Water-saving irrigation method
A technology of water depth and water layer, applied in fertilization methods, horticultural methods, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the difficulties of precise and quantitative irrigation, lack of precise quantitative indicators of irrigation, and insufficient coordination of rainfall utilization, etc. Problems, easy to master, practical and reliable, easy to use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
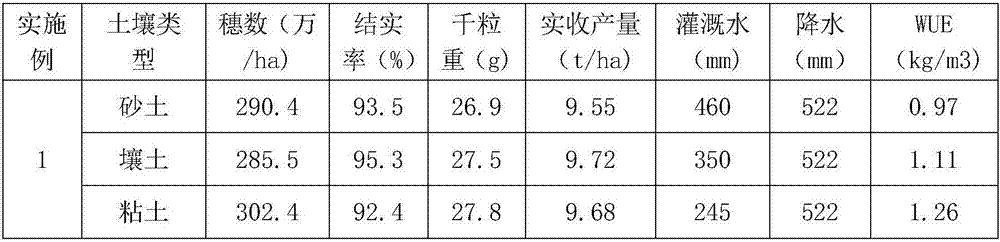
Embodiment 1
[0026] A water-saving irrigation method, comprising the following steps:
[0027] (1) During the greening period, when there is no rainfall, the lower limit of irrigation is soil saturation, and the upper limit of irrigation is 20 mm of the water layer on the field surface. In case of rainfall, the upper limit of rain storage is 35 mm of water depth on the field surface, and the excess water is discharged;
[0028] (2) At the tillering stage, when there is no rainfall, the field will dry naturally from the shallow water layer. When the soil buried water depth is 60mm for sandy soil, 80mm for loamy soil, and 100mm for clay soil, the irrigation layer is 10mm; the soil buried water depth is less than the above Do not irrigate when the value is on; in case of rainfall, the upper limit of rain storage is 70mm deep on the field surface, and the excess water will be discharged;
[0029] (3) During the jointing stage, when there is no rainfall, the field will dry naturally or drain dr...
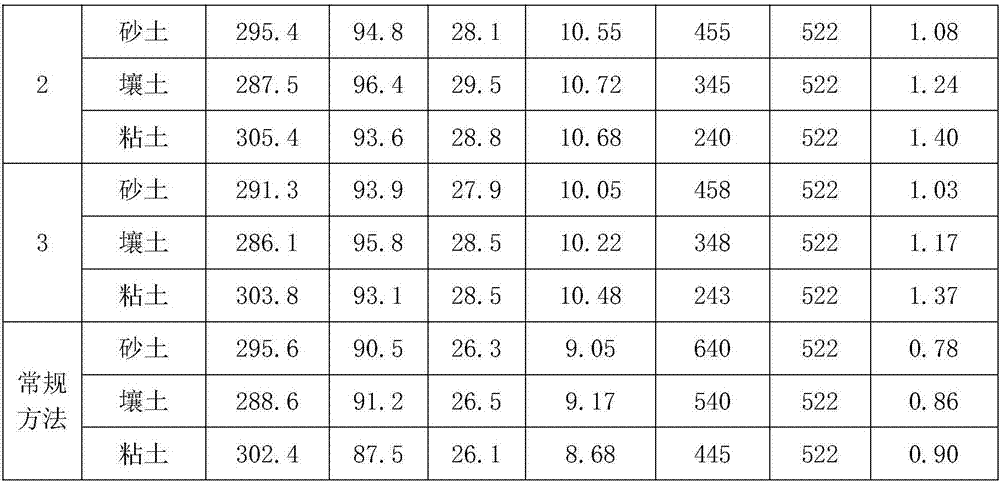
Embodiment 2
[0040] A water-saving irrigation method, comprising the following steps:
[0041] (1) During the greening period, when there is no rainfall, the lower limit of irrigation is soil saturation, and the upper limit of irrigation is 20 mm of water layer on the field surface. In case of rainfall, the upper limit of rain storage is 50 mm of water depth on the field surface;
[0042] (2) At the tillering stage, when there is no rainfall, the field will dry naturally from the shallow water layer. When the soil burial depth is 60mm for sandy soil, 80mm for loamy soil, and 100mm for clay soil, the irrigation layer is 20mm; the soil burial depth is less than the above No irrigation when the value is on; in case of rainfall, the upper limit of rain storage is 85mm of water depth on the field surface;
[0043](3) During the jointing period, when there is no rainfall, the field will dry naturally or drain dry. When the soil burial depth is 120mm for sandy soil, 180mm for loamy soil, and 200m...
Embodiment 3
[0050] A water-saving irrigation method, comprising the following steps:
[0051] (1) During the greening period, when there is no rainfall, the lower limit of irrigation is soil saturation, and the upper limit of irrigation is 20 mm of water layer on the field surface. In case of rainfall, the upper limit of rain storage is 45 mm of water depth on the field surface;
[0052] (2) At the tillering stage, when there is no rainfall, the field will dry naturally from the shallow water layer. When the soil burial depth is 60mm for sandy soil, 80mm for loamy soil, and 100mm for clay soil, the irrigation layer is 15mm; the soil burial depth is less than the above No irrigation when the value is on; in case of rainfall, the upper limit of rain storage is 80mm of water depth on the field surface;
[0053] (3) During the jointing stage, when there is no rainfall, the field will dry naturally or drain dry. When the soil burial depth is 120mm for sandy soil, 180mm for loamy soil, and 200m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com