Method for quantitative evaluation of characteristics of micro-pore structure of deeply-buried high-pressure low-permeability sandstone reservoir stratum
A quantitative evaluation, micro-porosity technology, used in measurement devices, permeability/surface area analysis, suspension and porous material analysis, etc. The problem of large radius
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] Select certain oil field sample below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and describe the present invention in detail.
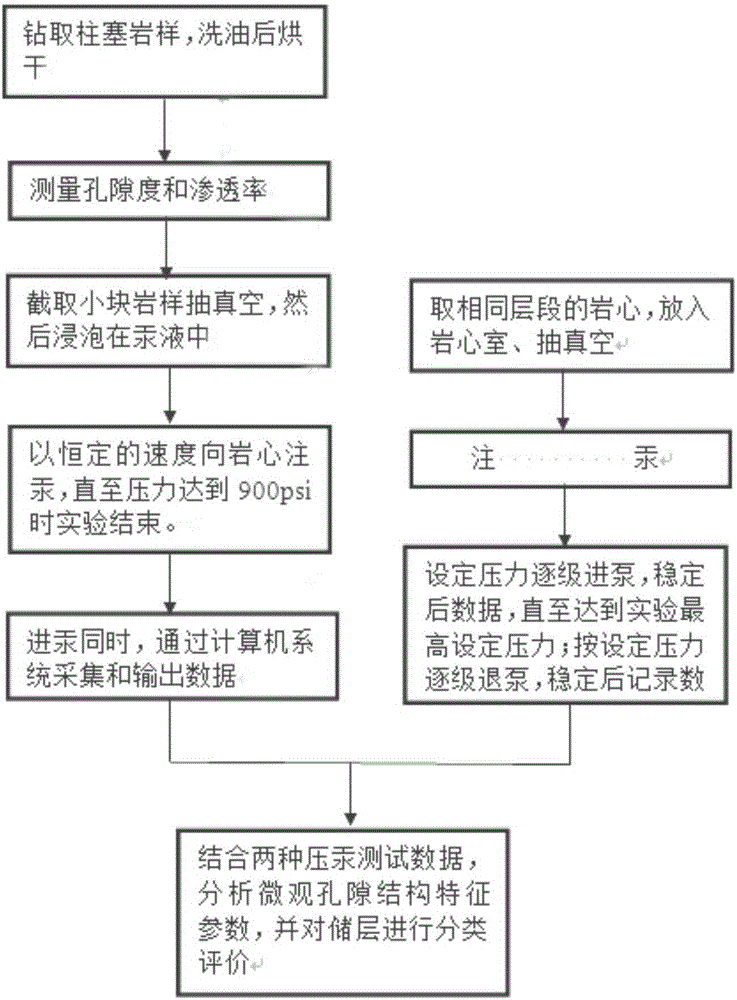
[0027] The present invention quantitatively evaluates the method for microscopic pore structure characteristics of deep high-pressure low-permeability sandstone reservoirs, see figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0028] Step 1: Drill a standard plunger rock sample with a diameter of 2.5 cm, wash the oil and dry it.
[0029] Step 2: Measuring the porosity and permeability of the standard core after oil washing and drying by means of gas detection.
[0030] Step 3: Take a small piece of rock sample from the plunger rock sample, vacuumize it, and then soak it in mercury solution.
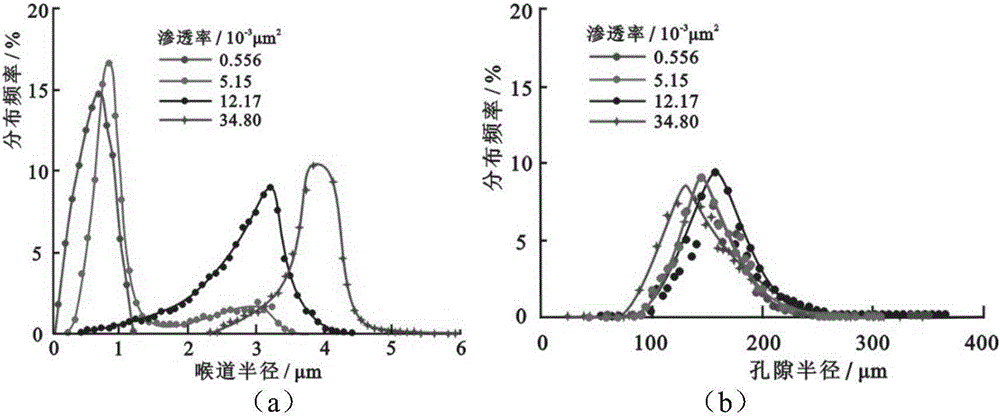
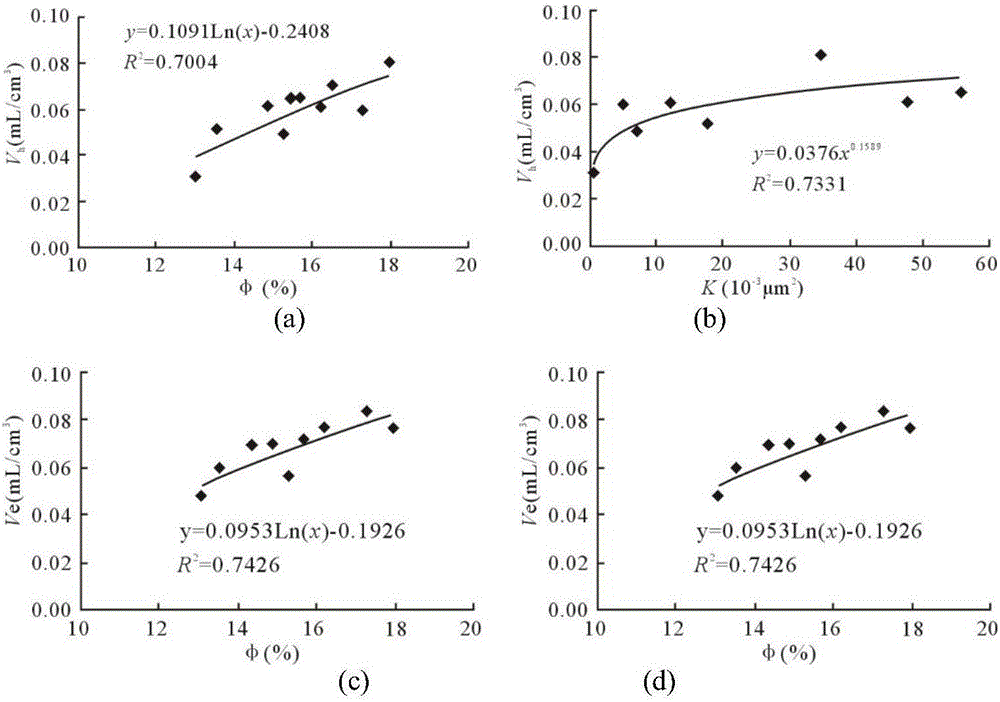
[0031] Step 4: Inject mercury into the core at a constant speed of 0.00005mL / min. During the mercury injection process, the pressure drops and rises periodically, and the experiment ends when the pressure reaches the highest pressure 900psi that the consta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com