Land-based and earthen-pond segmented relay-type culture method for alosa sapidissima
A breeding method, the technology of American shad, which is applied in the field of aquaculture, can solve the problems of interfering with the growth of individuals that are not up to the specification, the difficulty of breeding and selling operations, and the waste of pond breeding space. Accept and promote, avoid the effect of breeding space waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
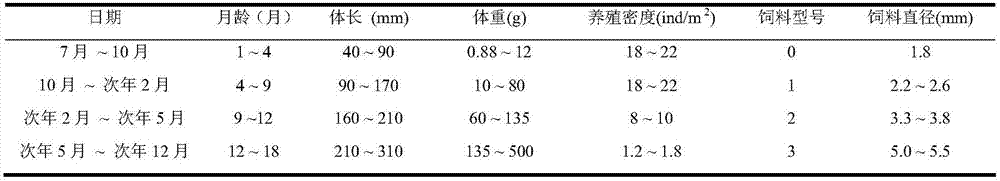
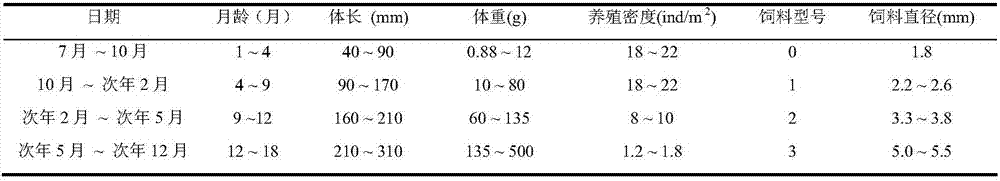
[0033] Embodiment 1: On July 30, 2015, 4000 juvenile American shads with a body length of 54.04 ± 6.07mm and a body weight of 2.03 ± 0.75g were put into the breeding pond at the Fengxian Research Base of the Shanghai Fisheries Research Institute, and were cultured for 84 days. Ends October 22, 2015. After 84 days of breeding, the survival rate of American shad fingerlings was 85%, and the feed coefficient was 1.84; the average body length of young fish was 115.49±7.29mm, the average weight was 22.72±4.20g, and the average body length and body weight increased by 1.14 times respectively and 10.19 times.
[0034] In November 2015, it entered land-based overwintering breeding. From land-based breeding until May 2016, the American shad from overwintering has a body length of (17.98±1.58) cm, a weight of (79.3±23.5) g, and a breeding survival rate of 90%. above.
[0035] In June 2016, American shad entered the earthen pond culture. Two adjacent ponds of 2.5 mu (number: 10 east an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com