An Opportunistic Network Routing Method Oriented to the Recognition of Temporal and Spatial Characteristics Variations
A characteristic, space-time technology, applied in the field of opportunistic network routing oriented to the cognition of changes in space-time characteristics, can solve problems such as ignoring mobile areas, not conforming to the network environment, increasing node storage space and algorithm complexity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
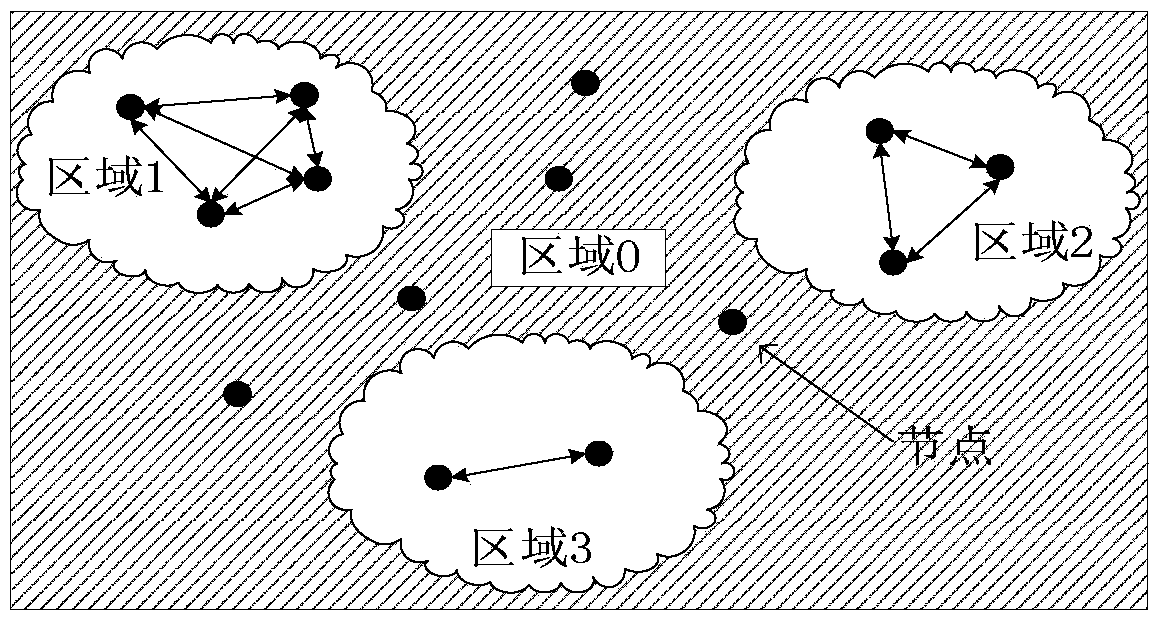
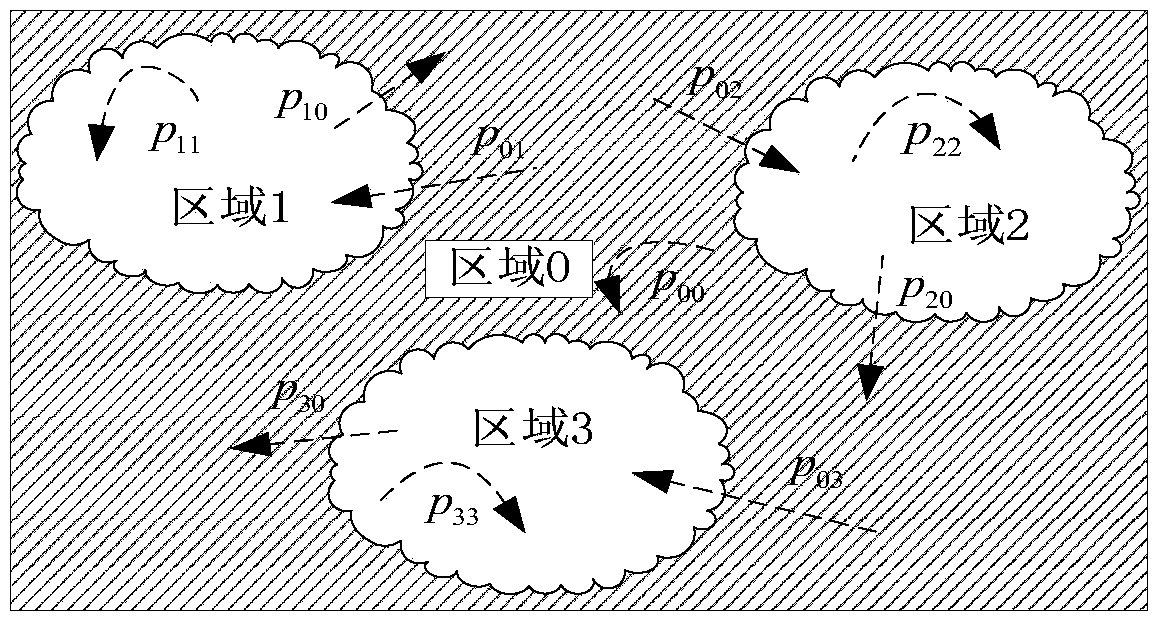
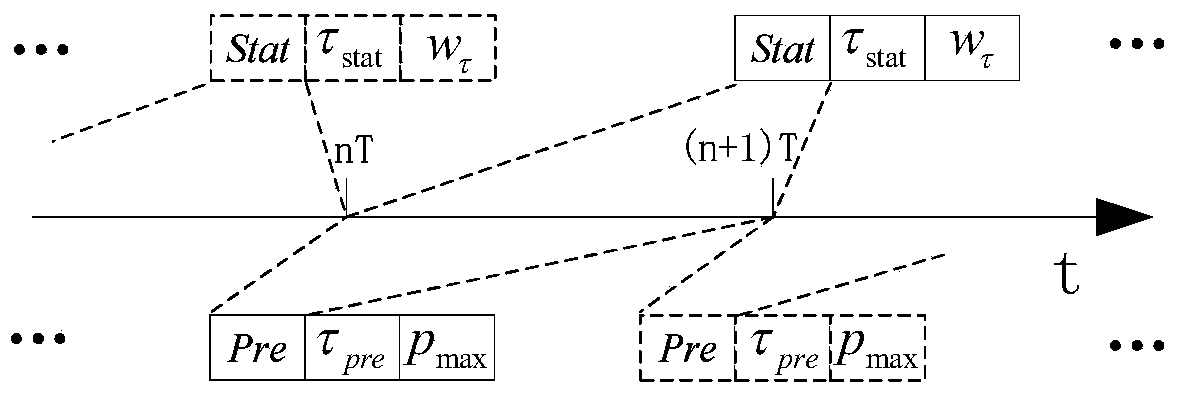
[0041] The present invention first establishes a semi-Markov model. When considering the transfer area, the space outside the geographic area is regarded as the same state in the semi-Markov model, which reduces the cache space of nodes and the time complexity of the algorithm. Secondly, in the routing method of the present invention, when it is recognized that the spatio-temporal characteristics of the node no longer conform to the semi-Markov model, the existing message forwarding mechanism is changed and the message is forwarded by multiple copies; when the spatio-temporal characteristics of the node are recognized again When conforming to the semi-Markov model, restore the original message forwarding mechanism. In this way, the adaptability of the routing method can be realized.
[0042] 1, figure 1 It is an application scenario of the r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com