Methods for rapid and sensitive detection of hotspot mutations
一种身体、样品的技术,应用在遗传和生物化学分析领域,能够解决不适用临床用途、误导疗法等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
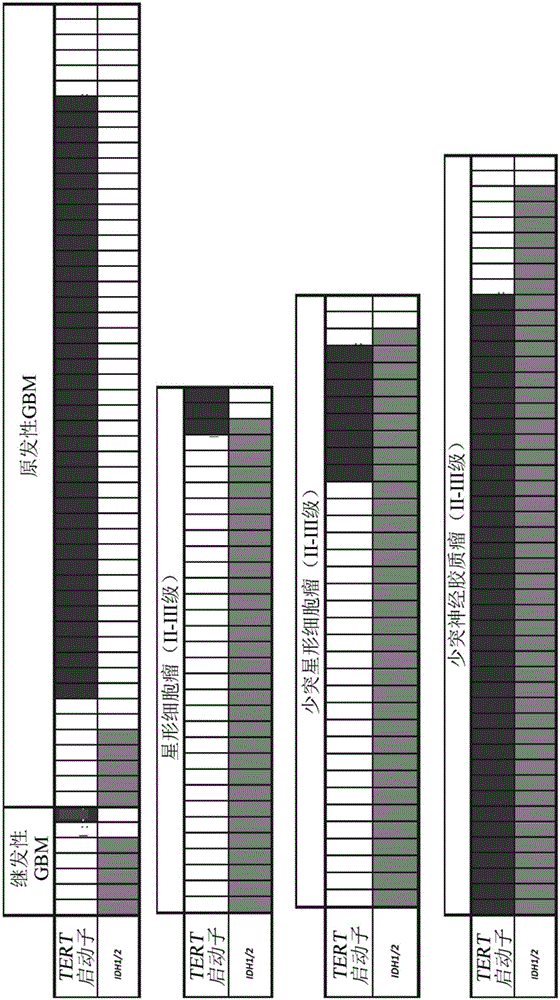
[0038] TERT promoter and IDH1 / 2 hotspot mutation AS LNA q-PCR analysis:
[0039] A. Background :
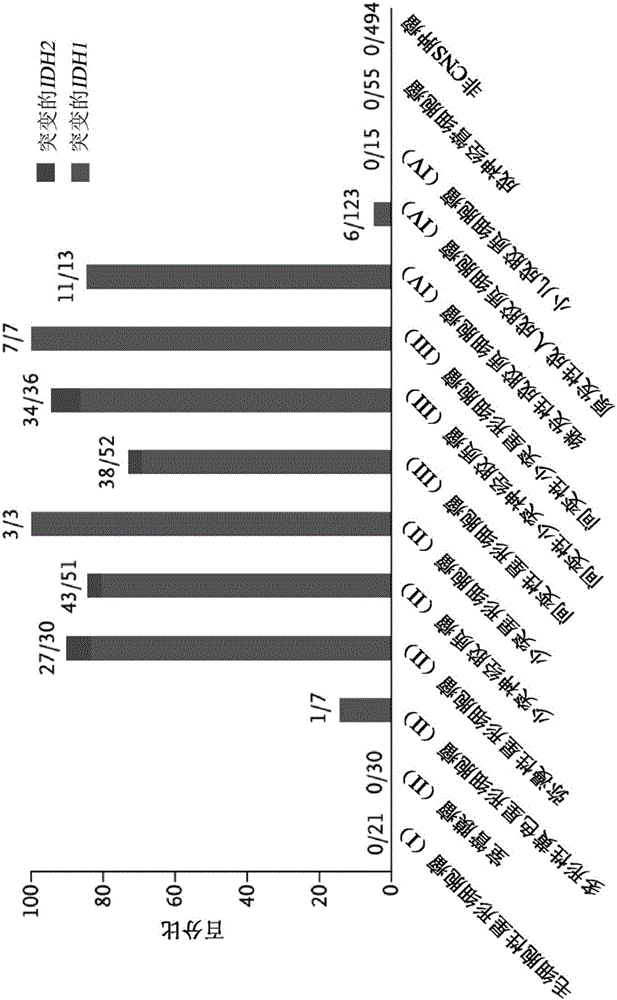
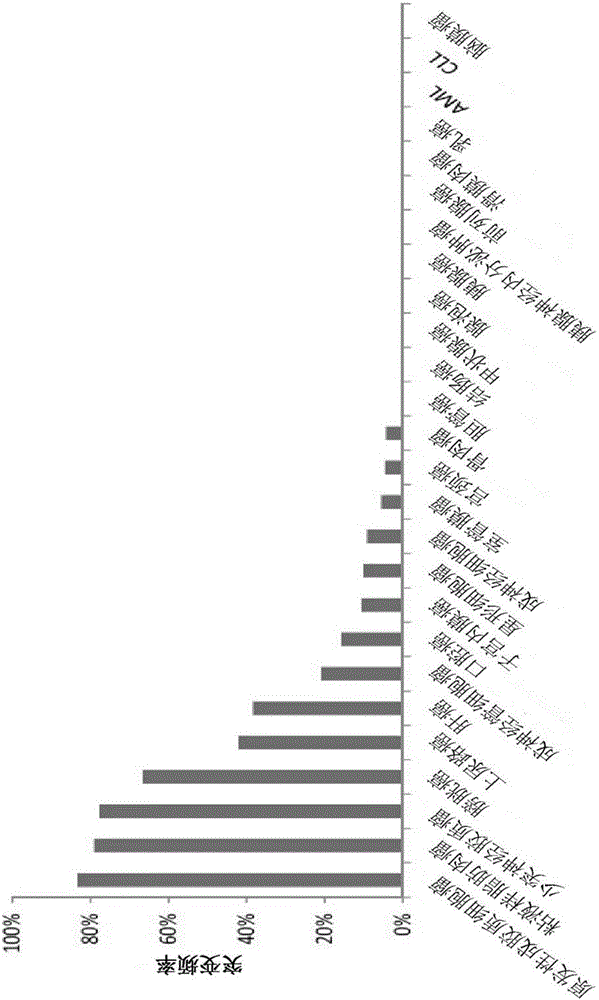
[0040] Allele-specific PCR is a form of DNA template amplification for the selective amplification of templates containing the variant of interest, and is thus a method for SNP genotyping 18 . Most methods rely on identifying primers with higher complementarity to target sequences with the genotype of interest. This is most commonly done by forcing the 3' of the primer to be at the mutation position and only complementary to the target variant or wild-type nucleotide. In this way, PCR efficiency decreases when primers bind to non-target alleles, imparting selective amplification ( Image 6 ).
[0041] The major advance in this region has been the use of candidate nucleic acids at the 3' end of these allele-specific primers called locked nucleic acids (LNAs). LNAs are nucleic acid analogs with a methylene bridge between the 2'-O and 4'-C of the nucleic acid, which creates...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com