A device for nitrogen arc in-situ metallurgy pre-laying nitride to realize nitrogen increase on steel surface
An in-situ metallurgy and nitride technology, which is used in supporting devices for protection, arc welding equipment, electrode supporting devices, etc., can solve the problems of insignificant effect, hydrogen-induced cracking, and drying time, etc., and achieve bonding strength. The effect of high and good high-strength corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
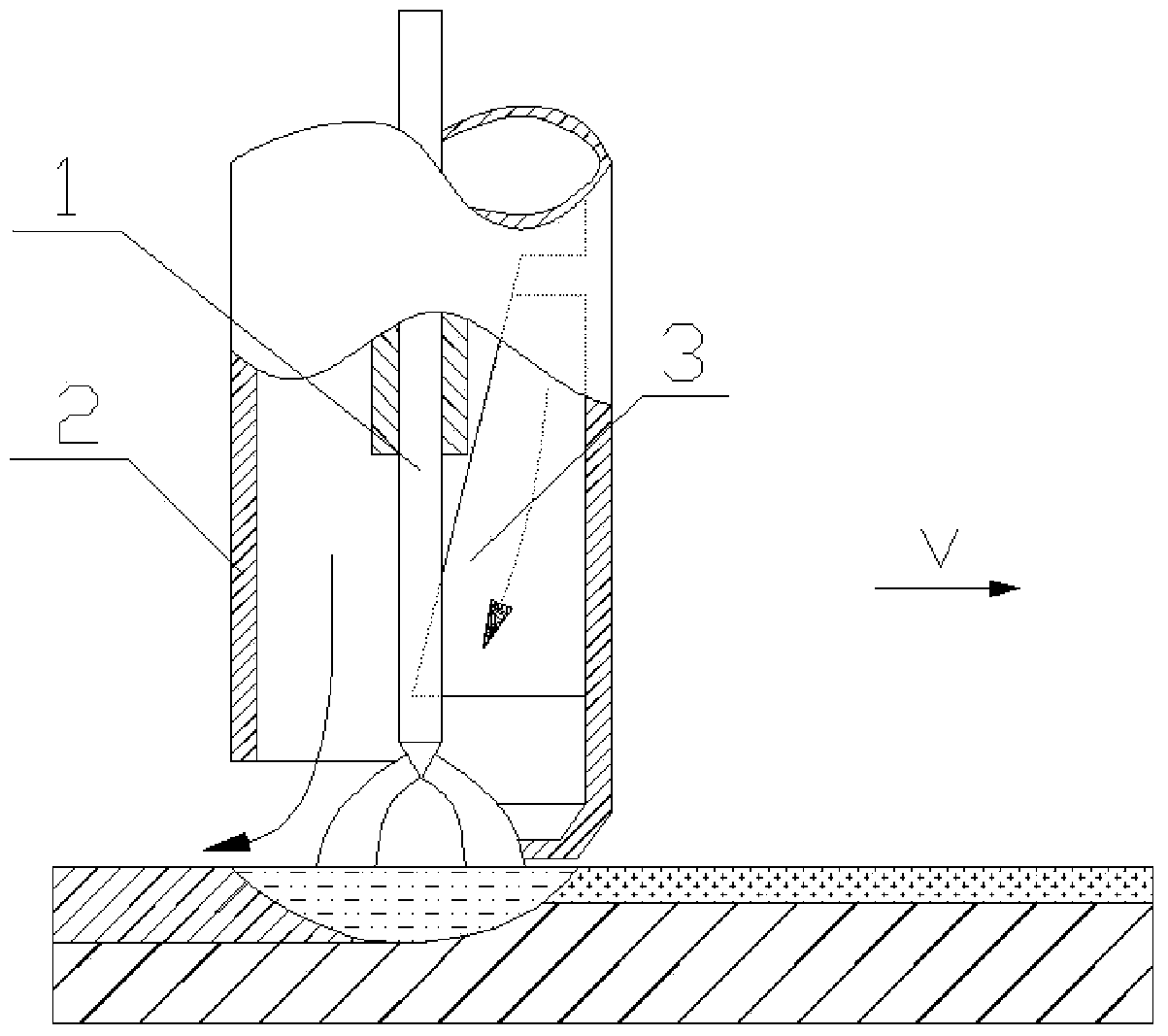
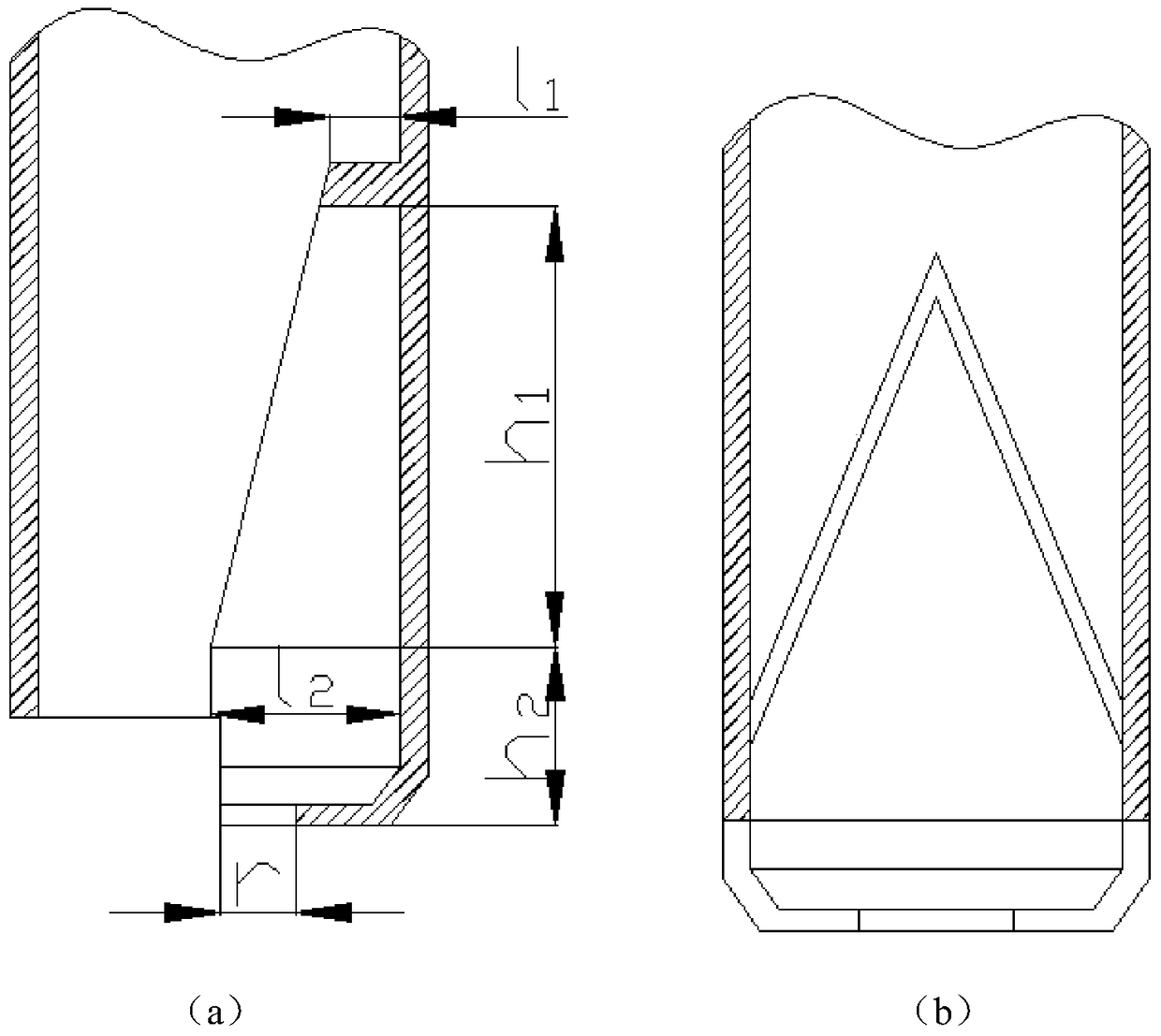
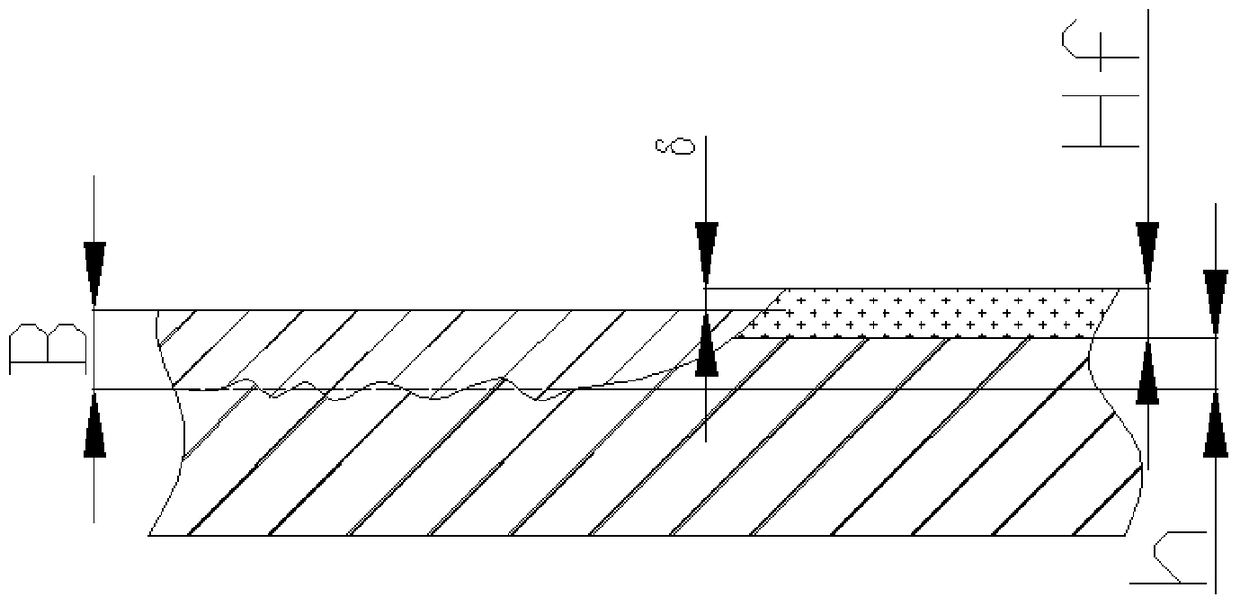
[0041] A method for increasing nitrogen on the steel surface by using nitrogen arc and nitride composite in-situ metallurgy according to the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific examples.
[0042] use as figure 1 The device shown uses nitrogen arc and nitride in-situ metallurgy to increase nitrogen on the steel surface, and obtains a high-nitrogen steel layer with a thickness of 2 mm on the surface of Q235B steel. The target composition of the high nitrogen steel layer is shown in Table 1.
[0043] Table 1 The chemical composition requirements of the target high nitrogen steel layer (%)
[0044] chemical composition
N
mn
Cr
Mo
Si
C
Fe
standard specification
0.8-2.4
12-18
18-23
1.0-2.5
≤1
≤0.1
margin
[0045]The present invention adopts nitrogen arc as a nitrogen atmosphere electric arc, including electric arc and plasma arc; first, the m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com