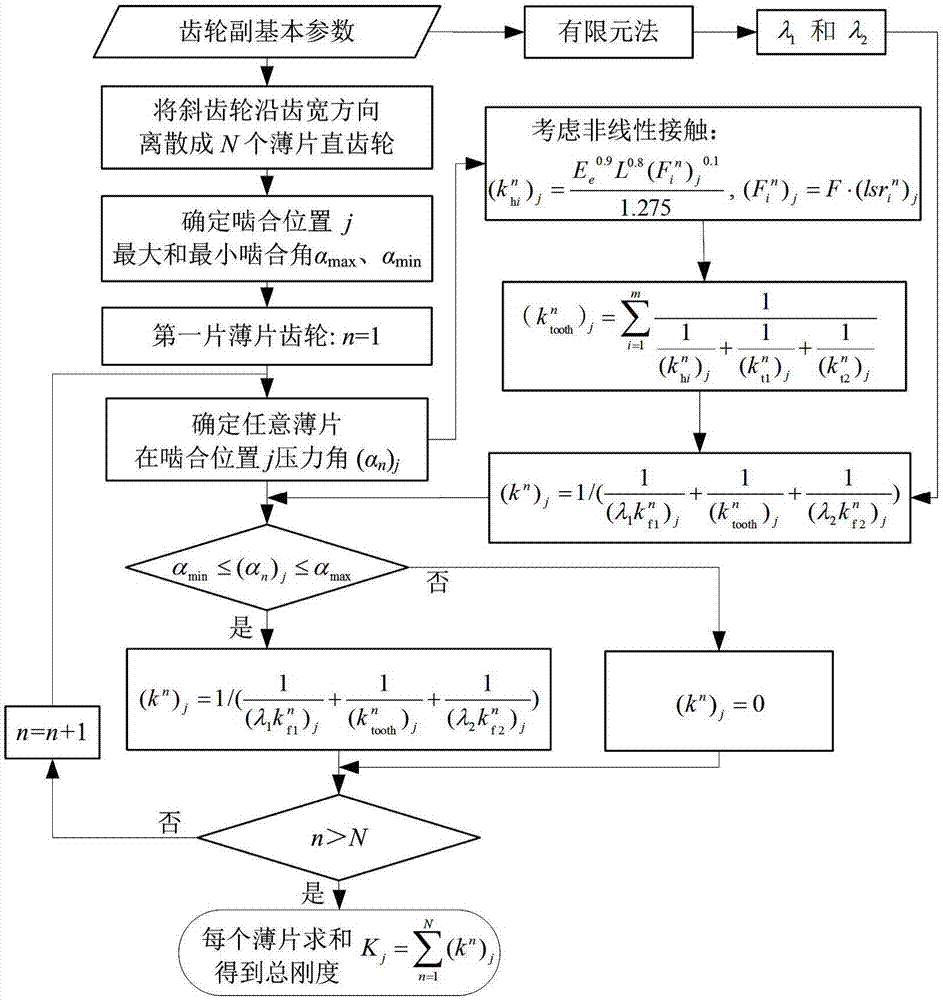
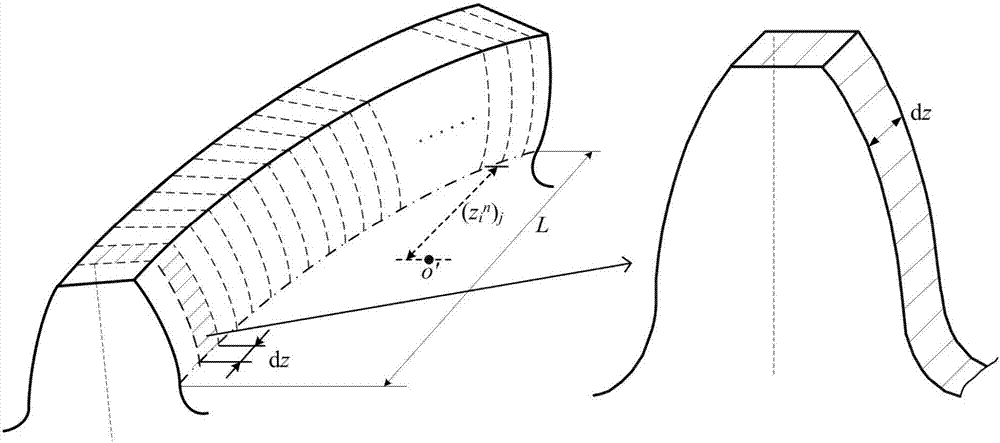
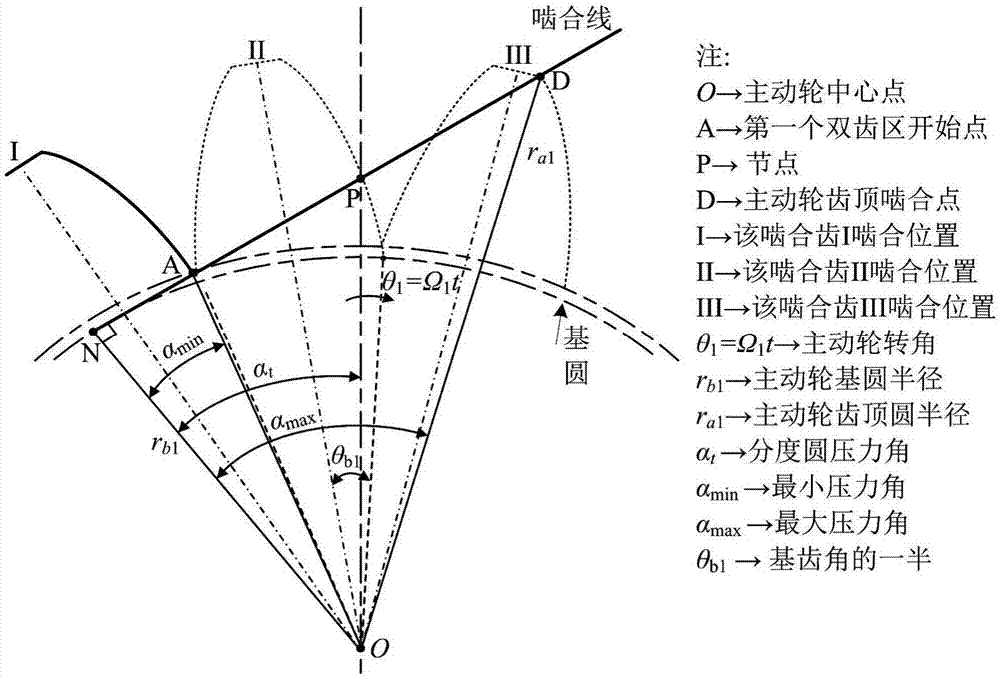
Method for calculating time-varying mesh stiffness of bevel gear pair
A technology of time-varying meshing stiffness and helical gear pairs, applied in the field of mechanical dynamics, can solve the problems of not considering nonlinear contact, correcting matrix stiffness and prolonging meshing effects, etc., to improve calculation accuracy, improve calculation accuracy, and improve analytical models Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0153] In this embodiment, the basic parameters of the helical gear pair are shown in Table 1:
[0154] Table 1 Basic parameters of helical gear pair
[0155]
[0156] Specifically, the helix angles are 12°, 16°, 20°, and 24°. When the entire tooth is engaged, the tooth width L is 60mm, R is 12.738>5, and E e It is 230.769GPa.
[0157] In this example, Figure 4 When the helix angle is 12° and the coincidence degree is 3.0614, the time-varying meshing stiffness diagram of the helical gear obtained by using analytical method, finite element method, ISO6336 or literature 1; Figure 5 When the helix angle is 16° and the coincidence degree is 3.4472, the time-varying meshing stiffness diagram of the helical gear obtained by using analytical method, finite element method, ISO6336 or literature 1; Image 6 When the helix angle is 20° and the coincidence degree is 3.8124, the time-varying meshing stiffness diagram of the helical gear obtained by using analytical method, finite ...
Embodiment 2
[0161] In this embodiment, the basic parameters of the helical gear pair are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
[0162] In this embodiment, the time-varying meshing stiffness fluctuation is measured by the parameter η, and its expression is as follows:
