Monocular vision and quick-response code road sign based indoor autonomous navigation method
An autonomous navigation and monocular vision technology, applied in the field of indoor navigation, can solve the problems of small field of view, poor flexibility, restricting the maximum running speed of the robot, etc., to achieve the effect of solving the complex calculation and meeting the accuracy requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] The technical content of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
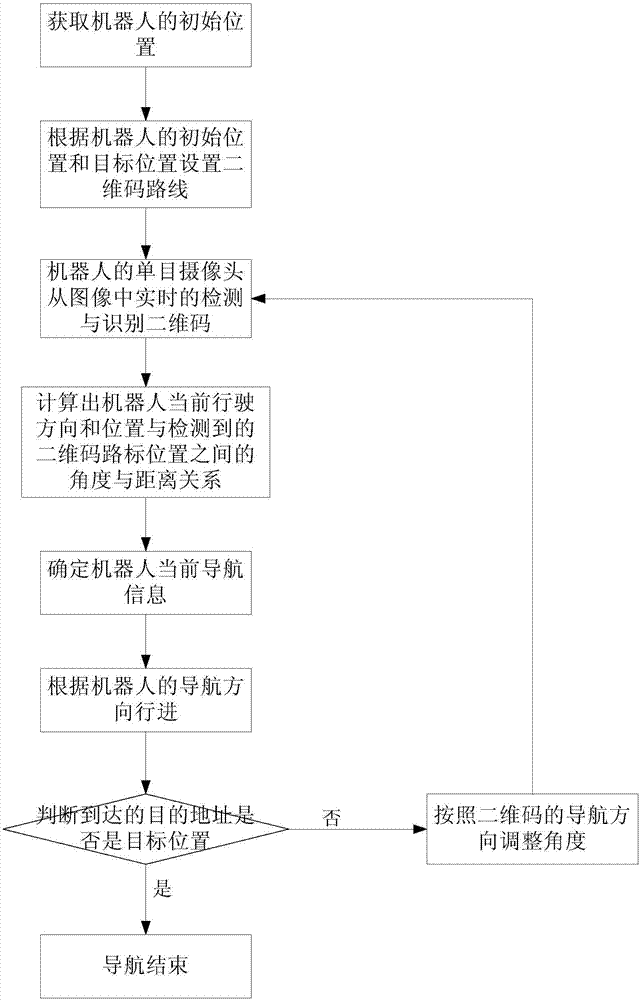
[0047] Such as figure 1As shown, the indoor autonomous navigation method based on monocular vision and two-dimensional code landmarks provided by the present invention includes the following steps: first, obtain the initial position of the robot, and set the two-dimensional code route according to the initial position and target position of the robot. Secondly, the monocular camera of the robot detects and recognizes the two-dimensional code in real time from the image, and calculates the angle and distance between the robot's current driving direction and position and the detected two-dimensional code landmark position according to the internal and external parameters of the monocular camera relationship, determine the current navigation information of the robot; then, according to the navigation direction of the rob...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com