Nonlinear system state deviation evolution method based on differential algebra and Gaussian sum
A technique of nonlinear systems and differential algebra, applied in the field of nonlinear system state and its deviation prediction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
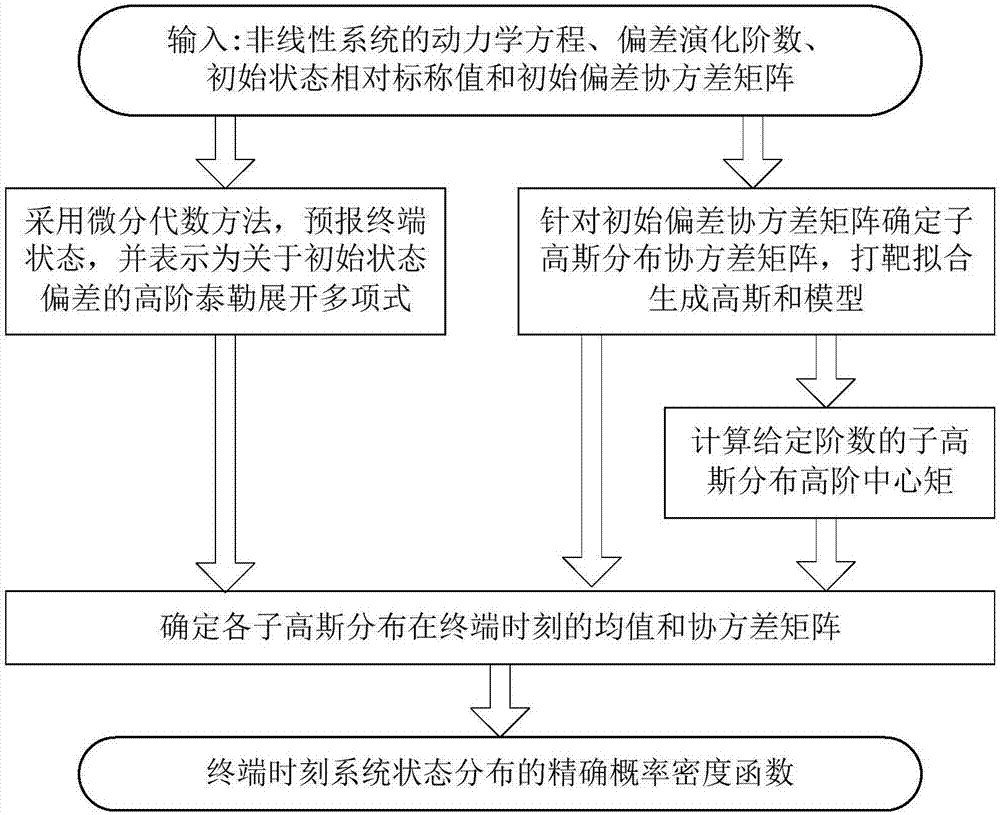
[0097] Such as figure 1 As shown, in this embodiment, the steps of the nonlinear system state deviation evolution method based on differential algebra and Gaussian sum include:
[0098] 1) Input the dynamic equation of the nonlinear system, the evolution order N of the deviation, and the relative nominal value of the initial state and the initial bias covariance matrix P 0 ;
[0099] 2) Using the differential algebra method to predict the terminal state of the nonlinear system according to the dynamic equation of the nonlinear system, and express it as the initial state deviation δx 0 Higher-order Taylor expansion polynomials of ;
[0100] 3) For the initial bias covariance matrix P 0 Determine the sub-Gaussian distribution covariance matrix P i , for a sub-Gaussian distribution covariance matrix P i The multiple sub-Gaussian distributions in the target are used to fit the initial deviation distribution to generate a Gaussian sum model;
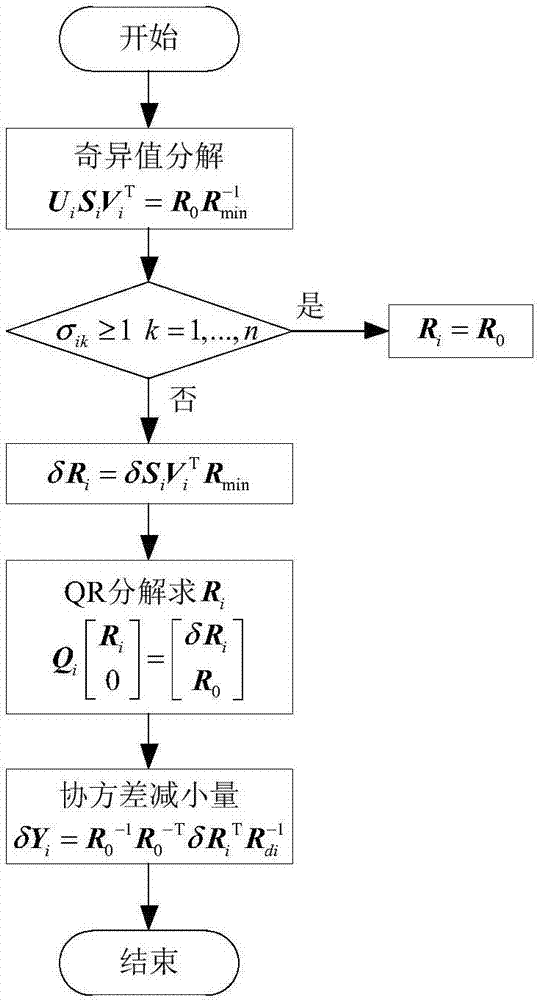
[0101] 4) Calculate the high-o...
