Temperature sensing real-time task scheduling method for coping with soft errors
A technology of real-time tasks and scheduling methods, applied in climate sustainability, instruments, data processing power supplies, etc., can solve problems such as ignoring system temperature, and achieve the effect of minimizing energy consumption and high application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
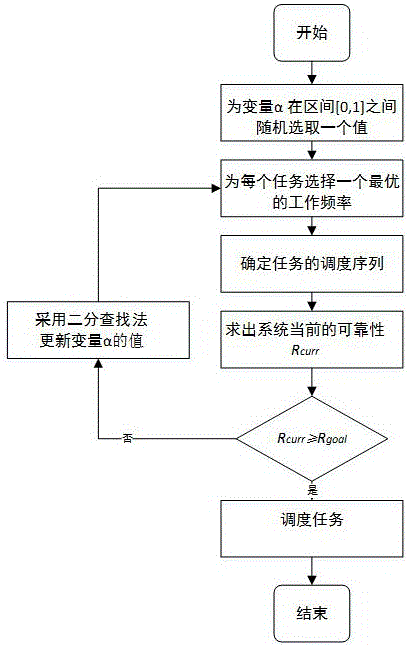
[0066] The task set is defined as Γ={τ 1 ,τ 2 ,τ 3}, when the standard frequency f=1.0, the task execution time e i 10, 20, 30 respectively, assuming that each task τ i The number of faults that can be tolerated k i is 1, the common deadline of tasks in the task set is D=1.4× The frequency set available to the processor is f={0.5,0.8,1.0}, the reliability target R of the system goal = 0.87. These parameters serve as input to the dispatch method.
[0067] Step 1: Randomly select a value for the variable α in the interval [0,1], and the variable α=0 at the beginning;
[0068] Step 2: Select the optimal operating frequency for each task;
[0069] First initialize the slack time of the system And select the first task in the task set as the current task. where D is the deadline of all tasks, e i is the task τ i (i=1,2,...,N) The deadline in the worst case. The next step is to determine the optimal frequency of operation for the task.
[0070] When selecting the opt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com