Annular speed reduction device with non-return function
A deceleration device and ring-type technology, which is applied in the direction of transmission, transmission parts, belts/chains/gears, etc., can solve the problems of large installation site and space, many unit components, high manufacturing and use costs, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Embodiment 1 (one shaft and two rings):
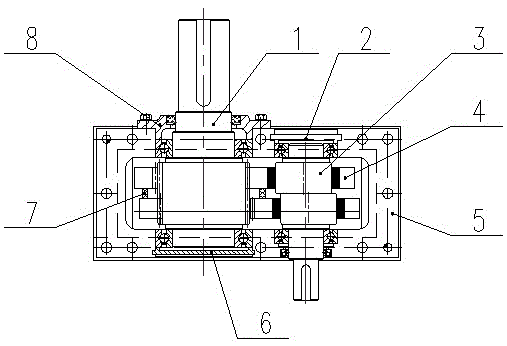
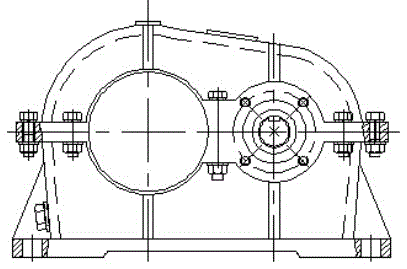
[0051] Such as Figures 1A to 1G As shown, the ring-type speed reducer with backstop function in this embodiment includes upper and lower housings, and the upper and lower housings form cavities for accommodating relevant parts therein.
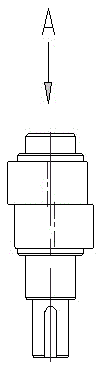
[0052] The eccentric shaft 3 is installed on the two side walls of the lower housing through bearings, and one end extends out of the housing to connect with the driving device to receive input torque, and the end of the other end is sealed by the end cover 2 of the eccentric shaft. Each eccentric shaft 3 is provided with a central shaft and two eccentric wheels uniformly distributed along the circumferential direction of the axis (that is, symmetrically arranged on both sides of the axis of the eccentric shaft, such as Figure 1C and Figure 1D ), each eccentric wheel is integrally formed with the central shaft.
[0053] The output shaft 1 is installed on the two side walls of the lower hou...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Embodiment 2 (one shaft and three rings):
[0059] Such as Figure 2A to Figure 2E As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that there are three eccentric wheels in this embodiment, and the difference between each eccentric wheel is 120 degrees (that is, the plane formed by the axis of each eccentric wheel and the axis of the eccentric shaft is 120 degrees), and the two eccentric wheels 14 and The central shaft is integrally formed (such as Figure 2C ), the other eccentric wheel 13 consists of an independent eccentric wheel (such as Figure 2B ) formed by pinning to the central shaft. There are also three inner tooth plates, and the eccentric wheels corresponding to the positions of the eccentric shafts are respectively accommodated in the through holes of the same inner tooth plate. This structure can also realize the functions of deceleration output and backstop, and compared with the two-ring structure, the operation is smoother. After installation, there i...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3 (one shaft and four rings):
[0061] Such as Figure 3A to Figure 3C As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that there are four eccentric wheels in this embodiment, and the difference between each adjacent eccentric wheel is 90 degrees (that is, the angle between the surfaces formed by the axes of each adjacent eccentric wheel and the axis of the eccentric shaft is 90° degree), wherein the two eccentric wheels 24 are integrally formed with the central shaft (such as Figure 3B ), the other two eccentric wheels 23 are formed by independent eccentric wheels fixed to the central shaft by pins. There are also four inner tooth plates, and the eccentric wheels corresponding to the positions of the eccentric shafts are respectively accommodated in the through holes of the same inner tooth plate. After installation, there is a 180-degree difference between the meshing points of each inner ring gear and the outer gear. This structure can also realize the f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com