Adaptive round-up method for multi-robot hunters rounding up a single moving target
A moving target, multi-robot technology, applied in adaptive control, instruments, two-dimensional position/channel control, etc., can solve the problems of increasing algorithm complexity, difficulty, inability to meet simulated reality, etc., and achieve the effect of efficient rounding up
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
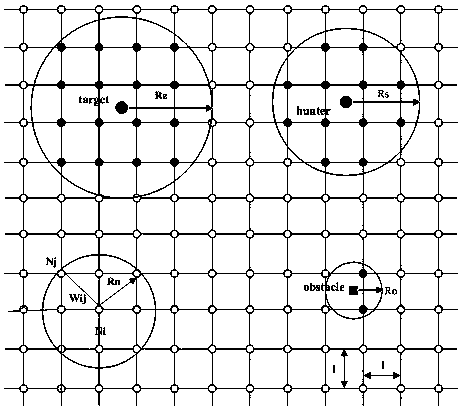
[0052] First, formally describe the round-up task, and set a round-up task as T={N c ,As}, where, N c is the number of hunters needed to round up a moving target, A s Indicates the area of the roundup mission. The initial position of the hunter in the hunting team Ω is random, marked as h i , i=1,2,…,n, the speed is V h , the coordinate position at time t is The moving target is marked as e, the initial position is random, and the speed is V e , the coordinate position at time t is (P e ) t =((x e ) t ,(y e ) t ). Assuming that the hunting team and the moving target are moving at a constant speed in the map, the position of the hunter at time t+1:
[0053]
[0054]
[0055]
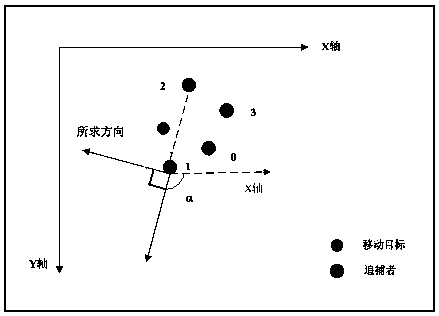
[0056] is the moving direction of the pursuer, put the pursuer and the moving target in the global coordinate system, is the angle between the velocity direction and the x-axis. Then the round-up problem boils down to calculating the movement direction of each hunter at each s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com