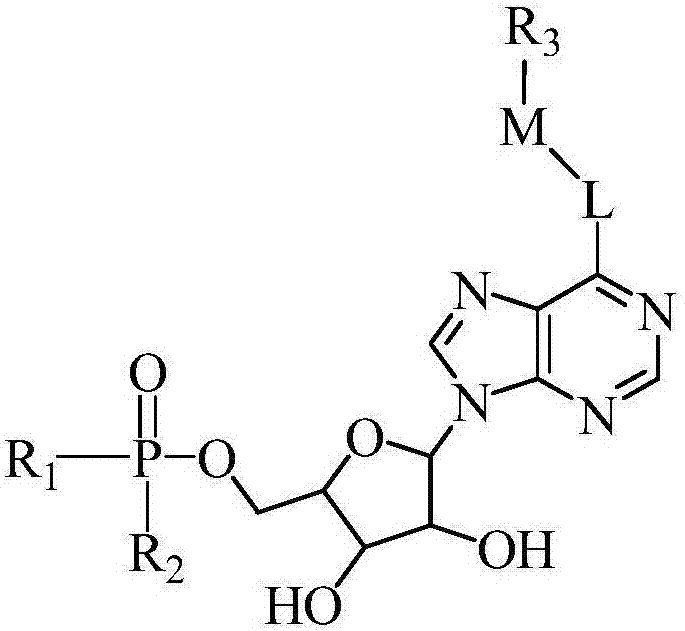
Fluorescent dyes containing high-energy phosphate bonds
A fluorescent dye and phosphoric acid technology, applied in the field of fluorescent dyes, can solve the problems of high membrane permeability and achieve the effects of low biological toxicity, good water solubility, and excellent cell membrane permeability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
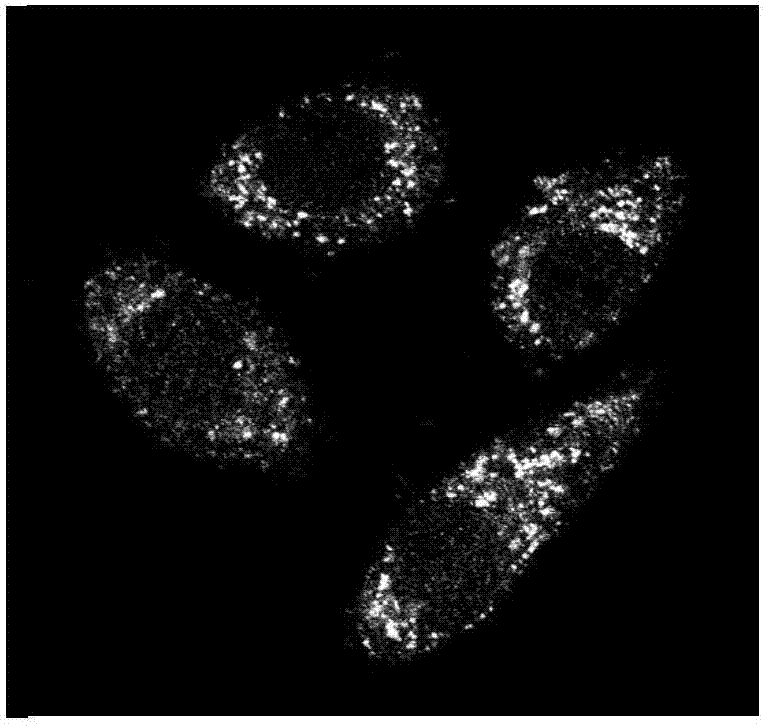
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0063] In another aspect, the present invention provides a method for preparing the above-mentioned fluorescent dye containing high-energy phosphate bonds of the present invention, comprising the following steps:
[0064] 1) H-M-Br and R 3 -H is reacted in a molar ratio of 1:1-1:5 to prepare compound R 3 -M-Br;
[0065] The reaction temperature is 0-200°C, the reaction time is 1-24 hours, and the reaction solvent is selected from dichloromethane, ethanol, methanol, acetone, 1,4-dioxane, glycerol, ethyl acetate, acetic acid or mixture;
[0066] In a specific embodiment, the reaction temperature in step 1) is preferably 25-180°C, more preferably 50-180°C, most preferably 60-150°C; the reaction time is preferably 1-23 hours, more preferably 1-22 hours , most preferably 1-20 hours; the reaction solvent is preferably dichloromethane, ethanol, methanol, acetone, 1,4-dioxane, glycerol, ethyl acetate, acetic acid or a mixture thereof, more preferably dichloromethane Methane, ethan...
