A Method for Autonomous Orbit Replanning of Space Vehicle
A space vehicle, autonomous orbit technology, applied in instruments, adaptive control, control/regulation systems, etc., can solve problems such as large manpower and material costs, inability to re-plan orbits, safety accidents, etc., to reduce manpower and material costs and improve tasks. Adaptability, effectiveness in reducing security risks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
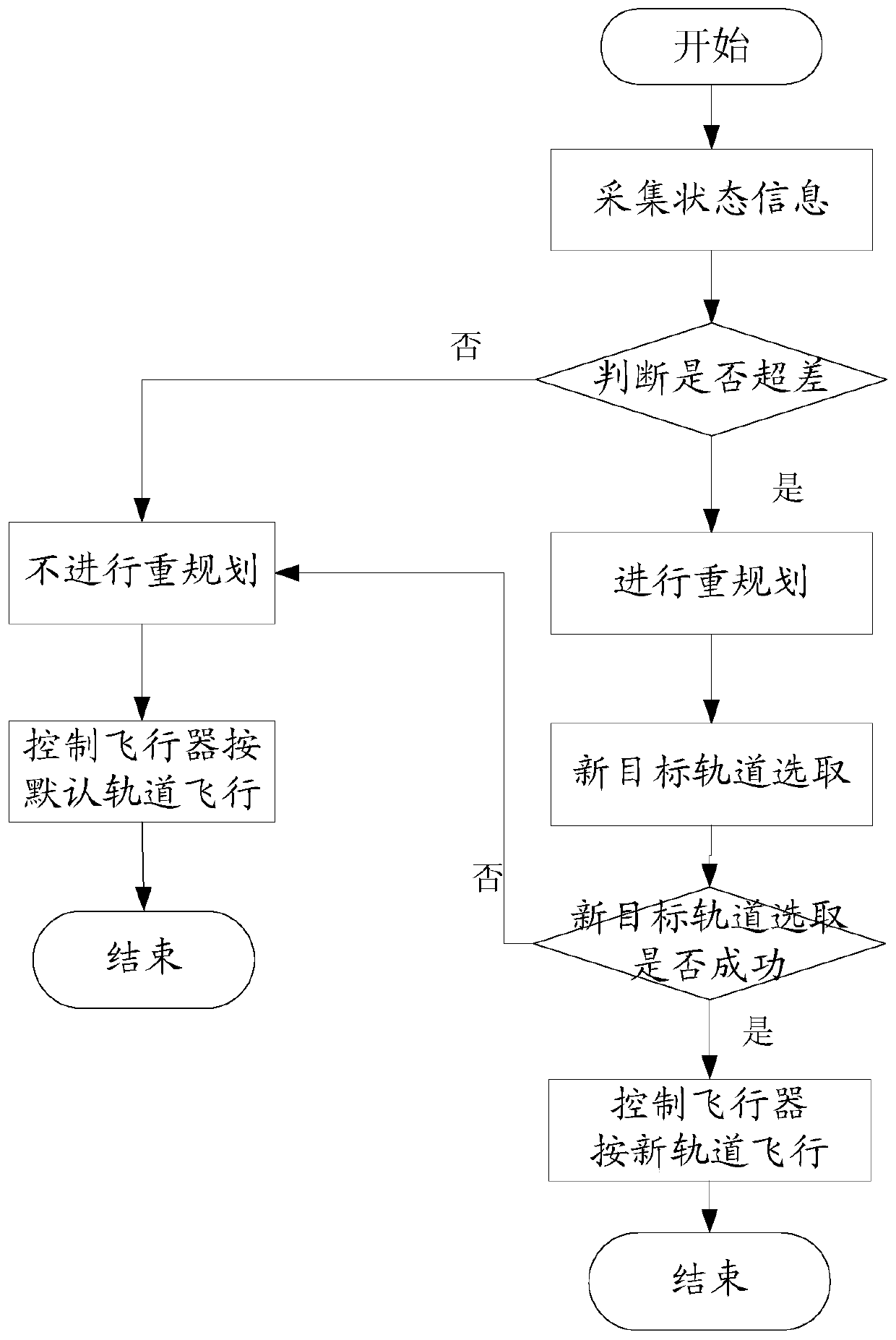
[0042] If the base-stage launch vehicle motor fails, the thrust drop does not put the spacecraft into orbit. The aircraft enters the taxiing segment and collects the status information of the spacecraft:
[0043] project
