Electric power communication network fault positioning method based on key alarm sets and supervised classification
A power communication network and fault location technology, applied in electrical components, data exchange networks, digital transmission systems, etc., to solve problems such as structural defects that are difficult to control, cannot guarantee the effect of location, and reduce the accuracy of fault location.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The present invention will be described in further detail below according to the drawings and embodiments.
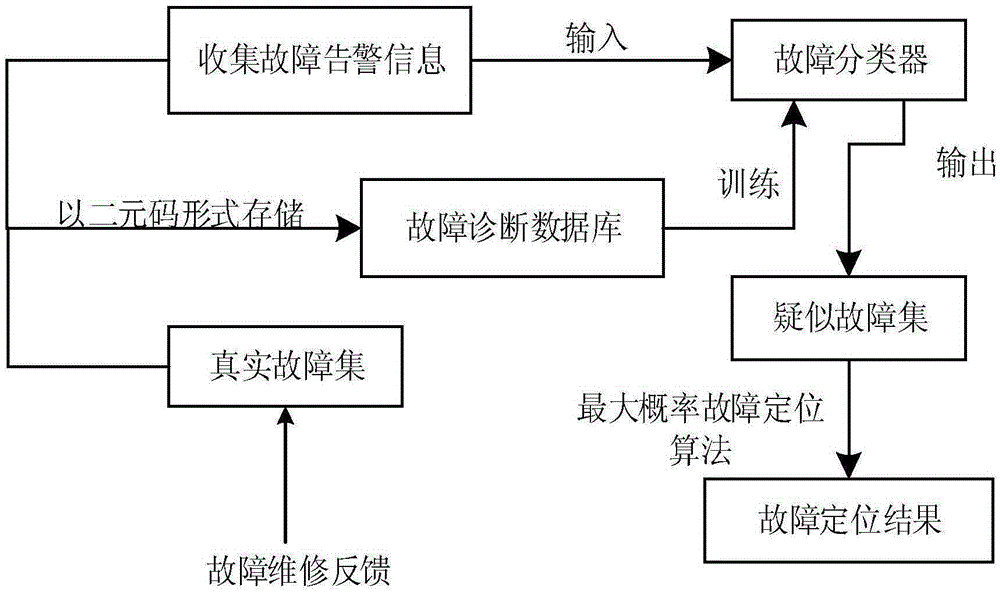
[0036] The present invention provides a fault location method in a power communication network, the step flow chart is as follows figure 1 shown, including:
[0037] Step S1, collecting the network fault alarm information sent by the fault monitoring equipment in a standardized format;
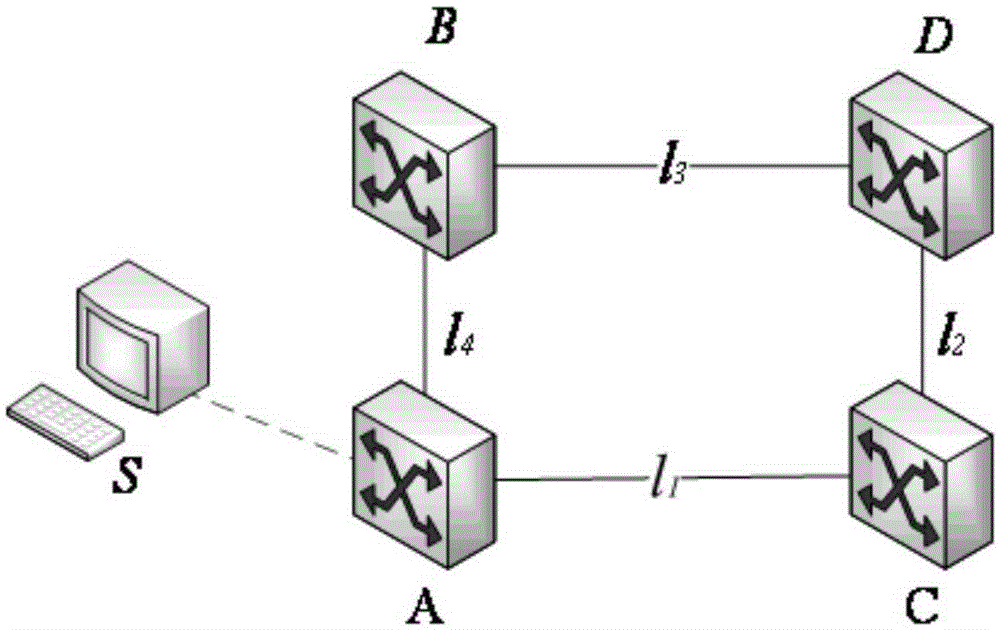
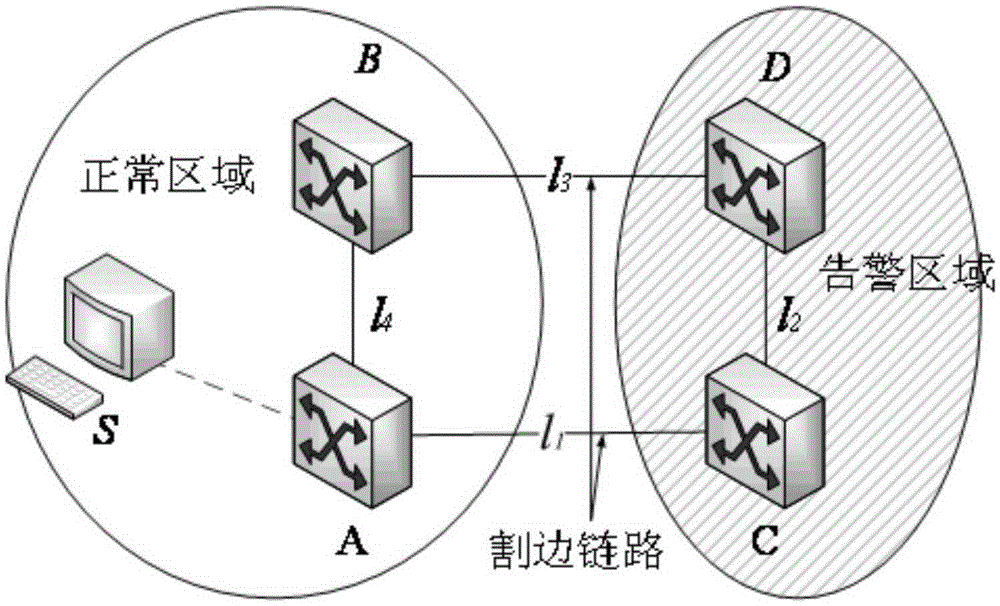
[0038] Step S2, dividing the alarm network area and the normal network area through topology analysis, and extracting key alarm sets including edge-cut link sets and edge alarm sets;
[0039] Step S3, building a fault diagnosis case knowledge base with fault source-fault alarm history information;
[0040] Step S4, using the standardized fault source-fault alarm code record in the fault diagnosis database as a training sample, training a fault classifier using SVM as a classification model, and using this alarm information as input to obtain a suspected fault source;
[0041] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com