Embodiment 1
[0083] Preparation of Fluorescent Dye Compound A 1 , using the following synthetic route:
[0084]
[0085] (1) Synthesis of compound 1-2
[0086] Add 20mmol of compound 1-1 and 30mmol of α-alanine into a round bottom flask containing 10ml of ethanol solution under nitrogen protection. The reaction was heated to reflux for 16h and then stopped. The mixture was poured into ice water, precipitated out, and suction filtered to obtain the crude product of purple solid powder, compound 1-2, with a yield of 93%.
[0087] (2) Compound A 1 Synthesis
[0088] Add 20mmol of compound 1-2 and 120mmol of compound B into a round bottom flask containing 20mmol of EDCl and a small amount of DMAP in 20ml of ethyl acetate, under nitrogen protection. The reaction was heated to reflux at 125°C for 12 hours and then stopped. The solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure and separated by column chromatography to obtain dark red solid powder Compound A 1 , yield 42%. 1 H NMR (400MH...
Embodiment 2
[0090] Fluorescent Dye Compound A 1 water solubility detection test
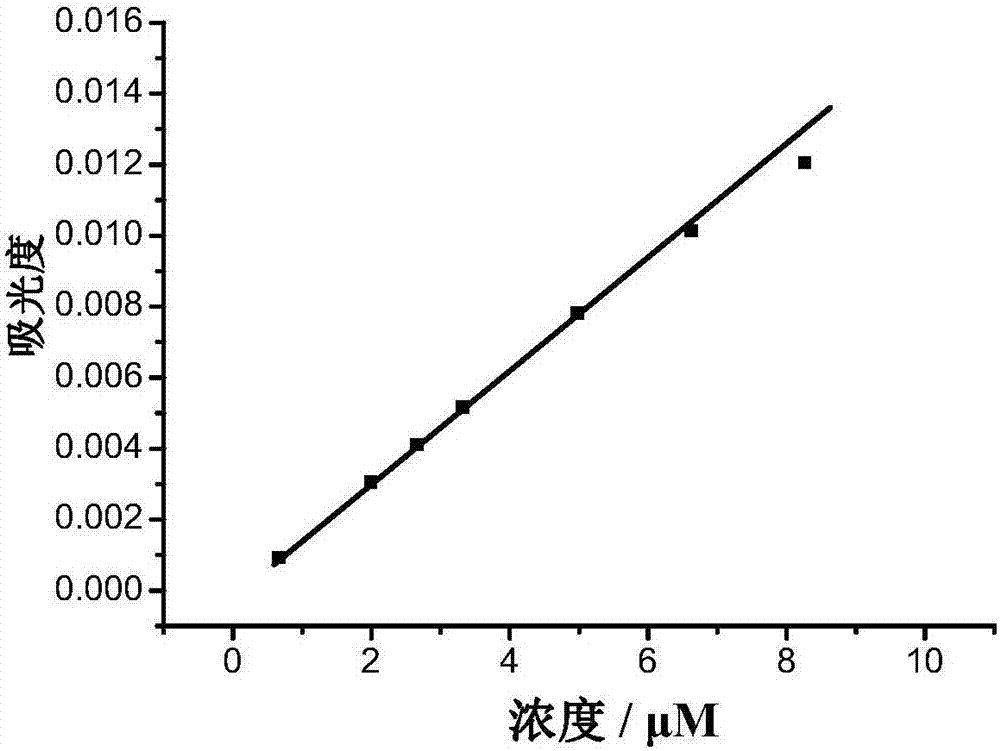
[0091] Fluorescent dye compound A synthesized using the above examples 1 Added to water, measured at different concentrations (0.6, 2.0, 2.7, 3.3, 5.0, 6.6, 9.0μM) A 1 Absorbance at the wavelength of maximum absorption of an aqueous solution. The test result is figure 2 , the results show that: when compound A 1 When the concentration is 9.0μM, the absorbance value does not shift, that is, the fluorescent dye compound A 1 The solubility in water is 9.0 μM. figure 2 for different probe A 1 Absorbance at the wavelength of maximum absorption of the concentration. The instruments used were Agilent 8453 UV spectrophotometer.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com