Identification method for turnout faults
A technology for fault identification and turnout, which is applied in the field of rail transit, can solve the problems of missed reporting and false reporting, and achieve the effects of strong practicability, wide application range and improved accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
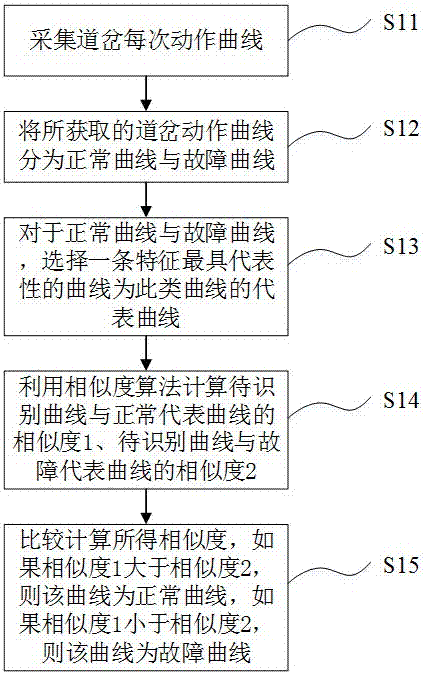
[0061] In this embodiment, a method for identification of a turnout fault is provided, figure 1 is a flow chart of a method for identifying a fault in a turnout according to an embodiment of the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, the flowchart includes the following steps:
[0062] Step S11: collect each action curve of the turnout;
[0063] Step S12: Divide the obtained switch action curves into normal curves and fault curves;
[0064] Step S13: For the normal curve and the fault curve, select a curve with the most representative characteristics as the representative curve of this type of curve;
[0065] Step S14: use the similarity algorithm to calculate the similarity 1 between the curve to be identified and the normal representative curve, and the similarity 2 between the curve to be identified and the fault representative curve;
[0066] Step S15: Compare the calculated similarities. If the similarity 1 is greater than the similarity 2, the curve is a normal...
Embodiment 2
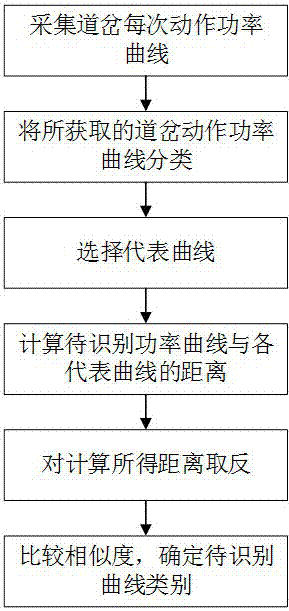
[0085] In this embodiment, a method for identifying a fault of a switch is also provided.
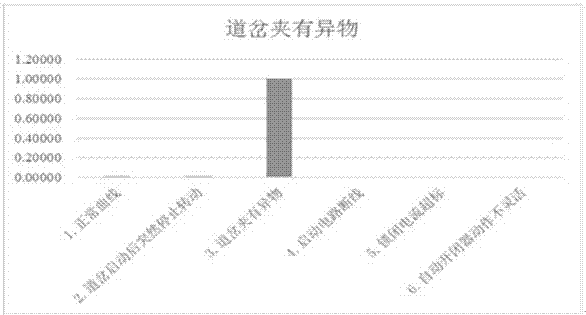
[0086] Figure 4 It is a flow chart of the method for identifying a fault in a turnout according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, such as Figure 4As shown, the method includes the following steps: collecting each action current curve of the turnout in the microcomputer monitoring system; classifying the acquired action current curves of the turnout, which can be divided into normal curves and fault curves, and the fault curves can be further divided into: The disconnection curve of the starting circuit, the sudden stop rotation curve after the turnout is started, the foreign body curve in the turnout, the stator-rotor mixed line curve of the switch machine, the inflexible action curve of the automatic switch, the start-up delay curve of the switch machine, and the locking current exceeding the standard The curve and the switch action current are zigzag curves; the average val...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com