Image classification method based on sparse nonlinear subspace migration
A classification method and subspace technology, which is applied in the directions of instruments, computing, character and pattern recognition, etc., can solve the problem of low accuracy of the subspace migration method, and achieve the effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0048] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and embodiment the present invention will be further described:
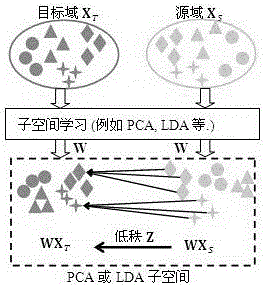
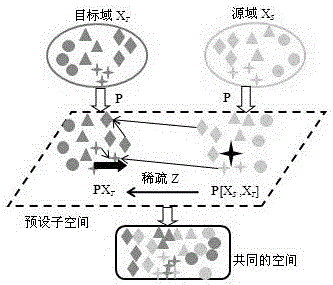
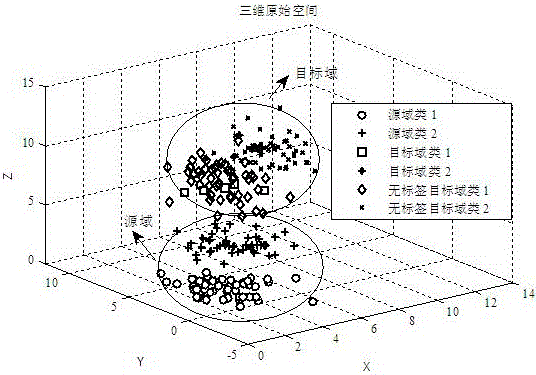
[0049] The present invention first maps data from the original space to the regenerated Kernel Hilbert space (RKHS) through the kernel method, and then through such as figure 2 The transformation shown, in the kernel Hilbert space, consists of a pre-defined basis transformation P that transforms the target domain training data X T The target data PX is obtained by mapping the basic transformation P to the preset subspace T , the source domain training data X S Get PX by mapping the basic transformation P to the preset subspace S , due to the present invention through the source domain and target domain data P[X S ,X T ] to reconstruct the target data, so P[X S ,X T ] is also collectively referred to as source domain data, and then use source domain data P[X S ,X T ] Transformed by the sparse matrix Z, and PX T Share distributions within preset subsp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com