Embodiment 2
[0191] The process of this embodiment is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, and its main difference is:
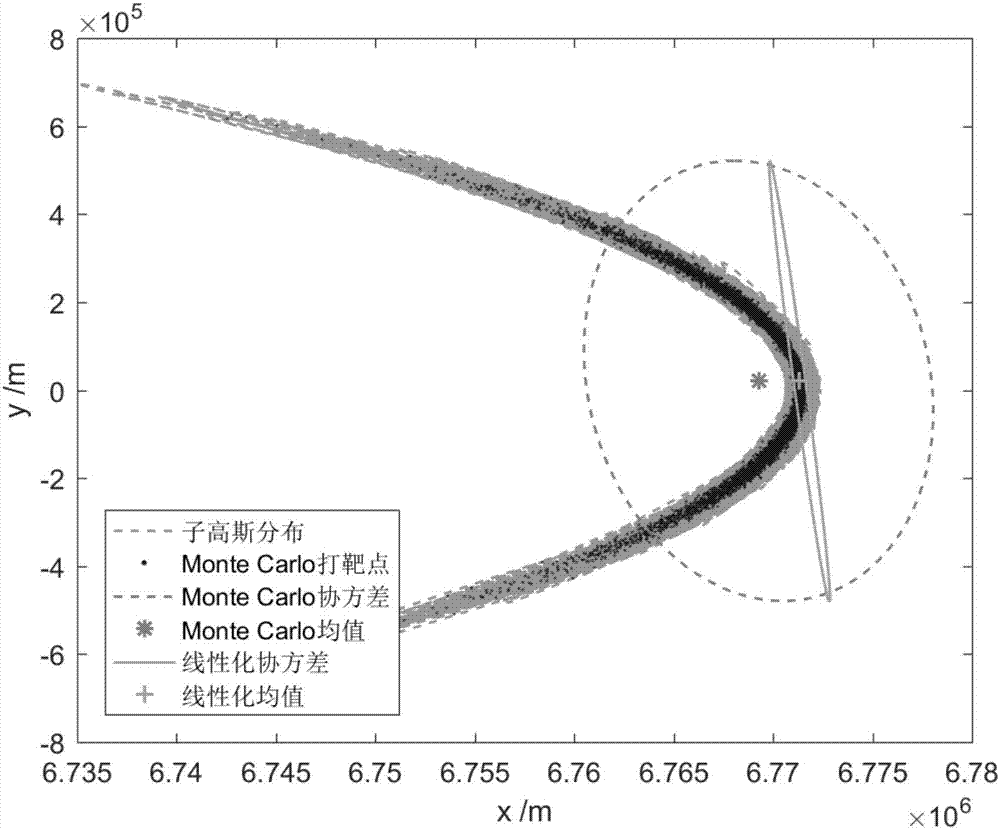
[0192] In step 2.1), the nonlinear system is the nonlinear relative trajectory of the spacecraft in geostationary orbit considering the solar light pressure, the system dimension n=6, and the state variable x is the relative position of the slave spacecraft in the orbital coordinate system of the master spacecraft and velocity vector, ie x=[r T v T ] T , where r=[x,y,z] T is the relative position vector, v=[v x ,v y ,v z ] T is the relative velocity vector.
[0193] In this embodiment, the dynamic equation of the nonlinear system is in the form of an ordinary differential equation, and the terminal state is obtained by the Runge-Kutta integration method with variable step size.
[0194] In this embodiment, the specific expression of the dynamic equation of the nonlinear system is:
[0195]
[0196] Wherein, a is the semi-major axis of the main spacecr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com