Method and system to calculate quantitative EEG
A processor, electrode technology, used in applications, diagnostic recording/measurement, medical science, etc., to solve problems such as unavailability, huge continuous monitoring, and difficult to observe types of relative changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
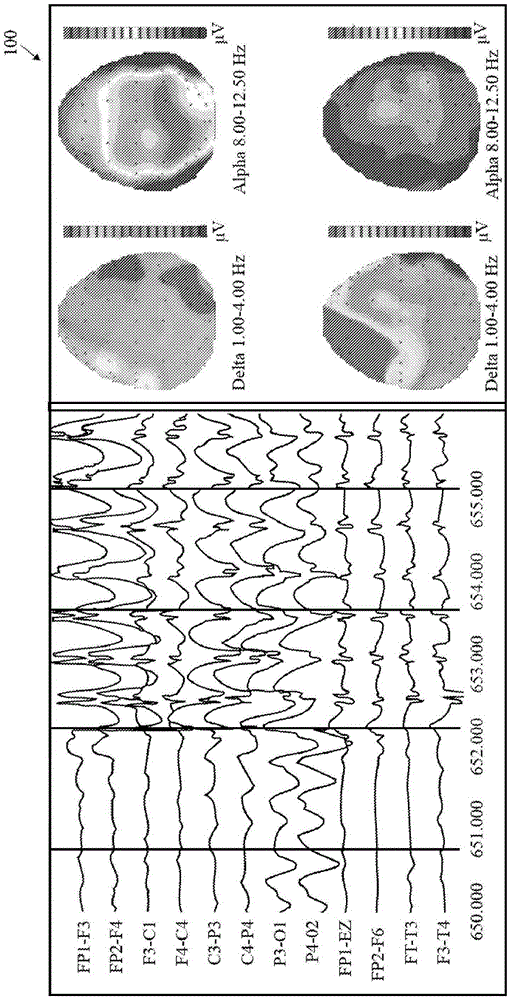
[0057] exist figure 1 An image 100 of a quantitative EEG ("qEEG") is shown in FIG. The method and system allow for the generation of qEEG from artifact-reduced EEG recordings without removing portions of the EEG recording to prevent artifacts from affecting the qEEG.
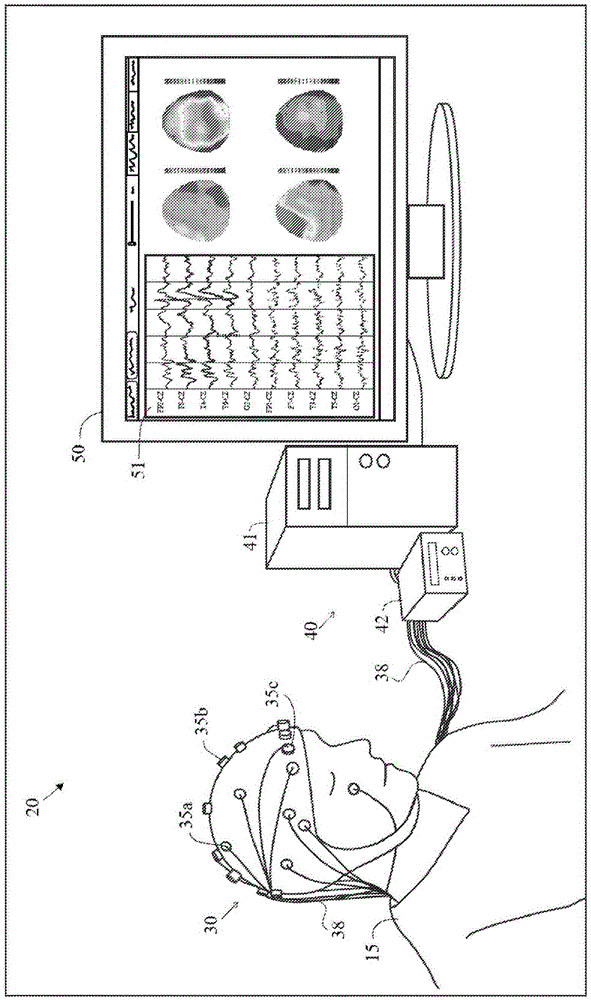
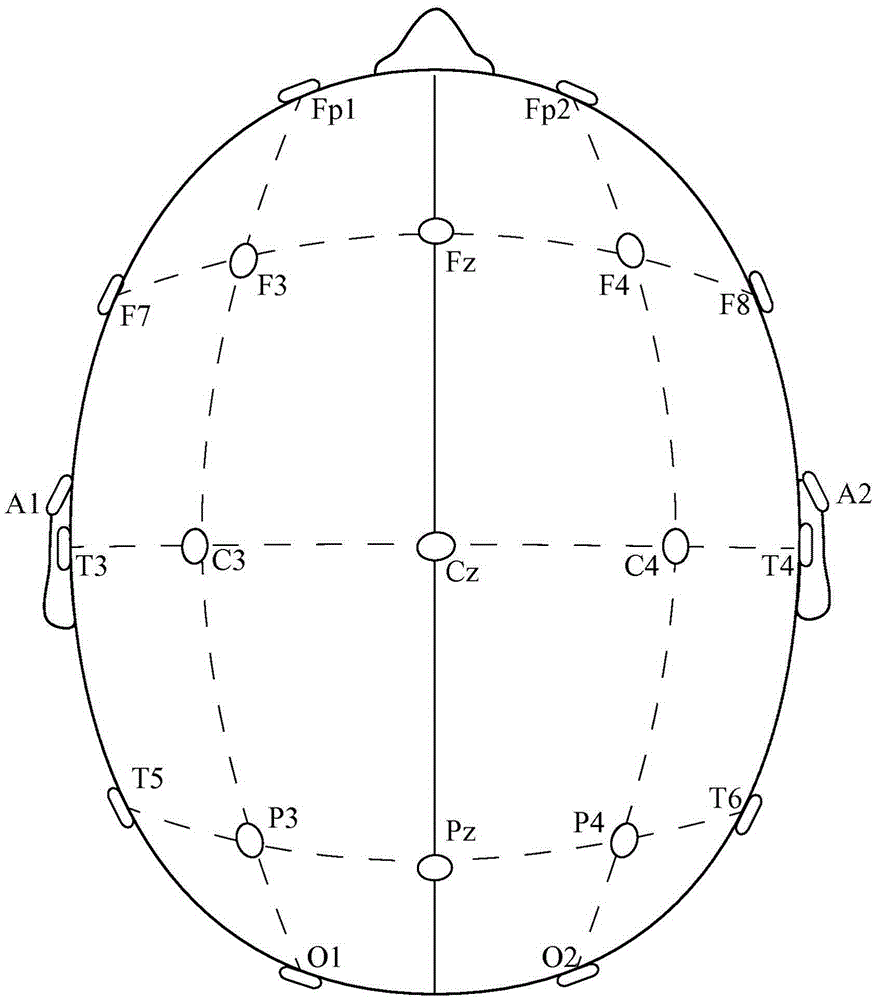
[0058] figure 2 A system 20 for computing quantitative EEG is illustrated. The patient 15 wears an electrode cap 31 comprising a plurality of electrodes 35a-35c attached to the patient's head, wherein a wire 38 connects from the electrode 35 to an EEG machine part 40, the EEG machine part 40 An amplifier 42 is included for amplifying the signal to a computer 41 having a processor for analyzing the signal from the electrodes 35 and generating an EEG recording 51 and qEEG which can be viewed on a display 50 . A more detailed description of the electrodes utilized in the present invention is detailed in "a Method And Device For Quick Press On EEG Electrode," US Patent No. 8,112,141 to Wilson et al., which is in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com