Physical layer procedures for LTE in unlicensed spectrum
A spectrum and processor technology, applied to the first sub-field based on the RRM measurement, can solve wireless link monitoring, inability to correctly measure the downlink channel of an eNodeB, and wireless link failure detection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
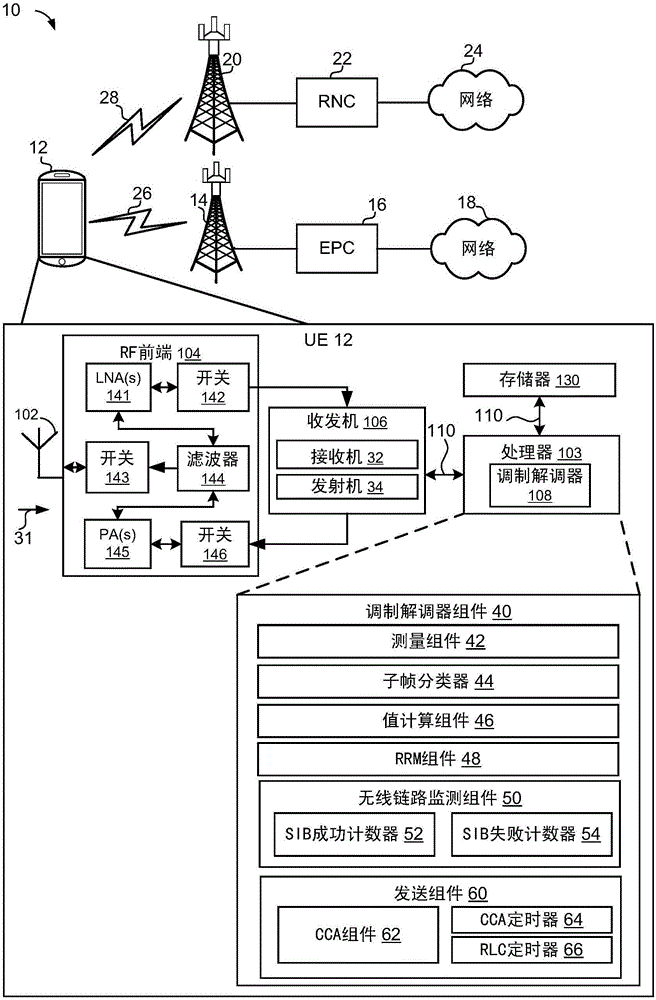
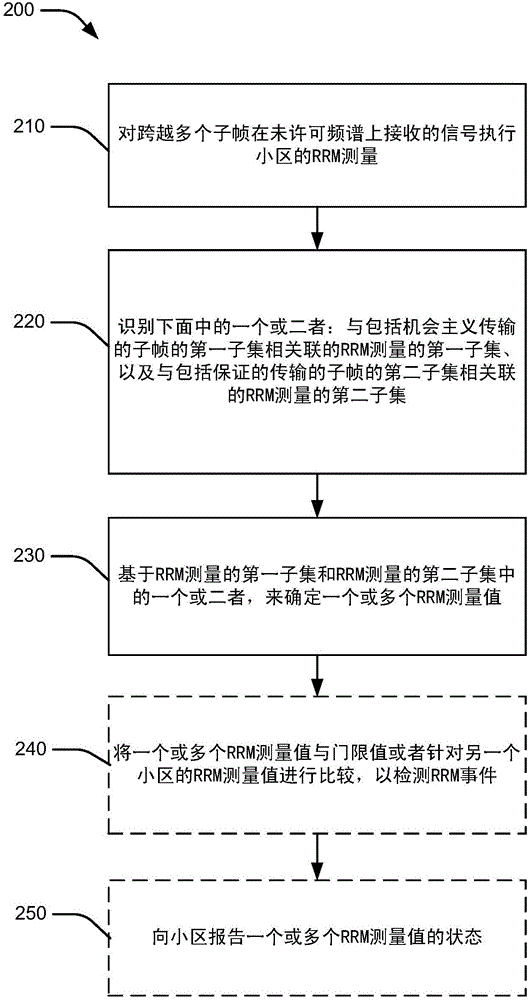
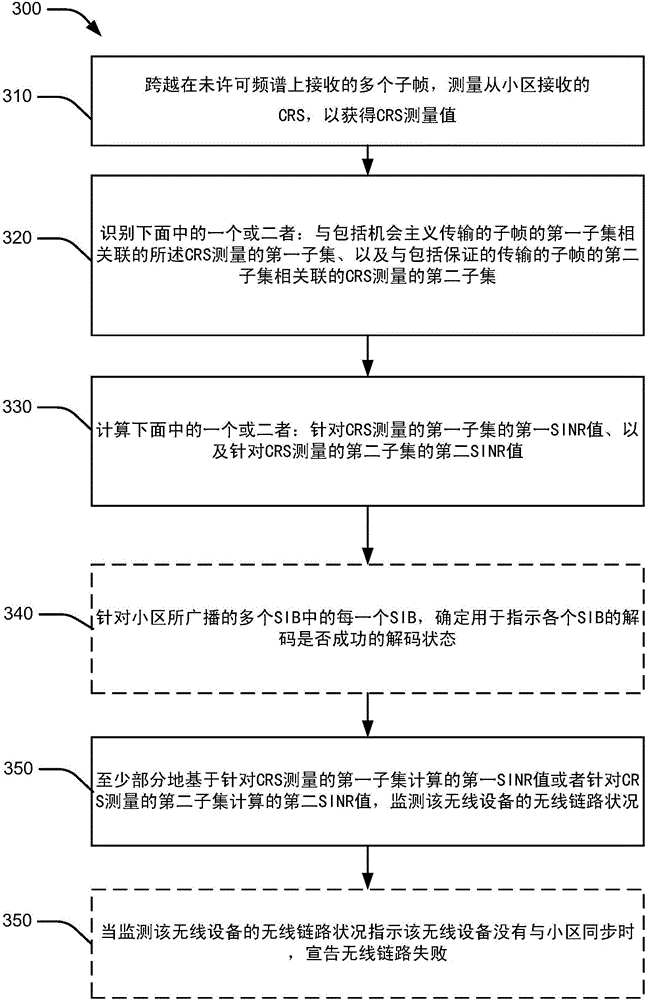
[0036] In some aspects, the present disclosure relates to measurements and monitoring performed by user equipment (UE) operating in unlicensed spectrum. The UE may perform measurements based on two types of downlink transmissions. A first type of downlink transmission may be an opportunistic transmission. As used herein, "opportunistic" transmissions may refer to transmissions that may only occur when a carrier or channel satisfies certain conditions (eg, when the carrier or channel is not in use). In one aspect, for example, opportunistic transmissions may be preceded by a CCA process or an extended CCA (E-CCA) process. The second type of downlink transmission may be a guaranteed transmission. As used herein, "guaranteed delivery" may refer to a delivery that is guaranteed to occur at a certain time. For example, guaranteed transmissions may be received from the eNodeB in certain subframes. In one aspect, the eNodeB may designate certain subframes for downlink clear chann...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com