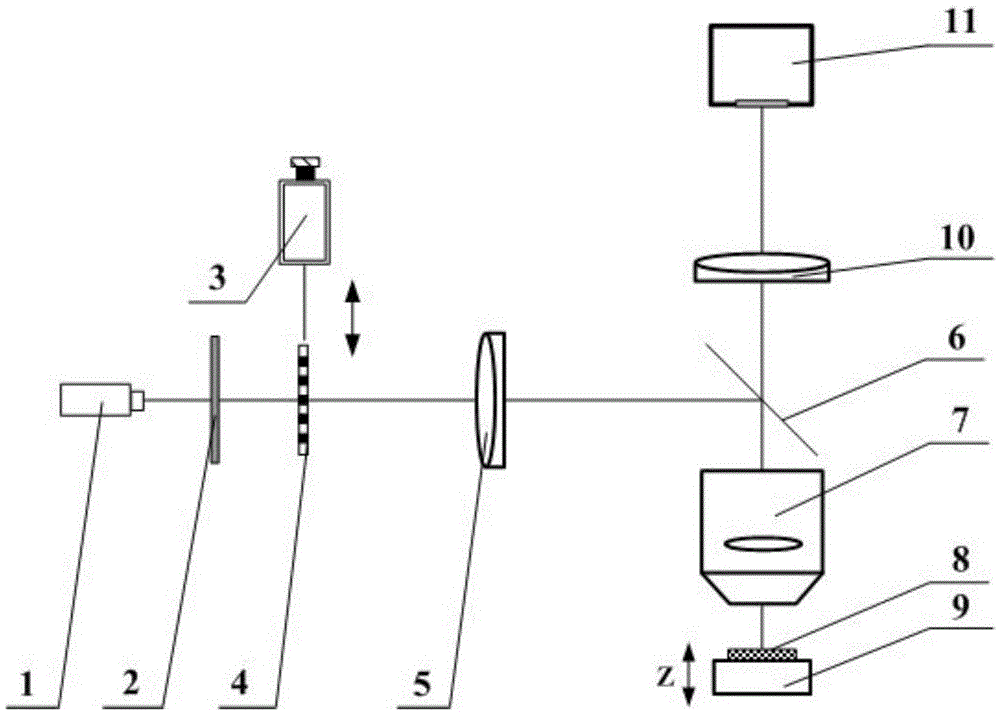
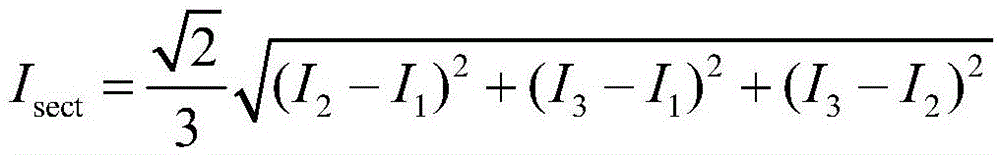Chromatography microscopic measurement method for parallel optical lines
A microscopic measurement and line layer technology, applied in measurement devices, optical devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as affecting measurement accuracy, limiting the application range of structured illumination obvious microtechnology, and reducing measurement efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
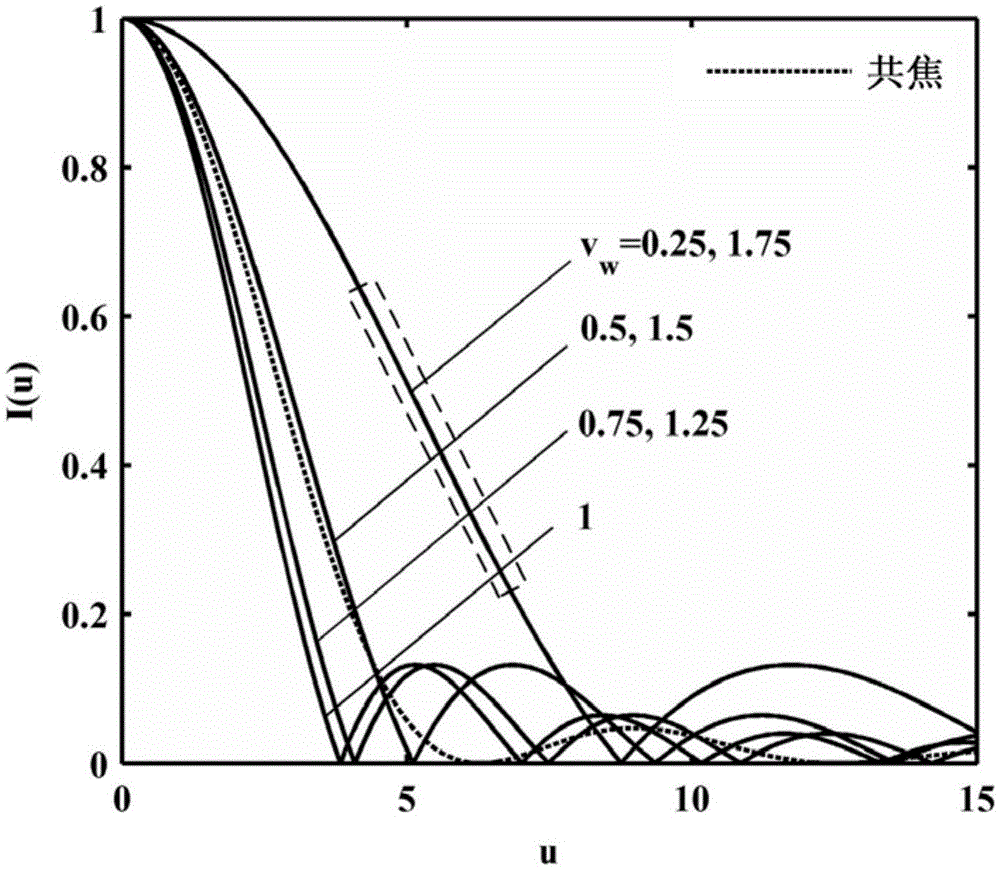
[0040] figure 2 Shown is the axial tomographic response curve of the structured light microscopy imaging system versus the normalized spatial frequency υ ω The law of change, when υ ω =1, ω=(sinα / λ) / M, the axial tomographic response curve is the narrowest, corresponding to the best axial resolution, that is, I(u)=|2J 1 (u) / u|, and the ideal confocal axial tomographic response I conf (u)=sinc 2 Compared with [u / (2π)] (shown by the dotted line in the figure), its full width at half maximum (FWHM) is narrower. Intercept the linear interval of the above curve (such as figure 2 As shown in the dotted line box), the theoretical correlation model between the intensity field and the sample surface height can be established, and a single scan can complete the detection of the three-dimensional tomographic structure of the sample surface morphology within a certain axial range.
[0041] According to the theoretical analysis of the present invention, design optical system paramete...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com