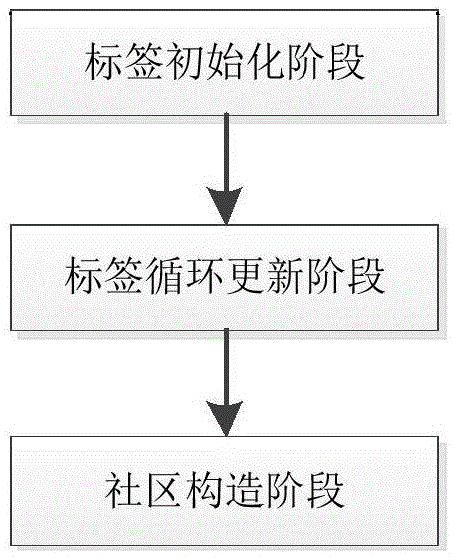
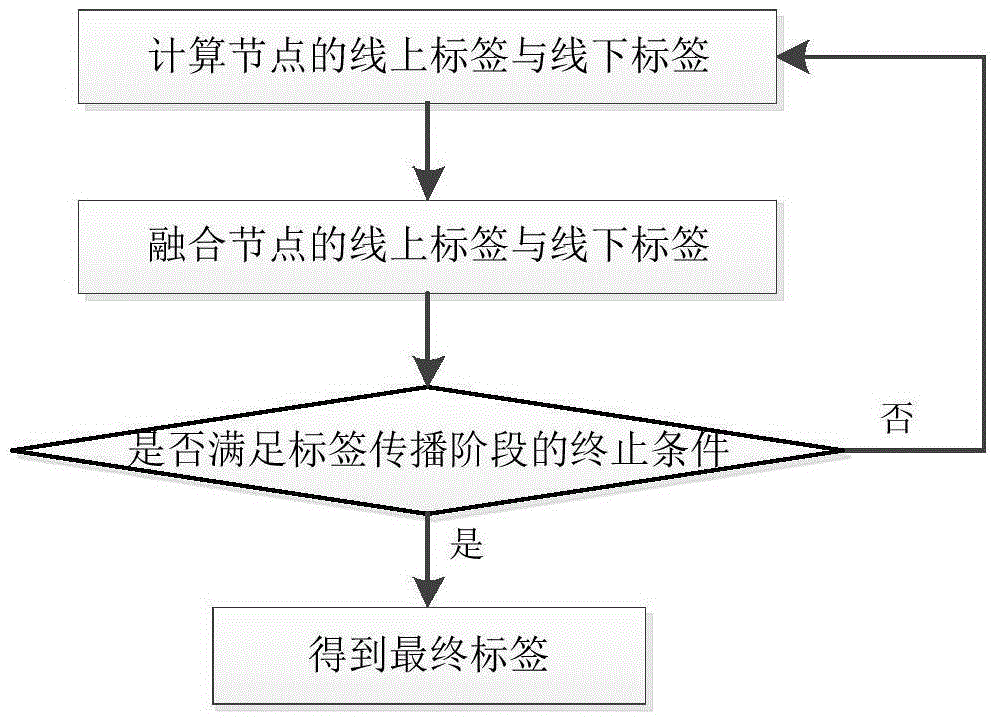
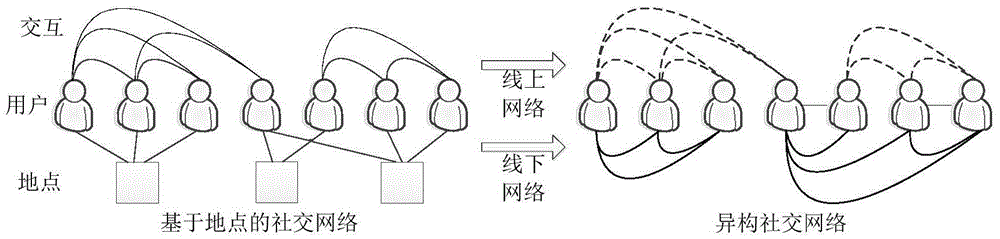
Parallel label propagation-based heterogeneous network community discovery method
A heterogeneous network and label propagation technology, applied in instruments, data processing applications, computing, etc., can solve the problems of slow convergence, affect the overall performance of the community structure, and reduce availability, and achieve the effect of integration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Example 1: Comparison of Different Membership Thresholds
[0064] For the community discovery method based on label propagation, the membership threshold θ mainly affects the number of communities v that a node can belong to, that is, θ=1 / v.
[0065] The experimental parameters are set as follows: the value range of the parameter v is [1,20], and the asynchronous update mechanism is selected. The experimental results are shown in the figure.
[0066] According to the experimental results, the following conclusions are drawn:
[0067] The larger the value of the parameter v, that is, the smaller the value of the membership threshold θ, the smaller the number of corresponding communities. The reason is that a smaller membership threshold makes the label more capable of spreading, and it is easier to form a larger community during the iterative process, resulting in a decrease in the number of communities.
[0068] The value of the parameter v has a great influence on t...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2: Comparison of Different Tag Update Mechanisms
[0072] The experimental parameters are set as follows: the value range of the parameter v is [1,20], and the experiment is carried out by using two kinds of label update mechanisms, synchronous and asynchronous, respectively. Experimental results such as Figure 10 shown.
[0073] According to the experimental results, the following conclusions are drawn:
[0074] Under the synchronous and asynchronous tag update mechanisms, HLPA has no significant difference in the two performance indicators of community number and community coverage, and there is only a slight difference when the value of the parameter v is small.
[0075] Under the synchronous and asynchronous tag update mechanisms, HLPA has significant differences in the two performance indicators of modularity and community overlap. When the value of the parameter v is small, the performances of the two label update mechanisms are relatively close; as v ...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Embodiment 3: Comparison of different label attenuation factors
[0078] The experimental parameters are set as follows: v is 3 and 5 respectively, the value range of δ is (0, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20, 0.25, 0.30, 0.35, 0.40), and the asynchronous label update mechanism is adopted. The related experimental results are shown in the figure.
[0079] According to the experimental results, the following conclusions are drawn:
[0080] With the increase of label decay factor δ, the largest community found by HLPA shows a decreasing trend. When δ increases from 0.00 to about 0.25, the largest community continues to decrease rapidly; and when the value of δ exceeds a certain threshold (about 0.25), the largest community found remains basically stable. This conclusion holds true when the value of the parameter v changes.
[0081] As the label attenuation factor δ increases, the modularity achieved by HLPA also shows a gradual decrease trend. Specifically, when δ increases from 0.00 t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com