A method for interplanting corn after harvesting wheat in orchards in southern Xinjiang
A technology for corn and fruit forests, applied in botany equipment and methods, applications, horticulture, etc., to achieve the effects of increasing meat supply, increasing local grain and forage production, and improving land utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] (1) Intercropping with intercropping of forest and fruit intercropping with wheat harvested and then interplanting with extremely early-maturing corn varieties. Site selection, site preparation, application of basal fertilizer for site preparation, and sowing are carried out in common ways.
[0041] (2) The corn varieties planted in inter-sowing require the growth period of the multi-sowing to be within 90 days, and the effective accumulated temperature of ≥10 degrees is required to be less than 2100 degrees.
[0042] (3) Requirements for the sown wheat: Plant according to conventional winter wheat.
[0043] (4) Technical requirements for forest-fruit intercropping: The types of fruit forests selected are jujube forests, grape forests, apricot forests, Badan apricot forests, and walnut forests. The average distance between the nearest leaves of two adjacent rows of fruit trees in apricot forest and walnut forest is not less than 3 meters.
[0044] (5) Smallpox should be ...
Embodiment 2
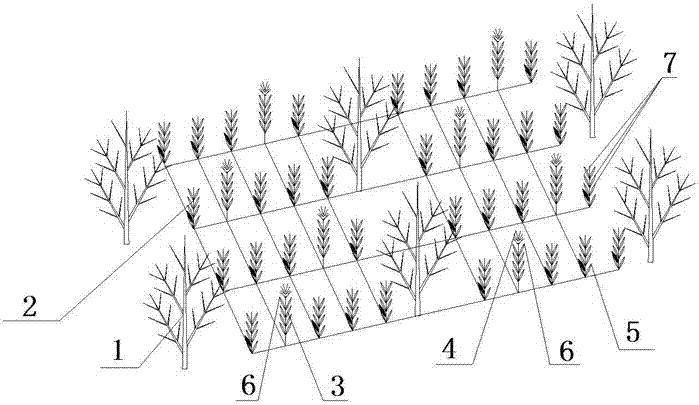
[0054] See attached figure 1 As can be seen, a kind of method that the present invention adopts is applicable to the method concrete steps of interplanting corn after the harvest of wheat in the fruit forests of southern Xinjiang region as follows:
[0055] Interplanting extremely early-maturing corn (2, 3) in the fruit tree (1) forest after wheat harvest; the corn plant (2) is close to the fruit tree (1), and the corn smallpox (4) and part of the leaves of the corn are removed according to the type of fruit tree (6); the corn plant (3) is far away from the fruit tree, and the corn plant (3) retains the smallpox (4) of the corn; when removing the smallpox (4) and part of the leaves (6) of the corn (2), use the corn (2) The corn ear (5) is the center, and 6-8 functional leaves (7) of corn must be reserved; the smallpox corn (3) plants account for 10-20℅ of the total number of corn plants in the entire field, so as to provide pollen for feeding All maize plants are pollinated b...
Embodiment 3
[0057] In 2013, the Economic Crops Research Institute of Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, according to the actual production of forestry and fruit industry in southern Xinjiang and the demand for interplanting corn after harvesting wheat in the fruit forest, provided the interplanting corn after harvesting wheat in the fruit forest according to the above-mentioned Examples 1 and 2. Methods: The experiment of planting extremely early-maturing maize varieties after wheat harvest was carried out in jujube forests, grape forests, apricot forests and walnut forests at the Institute of Agricultural Sciences in Hotan area, and the experiments were successful. The test uses 2316 very early-maturing corn variety as the test material. The re-sowing growth period of this variety is 85 days, and the effective accumulated temperature of 2100 degrees or more is required to be greater than or equal to 10 degrees. The test adopts the key cultivation technology provided by the present...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com