Device-to-device (D2D) discovery signal transmission method and D2D discovery signal transmission device in long-term evolution (LTE) network
A technology for discovering signals and sending methods, applied in the field of mobile communications, can solve problems such as limited number of patterns, no mature solutions, and limited resource allocation flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
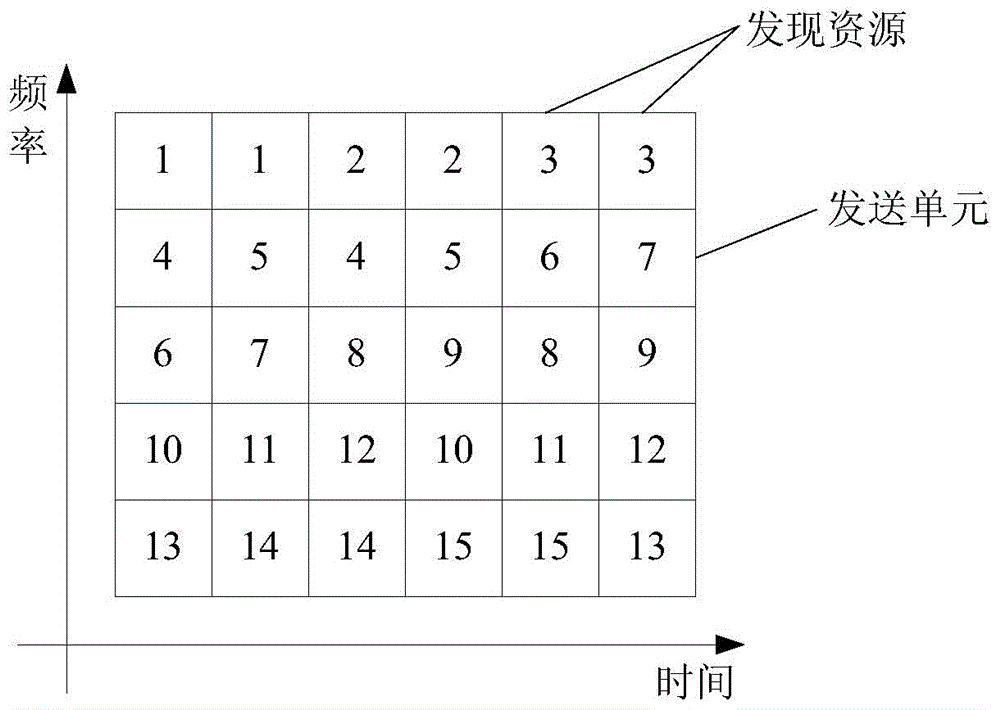
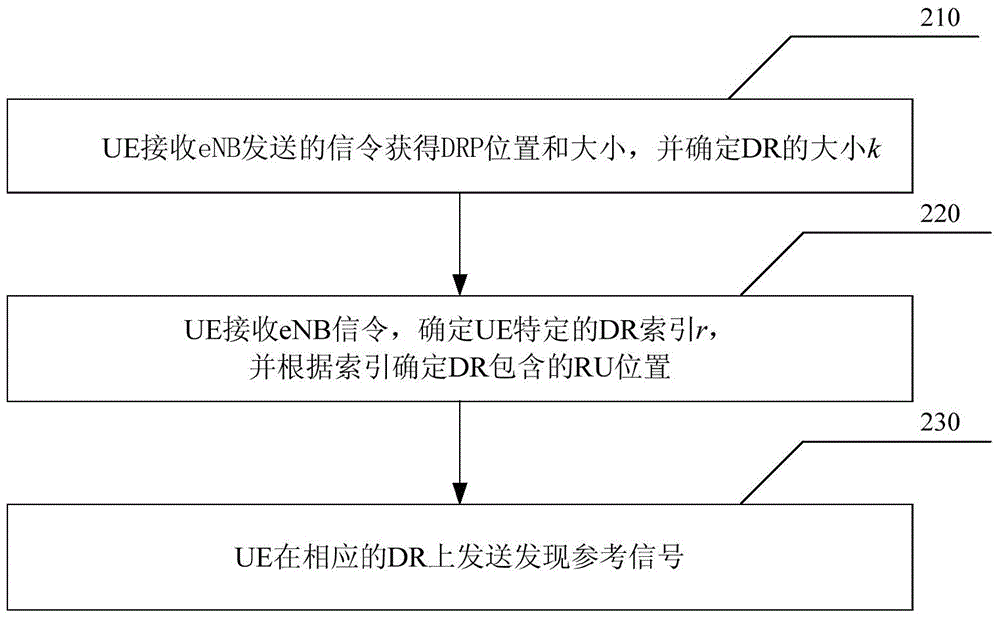
[0076] In this embodiment, the eNB informs the UE of the number of RUs T contained in the current DRP in the time domain through RRC signaling, and informs the UE of the specific DR index r in each cycle through specific signaling. The UE determines the number of RUs in each cycle through the above information. The number of RUs and RU locations included in the DR, the specific steps are as follows:
[0077] Step 310: The UE receives eNB signaling, and obtains the DRP position and the time domain size T of the DRP in a period.
[0078] Step 320: The UE determines the number k of RUs included in the DR and the frequency domain size F of the DRP.
[0079] at this time k = max k A [ 2 , T / 2 ] max ( C T - 1 k - 1 , B - 2 × R PUCCH ) , F = min ( C T - 1 k - 1 , B - 2 × P PUCCH ) .
[0080] Step 330: The UE receives eNB specific signaling in each cycle to obtain ...
Embodiment 2
[0087] In this embodiment, the eNB informs the UE of the number of RUs T contained in the current DRP in the time domain and the DR size k through RRC signaling, and indicates the UE-specific DR index r in the first period after the UE applies for resource discovery. o , The UE determines the number of RUs and RU positions included in the DR in each cycle through the above information, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0088] Step 410: The UE receives the eNB signaling, and obtains the DRP position and the time domain size T of the DRP in a period, and Δ c Value.
[0089] Step 420: The UE determines the frequency domain size F of the DRP.
[0090] at this time F = min ( C T - 1 k - 1 , B - 2 × R PUCCH ) .
[0091] Step 430: UE receives eNB specific signaling, and obtains UE specific DR index r o .
[0092] In this embodiment, the eNB only sends signaling to the UE in the first cycle, and carries the UE-specific DR index r in t...
Embodiment 3
[0102] In this embodiment, the eNB informs the UE of the number of RUs T contained in the current DRP in the time domain and the DR size k through RRC signaling, and indicates the UE-specific DR index r in the first period after the UE applies for resource discovery. o , The UE determines the number of RUs and RU positions included in the DR in each cycle through the above information, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0103] Step 510: The UE receives the eNB signaling, and obtains the DRP position and the value of the time domain size T and X of the DRP in a period.
[0104] Step 520: The UE receives eNB specific signaling and obtains UE specific DR index r o .
[0105] In this embodiment, the eNB only sends signaling to the UE in the first cycle, and carries the UE-specific DR index r in the first cycle. o , In the subsequent cycle, the UE itself according to the DR index r of the previous cycle p-1 Calculate the DR index r of the current period p .
[0106] Step 540: The UE r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com