[0044] According to the state information, calculate the number of orbital elements, where |a-a 0 |=2350kmΔa=100km, so the judgment result is that the orbit parameters are out of tolerance, and orbit re-planning is required
[0045] According to the state parameters and the orbit parameter database, select the new orbit parameters and get iresult=3, that is, select the third re-planned orbit, that is, the following figure 1 The spacecraft in the new target orbit, the new target orbit is selected successfully, the spacecraft needs to enter the following new orbit:
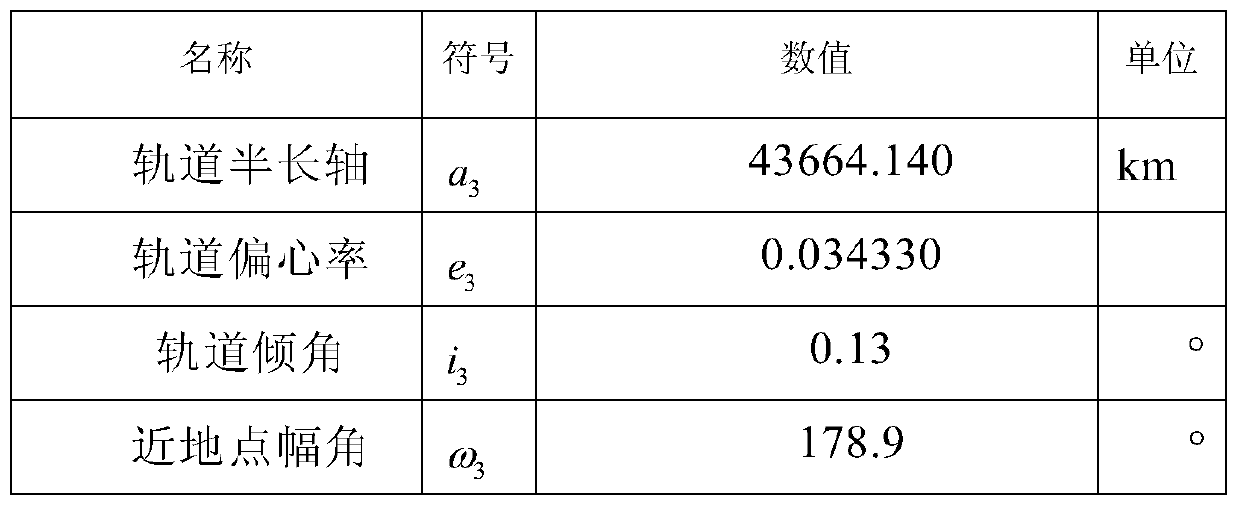
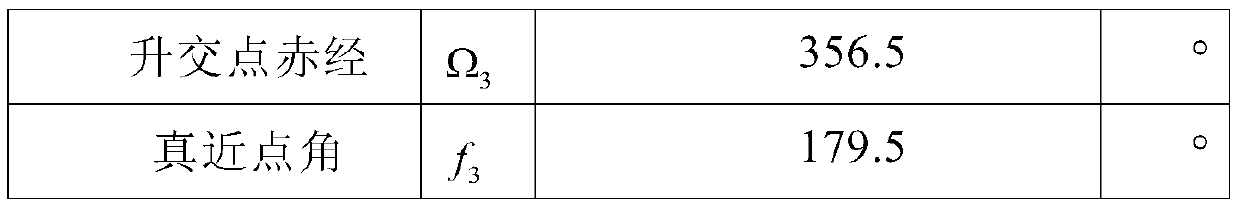
[0046] Table 1: New target orbits for spacecraft
[0047]
[0048]
[0049] If trajectory re-planning is not performed at this time, the spacecraft still adopts the original par...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com