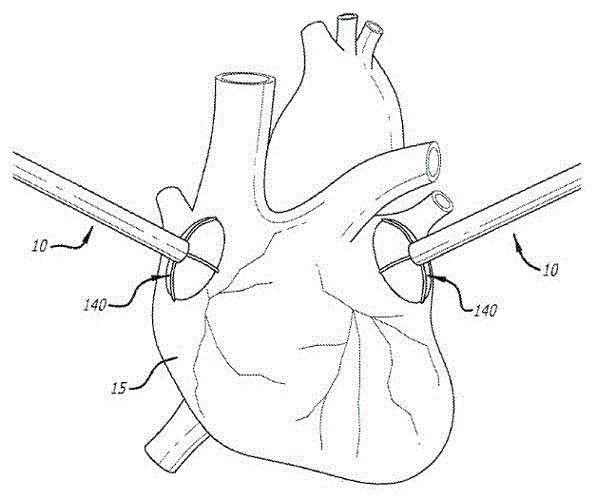
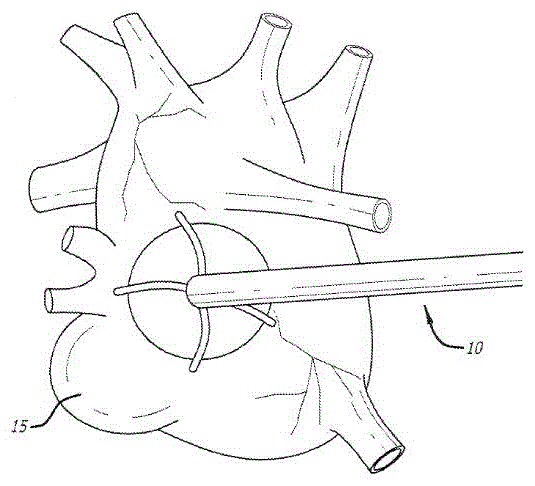
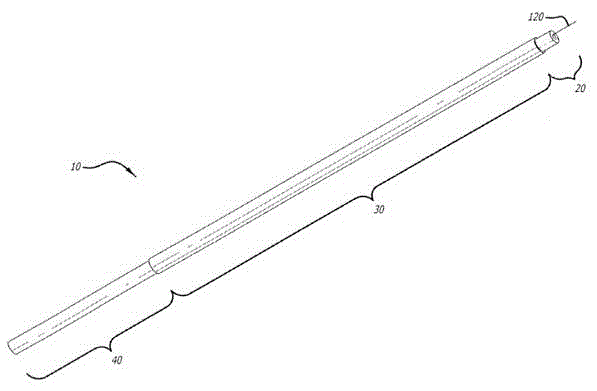
Device and methods for targeted tissue drug delivery
A technology for drug delivery and drug application in the field of new minimally invasive implantable devices, which can solve the problems of long-term serious demand for chronic atrial fibrillation and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0233] In this example, it is shown that the present invention can be effectively used for the targeted local administration of amiodarone, sulfasulfone and procainamide directly to cardiac tissue by traditional methods after surgery. In this example, Table 1 below lists the drugs, post-operative oral and intravenous doses (traditional therapy administration), and, for comparison, all used in the target tissue administration form of therapy using the device of the present invention. dose. As shown in Table 1, when the present invention is used for targeted drug delivery, the medication required for treatment is significantly reduced, which also means that when the present invention is used, systemic toxicity is significantly reduced.
[0234] It should be understood that Table 1 depicts representative drugs and dosages used in certain embodiments of the invention for purposes of illustration only. In no case should Table 1 be construed as limiting the scope of the invention. ...
Embodiment 2
[0238] In one experiment, two groups of pigs were used to determine the difference between intrapericardial (IPC) versus intravenous (IV) administration of the antiarrhythmic drug procainamide. Intrapericardial (n=6) or intrapericardial (n=7) administration with continuous intravenous doses of 2, 8, 16 mg / kg (cumulative 2, 10, 26 mg / kg), or continuous intrapericardial doses of 0.5 , 1, 2mg / kg (cumulative 0.5, 1.5, 3.5mg / kg). Each dose was resuspended in 10ml and administered at a rate of 1mL / min. The pharmacokinetics of both drug administrations were statistically significant. Peak drug concentrations obtained with intrapericardial administration were in the range of 250-900 μg / ml, while measurable levels in plasma were low (<1 μg / ml). Peak plasma concentrations obtained with intravenous administration range from <1 to 40 μg / ml, but concentrations in pericardial fluid are equivalent to those in plasma. It should be noted that pericardial fluid concentrations during intraven...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com