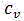Adaptive spectral clustering method of extracting network node community attribute
A technology of community attributes and network nodes, which is applied in the direction of instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer components, etc., can solve the problem of inaccurate node clustering, and achieve the effect of improving accuracy and numerical accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
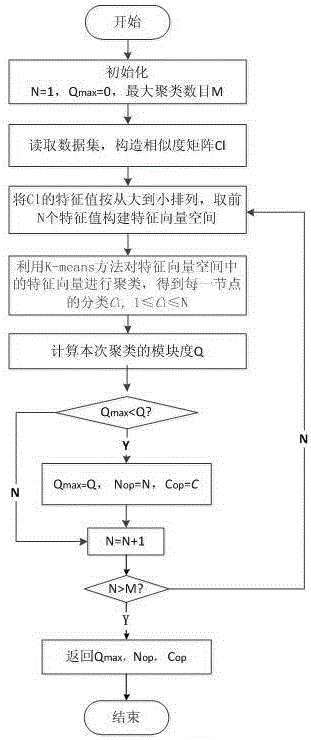
[0022] refer to figure 1 , the adaptive spectral clustering method of an embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0023] Step 1. Set the number of nodes in the mobile crowd-sensing network as M, and regard M nodes as a community, that is, initialize the number of communities N=1, and mark the community attribute of node v as , , , defining the modularity Q of a community composed of M nodes max =0;
[0024] Step 2. From the intimacy vector of node v to all M nodes Get the similarity matrix:
[0025] ,
[0026] in, is the intimacy between node v and node w, when there is no contact between nodes, =0;
[0027] Step 3, the similarity matrix The eigenvalues are arranged from large to small, and the first N eigenvalues are taken to construct a eigenvector space, and the K-means method is used to cluster the eigenvector space, and mark the community attribute of each node;
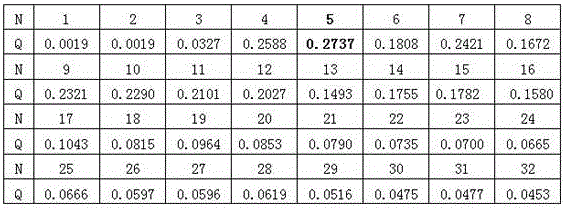
[0028] Step 4. According to the community attributes of al...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The adaptive spectral clustering method of another embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0038] Step 1. Set the number of nodes in the mobile crowd-sensing network as M, and regard M nodes as a community, that is, initialize the number of communities N=1, and mark the community attribute of node v as , , , defining the modularity Q of a community composed of M nodes max =0;
[0039] Step 2. From the intimacy vector of node v to all M nodes Get the similarity matrix:
[0040] ,
[0041] in, is the intimacy between node v and node w, when there is no contact between nodes, =0;
[0042] Step 3, the similarity matrix The eigenvalues are arranged from large to small, and the first N eigenvalues are taken to construct a eigenvector space, and the K-means method is used to cluster the eigenvector space, and mark the community attribute of each node;
[0043] Step 4. According to the community attributes of all nodes after cl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com