[0163]
[0164] In the formula, ΔK represents the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value of the time-varying meshing stiffness within a meshing period, and K mean Indicates the average stiffness of a meshing cycle, the unit of the two is the same, and the parameter η is just a dimensionless proportional value, which is used to measure the fluctuation of meshing stiffness.
[0165] Specifically, when the helix angle exceeds 30°, the calculation accuracy of the "slicing idea" will be affected. Therefore, in this embodiment, the helix angles are selected as 3°, 5°, 8°, 10°, 13°, 15°, 18°, 20°, 23°, 25°, 28°, 30°, L=60mm.
[0166] In this example, Figure 8 Indicates the relationship between the helix angl...
Embodiment 3
[0169] In this embodiment, the basic parameters of the helical gear pair are the same as those in the first embodiment except that the tooth width is different from that in the first embodiment.
[0170] In this embodiment, the tooth width L is taken to be 10 mm, 15 mm, 20 mm, and 25 mm, respectively.
[0171] In this example, Figure 10 It represents the time-varying meshing stiffness diagram of the helical gear pair when the tooth width is 10mm and 15mm, Figure 11 It is the time-varying mesh stiffness diagram of the helical gear pair when the tooth width is 20mm and 25mm. Wherein, for the working condition of L=10mm, there are single-tooth zone and double-tooth zone, and the single-tooth zone (the ratio of single-tooth zone is only 2.05% of one cycle) is not marked in the figure.
[0172] from Figure 10 with Figure 11 It can be seen that the time-varying meshing stiffness increases with the increase of tooth width, and when the tooth width increases from 10mm to 25mm,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com