Continuous scheduling resource allocation method and device and data transmission method through continuous scheduling resources and data transmission device thereof
A technology for continuous scheduling and data transmission, which is applied in the direction of adjusting transmission rate, transmission modification based on link quality, signaling allocation, etc., and can solve problems such as no longer applicable and no continuous scheduling solution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0114] This example is used to illustrate the implementation of allocating a persistent scheduling resource list on the network side.
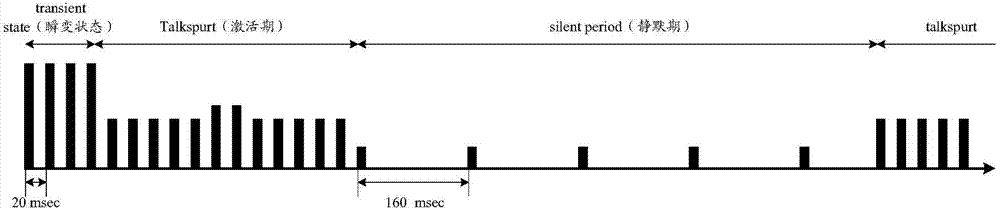
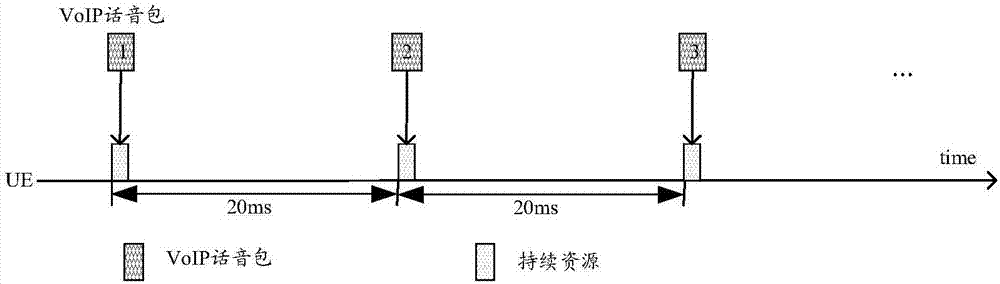
[0115] Step 1: On the network side, determine the terminal that needs to be allocated with persistent scheduling resources. The determination is based on the fact that the terminal has service data that needs to be transmitted using persistent scheduling resources, such as periodic small data packets (such as VoIP, MTC (Machine Type Communications, Machine Type Communications, Machine Type Communications, class communication) periodically report data, etc.). And determine the period, data packet size, transmission direction (downlink, uplink, D2D) etc. of using persistent scheduling resources to transmit service data.
[0116] Step 2: The network side determines the TTI length change requirements and TTI length options, as well as air interface resources for possible persistent scheduling resource allocation. A persistent scheduling resource ...
Embodiment 2
[0161] This example is an implementation of selecting persistent scheduling resources for transmission according to the TTI length.
[0162] Before performing persistent scheduling transmission, the network side has configured a persistent scheduling resource list for the terminal, and each persistent scheduling resource configuration corresponds to a different TTI length.
[0163] 1. Downlink transmission (network side to terminal):
[0164] Network side transmission point side:
[0165] Step 1: The transmission point on the network side determines the transmission time point according to the persistent scheduling period, and if the TTI at the time point corresponding to the period is not a downlink TTI, then the next nearest downlink TTI is used as the transmission TTI.
[0166] Step 2: The transmission point on the network side determines the length of the TTI for transmission, and determines the persistent scheduling resource for transmission according to the corresponden...
Embodiment 3
[0191] This example is an implementation of selecting persistent scheduling resources for transmission according to channel quality.
[0192] Before performing persistent scheduling transmission, the network side has configured a persistent scheduling resource list for the terminal, and each persistent scheduling resource configuration corresponds to a different channel quality.
[0193] sender:
[0194] Step 1: The sender determines the transmission time point according to the persistent scheduling cycle. If the TTI corresponding to the time point of the cycle is not the TTI corresponding to the transmission direction, the next available TTI is used as the transmission TTI.
[0195] Step 2: The sending end measures the transmission channel quality of the opposite end, and uses channel reciprocity to estimate the transmission channel quality sent to the opposite end; or, determines the transmission channel quality according to the channel quality feedback of the opposite end. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com