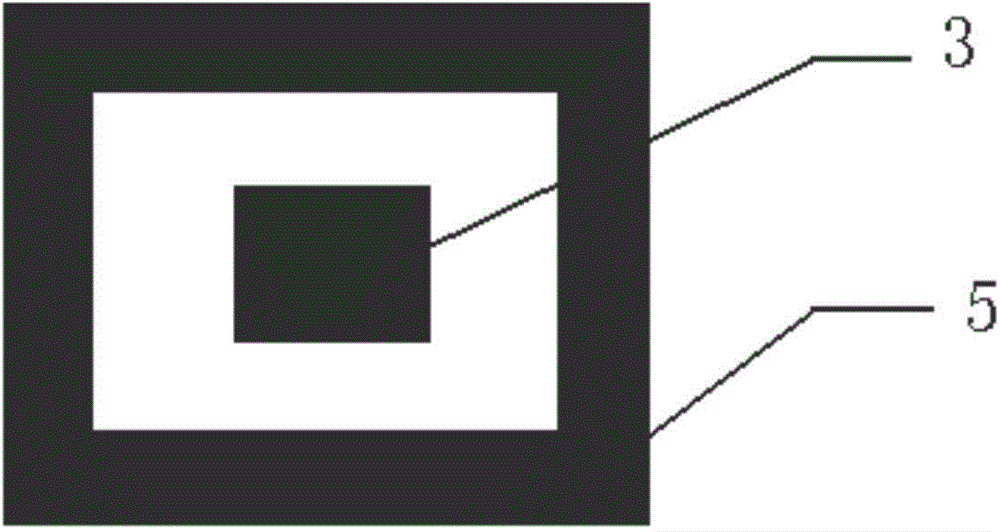
[0014] Such as figure 1 As shown, the sensor probe of the present invention is used to measure the electrical parameters of the sampled rock 1 . Rock 1 is wrapped by conductive mud 2 . The sensor probe of the present invention comprises a transmitter electrode 3, a collector electrode 4, a transmitter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com