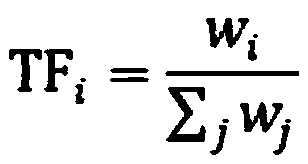The Method of Remote Vehicle Diagnosis and Spare Parts Retrieval Based on Decision Tree Classification and Trouble Code Classification
A technology of decision tree classification and remote diagnosis, which is applied in the direction of electrical testing/monitoring, etc., can solve problems such as maintenance labor costs that cannot be solved in detail, and achieve the effect of solving the problem of experience limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
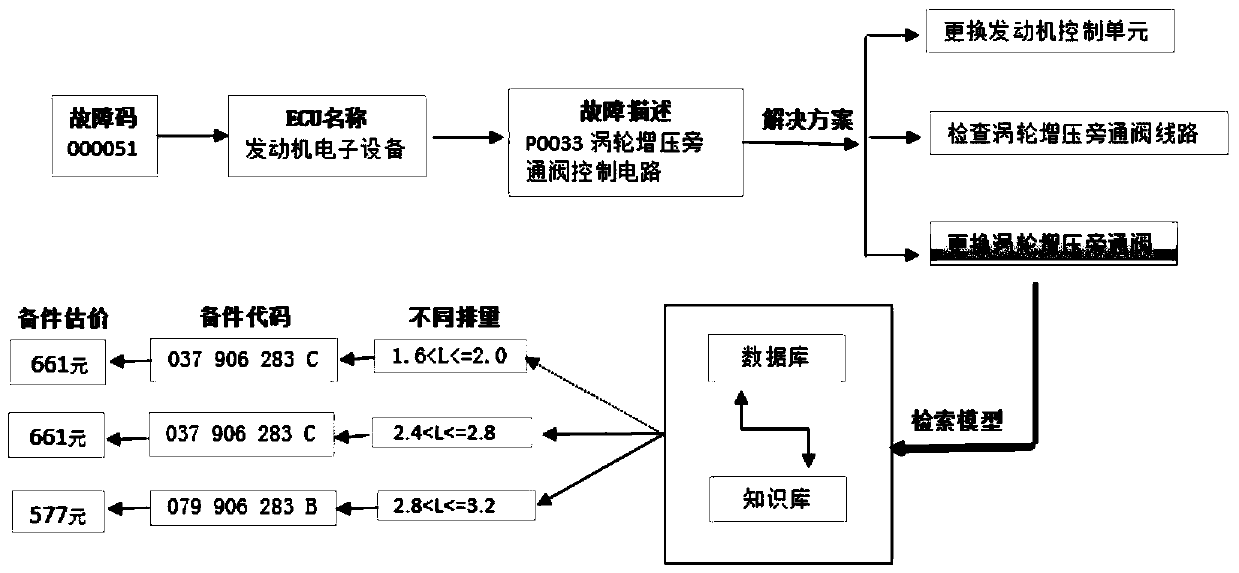
[0014] Example 1 : A method for remote vehicle diagnosis and spare parts retrieval based on decision tree classification and fault code classification, including
[0015] Step 1. Collect vehicle information data;
[0016] Step 2. Identify and classify fault codes;
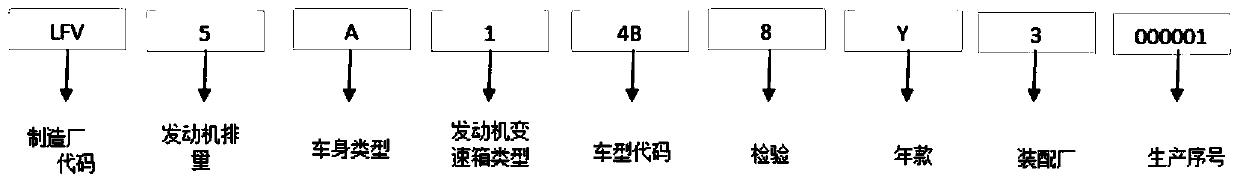
[0017] Step 3. Analyze the vehicle VIN code to obtain variables, the variables include the engine displacement, body type, and engine gearbox type obtained from the VIN code analysis;
[0018] Step 4. Make a decision tree analysis of the spare part codes corresponding to the variables, complete the classification of the variable data to form spare parts information, and establish an index to form a diagnostic knowledge base;
[0019] Step 5. Create a language model, establish a cell vocabulary, search for cell words in the cell vocabulary, arrange the cell words, and use the decision-making classification of the decision tree model to form a diagnostic database of fault code corresponding work items;
[0020] Step 6. Associa...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2: It has the same technical solution as the embodiment 1. More specifically, for step four of the embodiment 1,
[0023] In the fourth step, the historical records of the repair spare parts table are used as the data basis, and the spare parts are classified through the decision tree model. The sample repair spare parts table is shown in Table 1:
[0024] Table I
[0025] VIN123 VIN4 VIN6 VIN78 BJDM LFV514B 06J115403J LFV328K LN052167A21 LFV424F LN052167A24
[0026] The basic principles of the decision tree model are as follows:
[0027] First of all: Determine the entropy of the different categories of spare parts in each dimension. Taking VIN4 as an example, the entropy is defined as
[0028] E=sum(-p(I)*log(p(I)))
[0029] Among them, I=1:N (N-type results, such as 1 in this example, that is, the spare part belongs to this model, so the probability P(I)=1)
[0030] Then E(5)=-(1 / 1)Log2(1 / 1)-(0 / 1)Log2(0 / 1)=0+0=0
[0031] E(3)=-(1 / 1)Log2(1 / 1)-(0 / 1)Log2(0 / 1)=0+0=0
...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3: It has the same technical solution as Embodiment 1 or 2, and more specifically, for step 5 of Embodiment 1,
[0047] The establishment of the language model and the establishment of the cell vocabulary in the fifth step includes the following steps:
[0048] S1.1 Collect professional fault description language;
[0049] S1.2 Perform word vector decomposition on the professional fault description language.
[0050] The creation of the language model is based on the assumption that the appearance of the n-th cell word is only related to the preceding n-1 cell words; the calculation formula for the weight of the occurrence of the fault description sentence T is:
[0051] P(T)=P(w 1 ,w 2 ,w 3 ,...,W n )
[0052] =P(w 1 )×P(w 2 |w 1 )×P(w 3 |w 1 ,w 2 )×…×P(w n |w 1 ,w 2 ,...,W n-1 )
[0053] ≈P(w 1 )×P(w 2 |w 1 )×P(w 3 |w 2 )...P(w n |w n-1 );
[0054] Among them, P(T) is the weight of the fault description sentence T, P(w n |w 1 ,w 2 ,...,W n-1 ) Is the weight of the n-th ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com